Flash Pool SSD partitioning for Flash Pool local tiers (aggregates) using storage pools
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


-
 PDF of this doc site
PDF of this doc site
-
 Cluster administration
Cluster administration
-
 Volume administration
Volume administration
-
 Logical storage management with the CLI
Logical storage management with the CLI
-
-
 NAS storage management
NAS storage management
-
 Configure NFS with the CLI
Configure NFS with the CLI
-
 Manage NFS with the CLI
Manage NFS with the CLI
-
 Manage SMB with the CLI
Manage SMB with the CLI
-
 Manage file access using SMB
Manage file access using SMB
-
-
-
 Security and data encryption
Security and data encryption
-
 Data protection and disaster recovery
Data protection and disaster recovery
-
 Data protection with the CLI
Data protection with the CLI
-
-
Collection of separate PDF docs
Creating your file...
If you are providing cache to two or more Flash Pool local tiers (aggregates), you should use Flash Pool Solid-State Drive (SSD) partitioning. Flash Pool SSD partitioning allows SSDs to be shared by all the local tiers that use the Flash Pool. This spreads the cost of parity over multiple local tiers, increases SSD cache allocation flexibility, and maximizes SSD performance.
For an SSD to be used in a Flash Pool local tier, the SSD must be placed in a storage pool. You cannot use SSDs that have been partitioned for root-data partitioning in a storage pool. After the SSD is placed in the storage pool, the SSD can no longer be managed as a stand-alone disk and cannot be removed from the storage pool unless you destroy the local tiers associated with the Flash Pool and you destroy the storage pool.
SSD storage pools are divided into four equal allocation units. SSDs added to the storage pool are divided into four partitions and one partition is assigned to each of the four allocation units. The SSDs in the storage pool must be owned by the same HA pair. By default, two allocation units are assigned to each node in the HA pair. Allocation units must be owned by the node that owns the local tier it is serving. If more Flash cache is required for local tiers on one of the nodes, the default number of allocation units can be shifted to decrease the number on one node and increase the number on the partner node.
You use spare SSDs to add to an SSD storage pool. If the storage pool provides allocation units to Flash Pool local tiers owned by both nodes in the HA pair, then the spare SSDs can be owned by either node. However, if the storage pool provides allocation units only to Flash Pool local tiers owned by one of the nodes in the HA pair, then the SSD spares must be owned by that same node.
The following illustration is an example of Flash Pool SSD partitioning. The SSD storage pool provides cache to two Flash Pool local tiers:
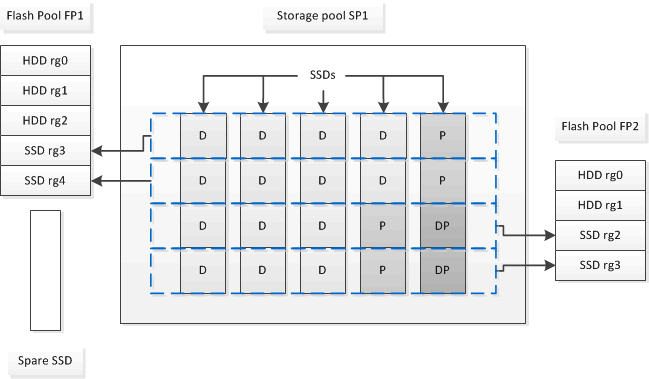
Storage pool SP1 is composed of five SSDs and a hot spare SSD. Two of the storage pool's allocation units are allocated to Flash Pool FP1, and two are allocated to Flash Pool FP2. FP1 has a cache RAID type of RAID4. Therefore, the allocation units provided to FP1 contain only one partition designated for parity. FP2 has a cache RAID type of RAID-DP. Therefore, the allocation units provided to FP2 include a parity partition and a double-parity partition.
In this example, two allocation units are allocated to each Flash Pool local tier. However, if one Flash Pool local tier required a larger cache, you could allocate three of the allocation units to that Flash Pool local tier, and only one to the other.



 Release notes
Release notes