Insights: Shared Resources Under Stress
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


High-impact workloads can reduce the performance of other workloads in a shared resource. This puts the shared resource under stress. Data Infrastructure Insights provides tools to help you investigate resource saturation and impact on your tenant.
Terminology
When talking about workload or resource impact, the following definitions are useful.
A Demanding Workload is a workload that is currently identified as impacting other resources in the shared storage pool. These workloads drive higher IOPS (for example), reducing IOPS in the Impacted Workloads. Demanding workloads are sometimes called high-consuming workloads.
An Impacted Workload is a workload that is affected by a high-consuming workload in the shared Storage Pool. These workloads are experiencing reduced IOPS and/or higher latency, caused by the Demanding Workloads.
Note that if Data Infrastructure Insights has not discovered the leading compute workload, the volume or internal volume itself will be recognized as the workload. This applies to both demanding and impacted workloads.
Shared Resource Saturation is the ratio of impacting IOPS to baseline.
Baseline is defined as the maximum reported data point for each workload in the hour immediately preceding the detected saturation.
A Contention or Saturation occurs when IOPS are determined to be affecting other resources or workloads in the shared storage pool.
Demanding Workloads
To start looking into Demanding and impacted workloads in your shared resources, click on Dashboards > Insights and select the Shared Resources Under Stress Insight.
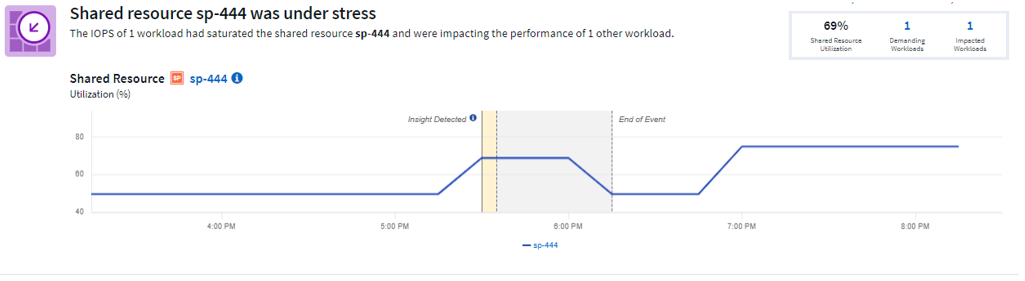
Data Infrastructure Insights displays a list of any workloads where a saturation has been detected. Note that Data Infrastructure Insights will show workloads where at least one demanding resource or impacted resource has been detected.
Click on a workload to view the details page for it. The top chart shows the activity on the shared resource (for example, a storage pool) on which the contention/saturation is occurring.
Below that are two charts showing the demanding workloads and the workloads that are impacted by those demanding workloads.
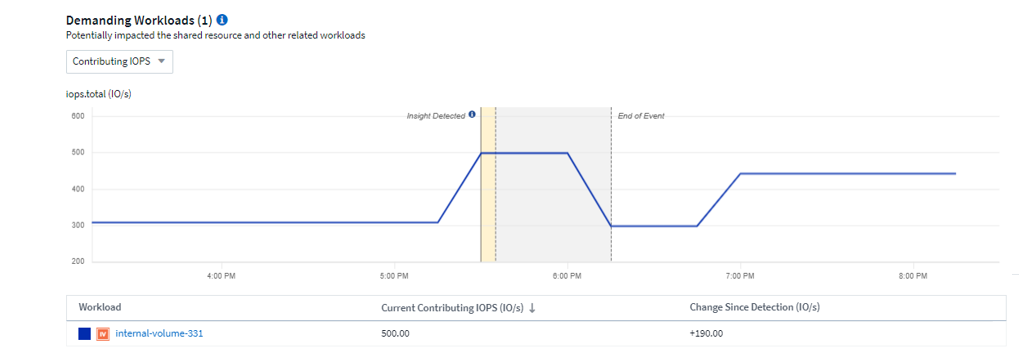
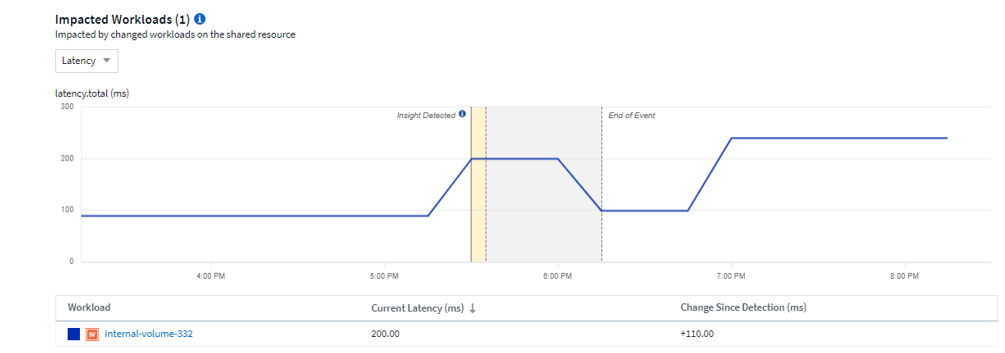
Below each table is a list of workloads and/or resources affecting or affected by the contention. Clicking on a resource (for example, a VM) opens a detail page for that resource. Clicking on a workload opens a query page showing the pods involved. Note that if the link opens an empty query, it may be because the affected pod is no longer part of the active contention. You can modify the query's time range to view the pod list in greater or more focused time range.
What do I do to resolve saturation?
There are a number of steps you can take to reduce or eliminate the chance of saturation on your tenant. These are shown by expanding the +Show Recommendations link on the page. Here are a few things you can try.
-
Move high-IOPS consumers
Move the "greedy" workloads to less-saturated Storage Pools. It is recommended to assess the tier and capacity of these pools before moving the workloads, to avoid unnecessary costs or additional contentions.
-
Implement a quality of service (QoS) policy
Implementing a QoS policy per workload to ensure enough free resources available will alleviate saturation on the Storage Pool. This is a long-term solution.
-
Add additional resources
If the shared resource (for example, Storage Pool) has reached the IOPS saturation point, adding more or faster disks to the pool will ensure enough free resources available to alleviate saturation.
Finally, you can click the Copy Insight Link to copy the page url to the clipboard, to more easily share with colleagues.


