Connect NetApp Ransomware Resilience to a SIEM for threat analysis and detection
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


A security information and event management system (SIEM) centralizes log and event data to provide insights into security events and compliance. NetApp Ransomware Resilience supports automatically sending data to your SIEM for streamlined threat analysis and detection.
Ransomware Resilience supports the following SIEMs:
-
AWS Security Hub
-
Microsoft Sentinel
-
Splunk Cloud
Before you enable SIEM in Ransomware Resilience, you need to configure your SIEM system.

|
Ransomware Resilience also supports security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) playbooks. |
Event data sent to a SIEM
Ransomware Resilience can send the following event data to your SIEM system:
-
context:
-
os: This is a constant with the value of ONTAP.
-
os_version: The version of ONTAP running on the system.
-
connector_id: The ID of the Console agent managing the system.
-
cluster_id: The cluster ID reported by ONTAP for the system.
-
svm_name: The name of the SVM where the alert was found.
-
volume_name: The name of the volume on which the alert is found.
-
volume_id: The ID of the volume reported by ONTAP for the system.
-
-
incident:
-
incident_id: The incident ID generated by Ransomware Resilience for the volume under attack in Ransomware Resilience.
-
alert_id: The ID generated by Ransomware Resilience for the workload.
-
severity: One of the following alert levels: "CRITICAL", "HIGH", "MEDIUM", "LOW".
-
description: Details about the alert that was detected, for example, "A Potential ransomware attack detected on workload arp_learning_mode_test_2630"
-
Configure AWS Security Hub for threat detection
Before you enable AWS Security Hub in Ransomware Resilience, you need to do the following high level steps in AWS Security Hub:
-
Set up permissions in AWS Security Hub.
-
Set up the authentication access key and secret key in AWS Security Hub. (These steps are not provided here.)
-
Go to AWS IAM console.
-
Select Policies.
-
Create a policy using the following code in JSON format:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "NetAppSecurityHubFindings", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "securityhub:BatchImportFindings", "securityhub:BatchUpdateFindings" ], "Resource": [ "arn:aws:securityhub:*:*:product/*/default", "arn:aws:securityhub:*:*:hub/default" ] } ] }
Configure Microsoft Sentinel for threat detection
Before you enable Microsoft Sentinel in Ransomware Resilience, you need to do the following high level steps in Microsoft Sentinel:
-
Prerequisites
-
Enable Microsoft Sentinel.
-
Create a custom role in Microsoft Sentinel.
-
-
Registration
-
Register Ransomware Resilience to receive events from Microsoft Sentinel.
-
Create a secret for the registration.
-
-
Permissions: Assign permissions to the application.
-
Authentication: Enter authentication credentials for the application.
-
Go to Microsoft Sentinel.
-
Create a Log Analytics workspace.
-
Enable Microsoft Sentinel to use the Log Analytics workspace you just created.
-
Go to Microsoft Sentinel.
-
Select Subscription > Access control (IAM).
-
Enter a Custom role name. Use the name Ransomware Resilience Sentinel Configurator.
-
Copy the following JSON and paste it into the JSON tab.
{ "roleName": "Ransomware Resilience Sentinel Configurator", "description": "", "assignableScopes":["/subscriptions/{subscription_id}"], "permissions": [ ] } -
Review and save your settings.
-
Go to Microsoft Sentinel.
-
Select Entra ID > Applications > App registrations.
-
For the Display name for the application, enter "Ransomware Resilience".
-
In the Supported account type field, select Accounts in this organizational directory only.
-
Select a Default Index where events will be pushed.
-
Select Review.
-
Select Register to save your settings.
After registration, the Microsoft Entra admin center displays the application Overview pane.
-
Go to Microsoft Sentinel.
-
Select Certificates & secrets > Client secrets > New client secret.
-
Add a description for your application secret.
-
Select an Expiration for the secret or specify a custom lifetime.
A client secret lifetime is limited to two years (24 months) or less. Microsoft recommends that you set an expiration value of less than 12 months. -
Select Add to create your secret.
-
Record the secret to use in the Authentication step. The secret is never displayed again after you leave this page.
-
Go to Microsoft Sentinel.
-
Select Subscription > Access control (IAM).
-
Select Add > Add role assignment.
-
For the Privileged administrator roles field, select Ransomware Resilience Sentinel Configurator.
This is the custom role that you created earlier. -
Select Next.
-
In the Assign access to field, select User, group, or service principal.
-
Select Select Members. Then, select Ransomware Resilience Sentinel Configurator.
-
Select Next.
-
In the What user can do field, select Allow user to assign all roles except privileged administrator roles Owner, UAA, RBAC (Recommended).
-
Select Next.
-
Select Review and assign to assign the permissions.
-
Go to Microsoft Sentinel.
-
Enter the credentials:
-
Enter the tenant ID, the client application ID, and the client application secret.
-
Select Authenticate.
After the authentication is successful, an "Authenticated" message appears.
-
-
Enter the Log Analytics workspace details for the application.
-
Select the subscription ID, the resource group, and the Log Analytics workspace.
-
Configure Splunk Cloud for threat detection
Before you enable Splunk Cloud in Ransomware Resilience, you'll need to do the following high level steps in Splunk Cloud:
-
Enable an HTTP Event Collector in Splunk Cloud to receive event data via HTTP or HTTPS from the Console.
-
Create an Event Collector token in Splunk Cloud.
-
Go to Splunk Cloud.
-
Select Settings > Data Inputs.
-
Select HTTP Event Collector > Global Settings.
-
On the All Tokens toggle, select Enabled.
-
To have the Event Collector listen and communicate over HTTPS rather than HTTP, select Enable SSL.
-
Enter a port in HTTP Port Number for the HTTP Event Collector.
-
Go to Splunk Cloud.
-
Select Settings > Add Data.
-
Select Monitor > HTTP Event Collector.
-
Enter a Name for the token and select Next.
-
Select a Default Index where events will be pushed, then select Review.
-
Confirm that all settings for the endpoint are correct, then select Submit.
-
Copy the token and paste it in another document to have it ready for the Authentication step.
Connect SIEM in Ransomware Resilience
Enabling SIEM sends data from Ransomware Resilience to your SIEM server for threat analysis and reporting.
-
From the Console menu, select Protection > Ransomware Resilience.
-
From the Ransomware Resilience menu, select the vertical
 … option at the top right.
… option at the top right. -
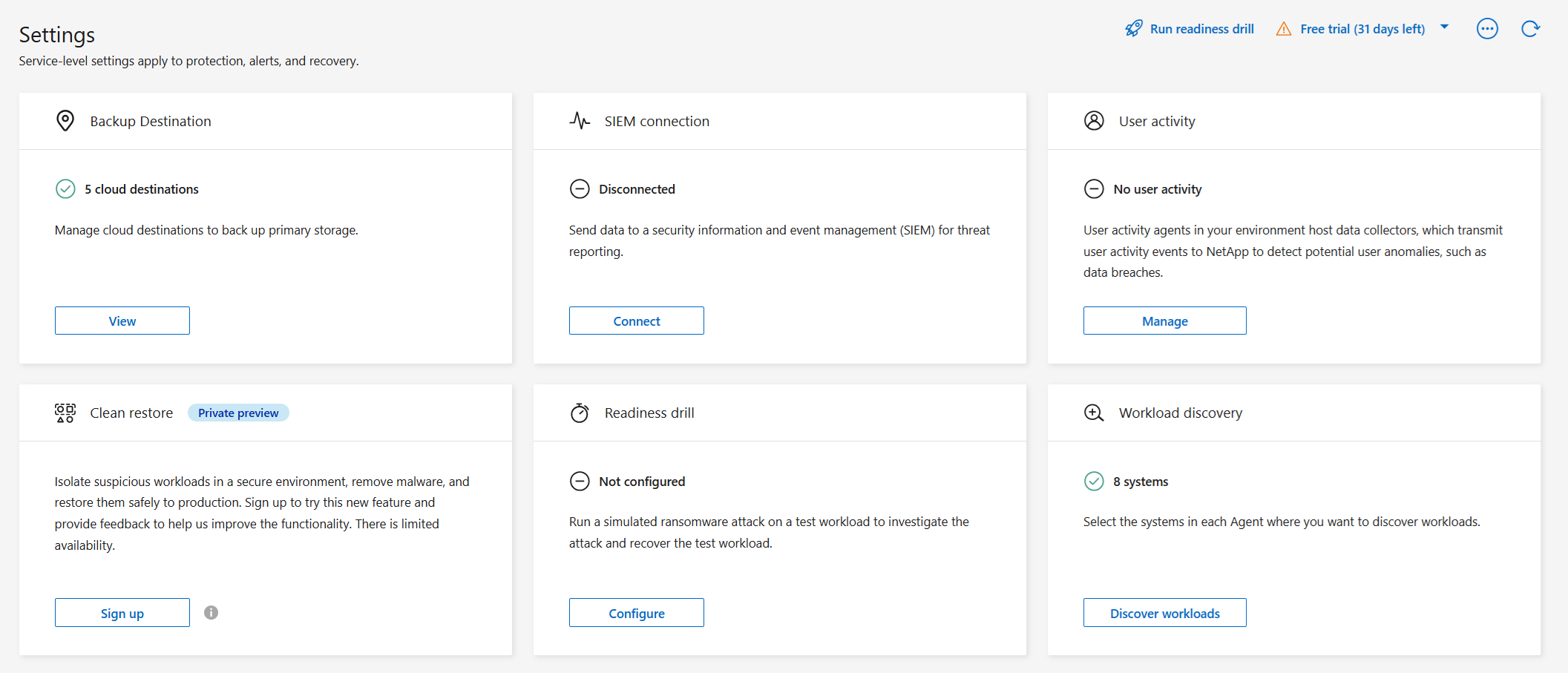
Select Settings.
The Settings page appears.
-
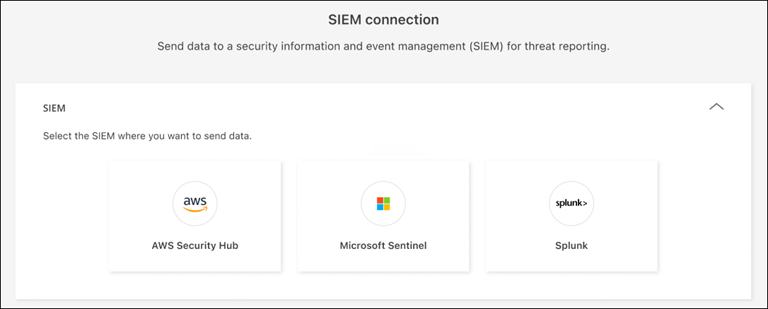
In the Settings page, select Connect in the SIEM connection tile.
-
Choose one of the SIEM systems.
-
Enter the token and authentication details you configured in AWS Security Hub or Splunk Cloud.
The information that you enter depends on the SIEM you selected. -
Select Enable.
The Settings page shows "Connected."



