NetApp HCI Overview
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


NetApp HCI is a hybrid cloud infrastructure that consists of a mix of storage nodes and compute nodes. It is available as either a two-rack unit or single-rack unit, depending on the model. The installation and configuration required to deploy VMs are automated with the NetApp Deployment Engine (NDE). Compute clusters are managed with VMware vCenter, and storage clusters are managed with the vCenter Plug-in deployed with NDE. A management VM called the mNode is deployed as part of the NDE.
NetApp HCI handles the following functions:
-
Version upgrades
-
Pushing events to vCenter
-
vCenter Plug-In management
-
A VPN tunnel for support
-
The NetApp Active IQ collector
-
The extension of NetApp Cloud Services to on the premises, enabling a hybrid cloud infrastructure. The following figure depicts HCI components.
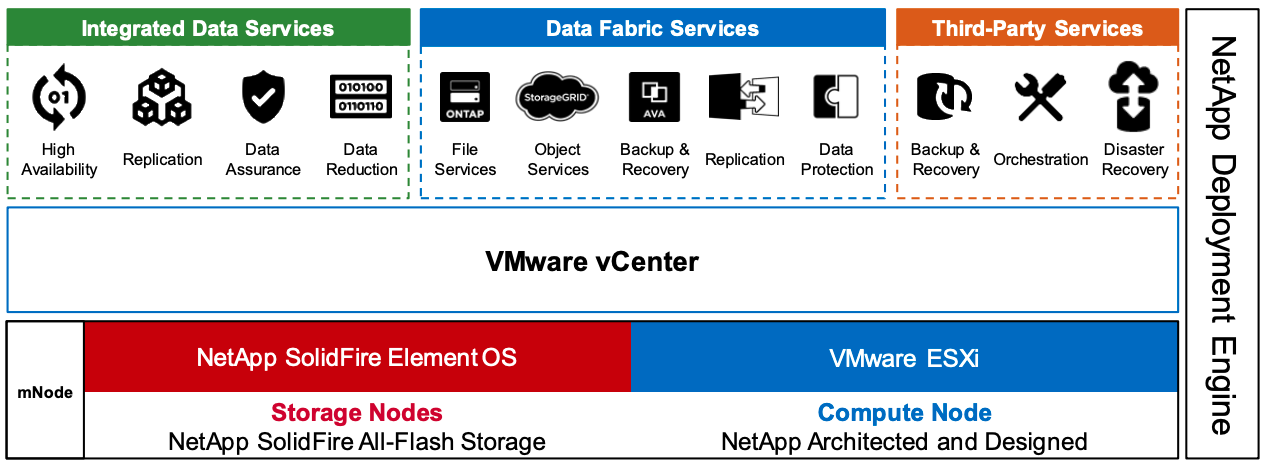
Storage Nodes
Storage nodes are available as either a half-width or full-width rack unit. A minimum of four storage nodes is required at first, and a cluster can expand to up to 40 nodes. A storage cluster can be shared across multiple compute clusters. All the storage nodes contain a cache controller to improve write performance. A single node provides either 50K or 100K IOPS at a 4K block size.
NetApp HCI storage nodes run NetApp Element software, which provides minimum, maximum, and burst QoS limits. The storage cluster supports a mix of storage nodes, although one storage node cannot exceed one-third of total capacity.
Compute Nodes
Compute nodes are available in half-width, full-width, and two rack-unit sizes. The NetApp HCI H410C and H610C are based on scalable Intel Skylake processors. The H615C is based on second-generation scalable Intel Cascade Lake processors. There are two compute models that contain GPUs: the H610C contains two NVIDIA M10 cards and the H615C contains three NVIDIA T4 cards.

The NVIDIA T4 has 40 RT cores that provide the computation power needed to deliver real-time ray tracing. The same server model used by designers and engineers can now also be used by artists to create photorealistic imagery that features light bouncing off surfaces just as it would in real life. This RTX-capable GPU produces real-time ray tracing performance of up to five Giga Rays per second. The NVIDIA T4, when combined with Quadro Virtual Data Center Workstation (Quadro vDWS) software, enables artists to create photorealistic designs with accurate shadows, reflections, and refractions on any device from any location.
Tensor cores enable you to run deep learning inferencing workloads. When running these workloads, an NVIDIA T4 powered with Quadro vDWS can perform up to 25 times faster than a VM driven by a CPU-only server. A NetApp H615C with three NVIDIA T4 cards in one rack unit is an ideal solution for graphics and compute-intensive workloads.
The following figure lists NVIDIA GPU cards and compares their features.
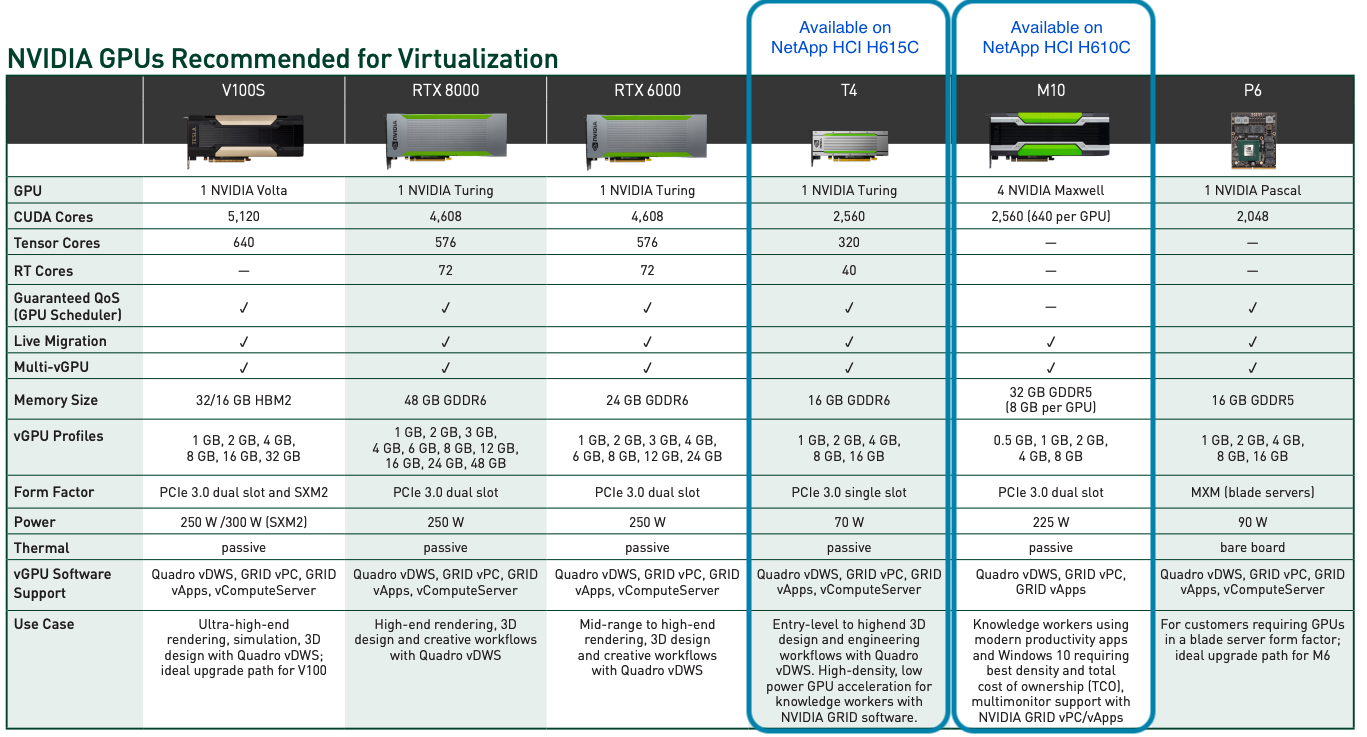
The M10 GPU remains the best TCO solution for knowledge-worker use cases. However, the T4 makes a great alternative when IT wants to standardize on a GPU that can be used across multiple use cases, such as virtual workstations, graphics performance, real-time interactive rendering, and inferencing. With the T4, IT can take advantage of the same GPU resources to run mixed workloads―for example, running VDI during the day and repurposing the resources to run compute workloads at night.
The H610C compute node is two rack units in size; the H615C is one rack unit in size and consumes less power. The H615C supports H.264 and H.265 (High Efficiency Video Coding [HEVC]) 4:4:4 encoding and decoding. It also supports a VP9 decoder, which is becoming more mainstream; even the WebM container package served by YouTube uses the VP9 codec for video.
The number of nodes in a compute cluster is dictated by VMware; currently, it is 96 with VMware vSphere 7.0 Update 1. Mixing different models of compute nodes in a cluster is supported when Enhanced vMotion Compatibility (EVC) is enabled.


