Storage controller setup
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


This section describes the configuration of the NetApp storage system. You must complete the primary installation and setup according to the corresponding Data ONTAP setup and configuration guides.
Storage efficiency
Inline deduplication, cross-volume inline deduplication, inline compression, and inline compaction are supported with SAP HANA in an SSD configuration.
NetApp FlexGroup Volumes
The usage of NetApp FlexGroup Volumes is not supported for SAP HANA. Due to the architecture of SAP HANA the usage of FlexGroup Volumes does not provide any benefit and may results in performance issues.
NetApp Volume and Aggregate Encryption
The use of NetApp Volume Encryption (NVE) and NetApp Aggregate Encryption (NAE) are supported with SAP HANA.
Quality of Service
QoS can be used to limit the storage throughput for specific SAP HANA systems or non-SAP applications on a shared controller.
Production and Dev/Test
One use case would be to limit the throughput of development and test systems so that they cannot influence production systems in a mixed setup.
During the sizing process, you should determine the performance requirements of a nonproduction system. Development and test systems can be sized with lower performance values, typically in the range of 20% to 50% of a production-system KPI as defined by SAP.
Large write I/O has the biggest performance effect on the storage system. Therefore, the QoS throughput limit should be set to a percentage of the corresponding write SAP HANA storage performance KPI values in the data and log volumes.
Shared Environments
Another use case is to limit the throughput of heavy write workloads, especially to avoid that these workloads have an impact on other latency sensitive write workloads.
In such environments it is best practice to apply a non-shared throughput ceiling QoS group-policy to each LUN within each Storage Virtual Machine (SVM) to restrict the max throughput of each individual storage object to the given value. This reduces the possibility that a single workload can negatively influence other workloads.
To do so, a group-policy needs to be created using the CLI of the ONTAP cluster for each SVM:
qos policy-group create -policy-group <policy-name> -vserver <vserver name> -max-throughput 1000MB/s -is-shared false
and applied to each LUN within the SVM. Below is an example to apply the policy group to all existing LUNs within an SVM:
lun modify -vserver <vserver name> -path * -qos-policy-group <policy-name>
This needs to be done for every SVM. The name of the QoS police group for each SVM needs to be different.
For new LUNs, the policy can be applied directly:
lun create -vserver <vserver_name> -path /vol/<volume_name>/<lun_name> -size <size> -ostype <e.g. linux> -qos-policy-group <policy-name>
It is recommended to use 1000MB/s as maximum throughput for a given LUN. If an application requires more throughput, multiple LUNs with LUN striping shall be used to provide the needed bandwidth. This guide provides an example for SAP HANA based on Linux LVM in section Host Setup.

|
The limit applies also to reads. Therefore use enough LUNs to fulfil the required SLAs for SAP HANA database startup time and for backups. |
NetApp FabricPool
NetApp FabricPool technology must not be used for active primary file systems in SAP HANA systems. This includes the file systems for the data and log area as well as the /hana/shared file system. Doing so results in unpredictable performance, especially during the startup of an SAP HANA system.
You can use the Snapshot-Only tiering policy along with FabricPool at a backup target such as SnapVault or SnapMirror destination.

|
Using FabricPool for tiering Snapshot copies at primary storage or using FabricPool at a backup target changes the required time for the restore and recovery of a database or other tasks such as creating system clones or repair systems. Take this into consideration for planning your overall lifecycle-management strategy, and check to make sure that your SLAs are still being met while using this function. |
FabricPool is a good option for moving log backups to another storage tier. Moving backups affects the time needed to recover an SAP HANA database. Therefore, the option tiering-minimum-cooling-days should be set to a value that places log backups, which are routinely needed for recovery, on the local fast storage tier.
Configure storage
The following overview summarizes the required storage configuration steps. Each step is covered in more detail in the subsequent sections. In this section, we assume that the storage hardware is set up and that the ONTAP software is already installed. Also, the connection of the storage FCP ports to the SAN fabric must already be in place.
-
Check the correct disk shelf configuration, as described in Disk shelf connections.
-
Create and configure the required aggregates, as described in Aggregate configuration.
-
Create a storage virtual machine (SVM), as described in Storage virtual machine configuration.
-
Create logical interfaces (LIFs), as described in Logical interface configuration.
-
Create initiator groups (igroups) with worldwide names (WWNs) of HANA servers as described in the section Initiator groups.
-
Create and configure volumes and LUNs within the aggregates as described in the section Single Host Setup for single hosts
or in section Multiple Host Setup
Disk shelf connections
SAS-based disk shelves
A maximum of one disk shelf can be connected to one SAS stack to provide the required performance for the SAP HANA hosts, as shown in the following figure. The disks within each shelf must be distributed equally between both controllers of the HA pair. ADPv2 is used with ONTAP 9 and the DS224C disk shelves.

|
With the DS224C disk shelf, quad-path SAS cabling can also be used but is not required. |

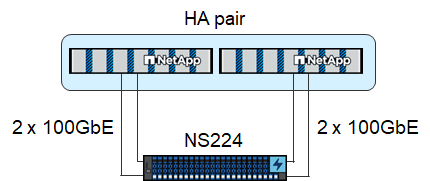
NVMe-based disk shelves
Each NS224 NVMe disk shelf is connected with two 100GbE ports per controller, as shown in the following figure. The disks within each shelf must be distributed equally to both controllers of the HA pair. ADPv2 is also used for the NS224 disk shelf.
Aggregate configuration
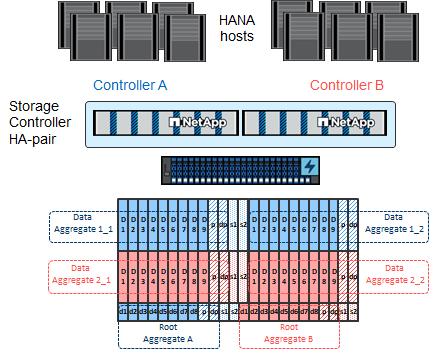
In general, you must configure two aggregates per controller, independent of which disk shelf or disk technology (SSD or HDD) is used. This step is necessary so that you can use all available controller resources.

|
ASA systems launched after August 2024 do not require this step as it as automatically done |
The following figure shows a configuration of 12 SAP HANA hosts running on a 12Gb SAS shelf configured with ADPv2. Six SAP HANA hosts are attached to each storage controller. Four separate aggregates, two at each storage controller, are configured. Each aggregate is configured with 11 disks with nine data and two parity disk partitions. For each controller, two spare partitions are available.
Storage virtual machine configuration
Multiple SAP landscapes with SAP HANA databases can use a single SVM. An SVM can also be assigned to each SAP landscape, if necessary, in case they are managed by different teams within a company.
If there is a QoS profile automatically created and assigned while creating a new SVM, remove this automatically created profile from the SVM to ensure the required performance for SAP HANA:
vserver modify -vserver <svm-name> -qos-policy-group none
Logical interface configuration
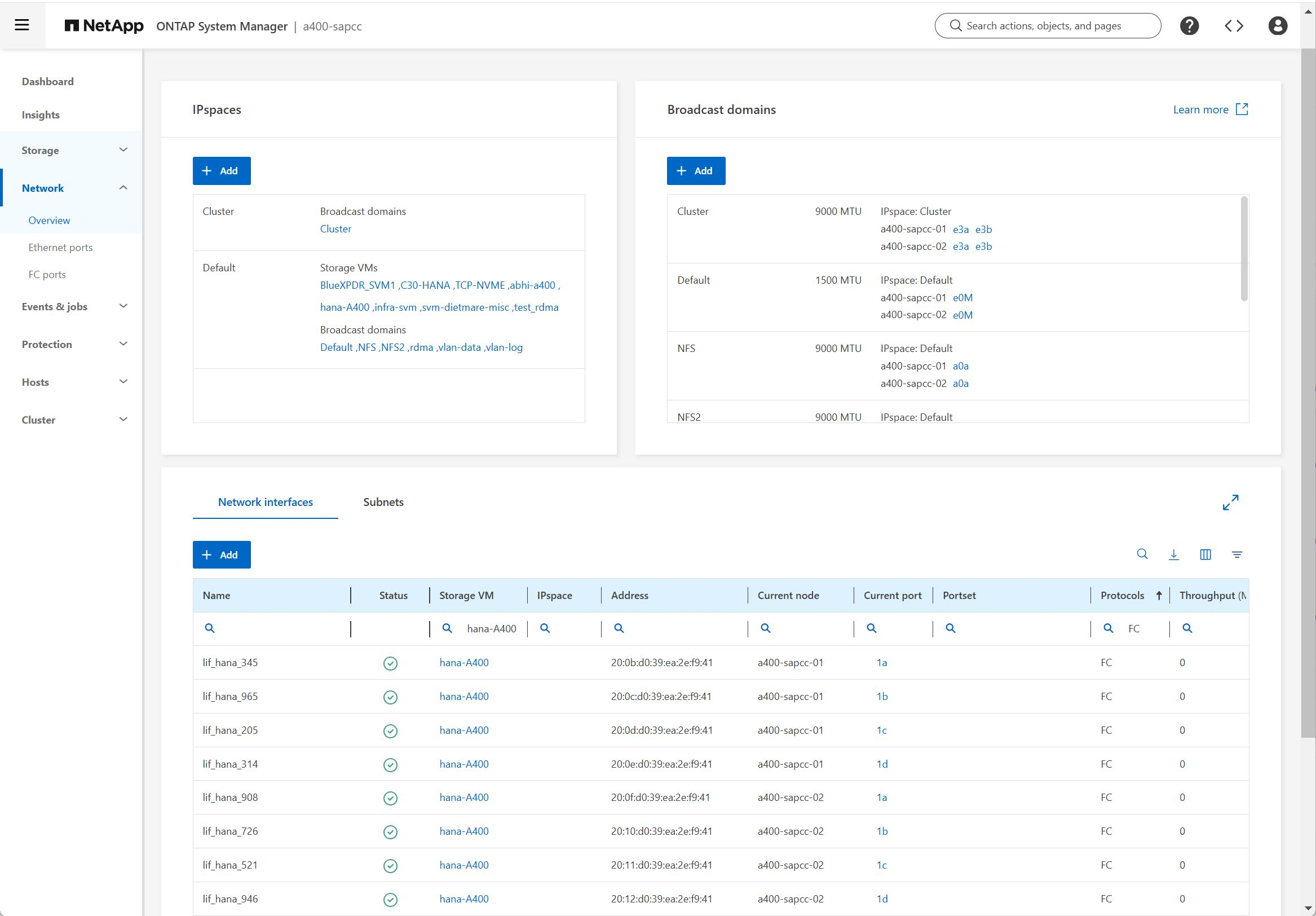
Within the storage cluster configuration, one network interface (LIF) must be created and assigned to a dedicated FCP port. If, for example, four FCP ports are required for performance reasons, four LIFs must be created. The following figure shows a screenshot of the eight LIFs that were configured on the SVM.
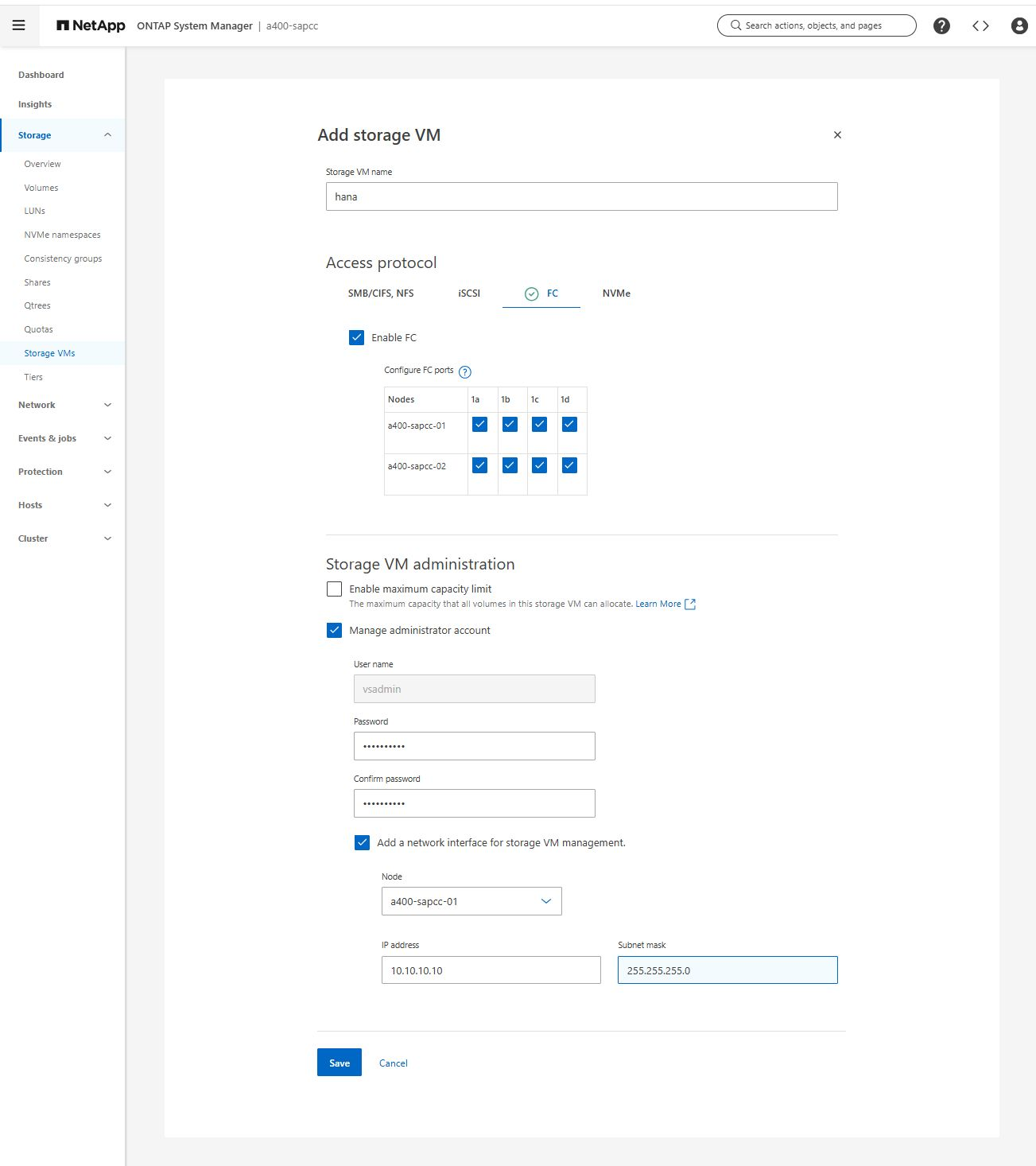
During the SVM creation with ONTAP System Manager, you can select all of the required physical FCP ports, and one LIF per physical port is created automatically.
Initiator groups
An igroup can be configured for each server or for a group of servers that require access to a LUN. The igroup configuration requires the worldwide port names (WWPNs) of the servers.
Using the sanlun tool, run the following command to obtain the WWPNs of each SAP HANA host:
stlrx300s8-6:~ # sanlun fcp show adapter /sbin/udevadm /sbin/udevadm host0 ...... WWPN:2100000e1e163700 host1 ...... WWPN:2100000e1e163701

|
The sanlun tool is part of the NetApp Host Utilities and must be installed on each SAP HANA host. More details can be found in section Host setup.
|
The initiator groups can be created using the CLI of the ONTAP Cluster.
lun igroup create -igroup <igroup name> -protocol fcp -ostype linux -initiator <list of initiators> -vserver <SVM name>


