Architecture overview
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


The BeeGFS on NetApp solution includes architectural design considerations used to determine the specific equipment, cabling, and configurations required to support validated workloads.
Building block architecture
The BeeGFS file system can be deployed and scaled in different ways depending on the storage requirements. For example, use cases primarily featuring numerous small files will benefit from extra metadata performance and capacity, whereas use cases featuring fewer large files might favor more storage capacity and performance for actual file contents. These multiple considerations impact different dimensions of the parallel file system deployment, which adds complexity to designing and deploying the file system.
To address these challenges, NetApp has designed a standard building block architecture that is used to scale out each of these dimensions. Typically, BeeGFS building blocks are deployed in one of three configuration profiles:
-
A single base building block, including BeeGFS management, metadata, and storage services
-
A BeeGFS metadata plus storage building block
-
A BeeGFS storage only building block
The only hardware change between these three options is the use of smaller drives for BeeGFS metadata. Otherwise, all configuration changes are applied through software. And with Ansible as the deployment engine, setting up the desired profile for a particular building block makes configuration tasks straightforward.
For further details, see Verified hardware design.
File system services
The BeeGFS file system includes the following main services:
-
Management service. Registers and monitors all other services.
-
Storage service. Stores the distributed user file contents known as data chunk files.
-
Metadata service. Keeps track of the file system layout, directory, file attributes, and so on.
-
Client service. Mounts the file system to access the stored data.
The following figure shows BeeGFS solution components and relationships used with NetApp E-Series systems.
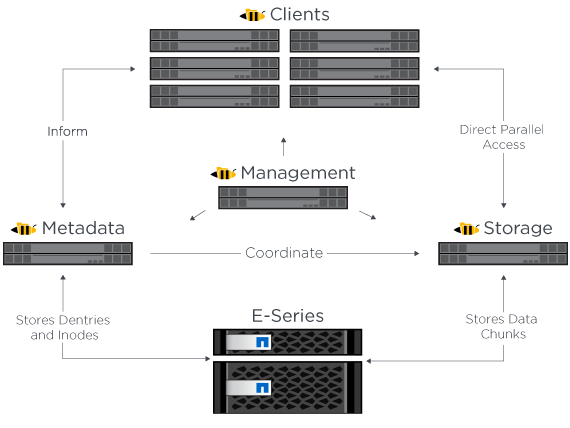
As a parallel file system, BeeGFS stripes its files over multiple server nodes to maximize read/write performance and scalability. The server nodes work together to deliver a single file system that can be simultaneously mounted and accessed by other server nodes, commonly known as clients. These clients can see and consume the distributed file system similarly to a local file system such as NTFS, XFS, or ext4.
The four main services run on a wide range of supported Linux distributions and communicate via any TCP/IP or RDMA-capable network, including InfiniBand (IB), Omni-Path (OPA), and RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE). The BeeGFS server services (management, storage, and metadata) are user space daemons, while the client is a native kernel module (patchless). All components can be installed or updated without rebooting, and you can run any combination of services on the same node.
HA architecture
BeeGFS on NetApp expands the functionality of the BeeGFS enterprise edition by creating a fully integrated solution with NetApp hardware that enables a shared-disk high availability (HA) architecture.

|
While the BeeGFS community edition can be used free of charge, the enterprise edition requires purchasing a professional support subscription contract from a partner like NetApp. The enterprise edition allows use of several additional features including resiliency, quota enforcement, and storage pools. |
The following figure compares the shared-nothing and shared-disk HA architectures.
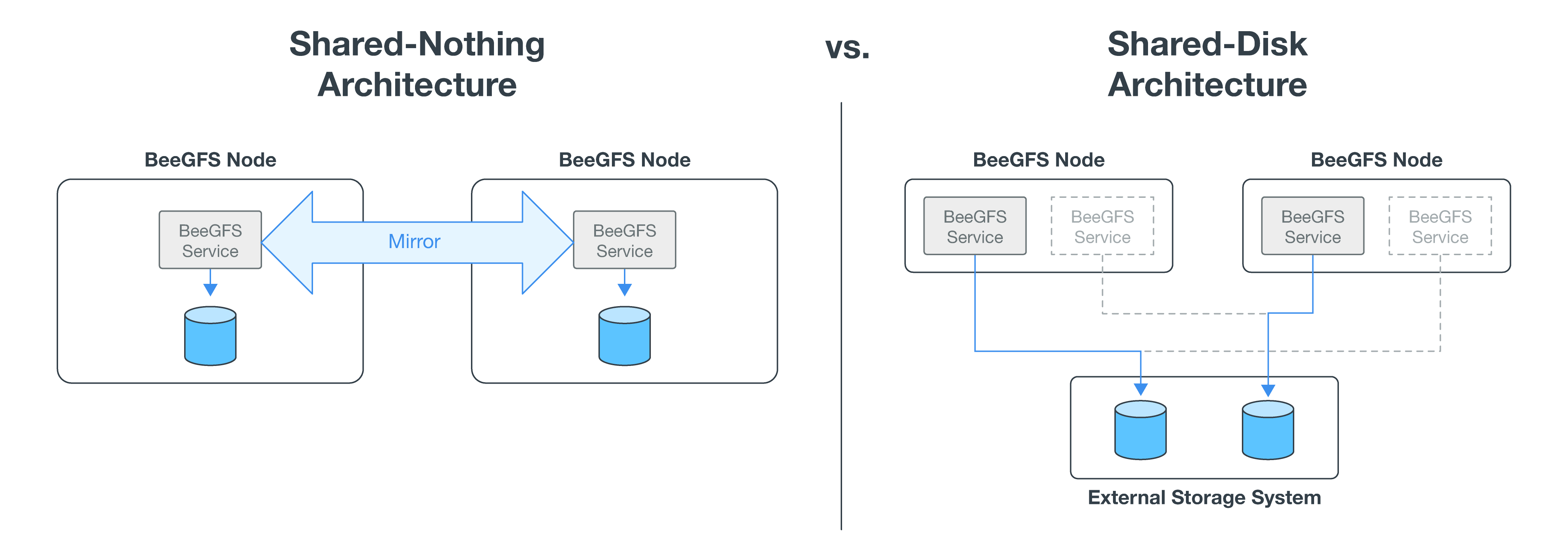
For more information, see Announcing High Availability for BeeGFS Supported by NetApp.
Verified nodes
The BeeGFS on NetApp solution has verified the nodes listed below.
| Node | Hardware | Details |
|---|---|---|
Block |
NetApp EF600 Storage System |
A high-performance, all-NVMe 2U storage array designed for demanding workloads. |
File |
Lenovo ThinkSystem SR665 V3 Server |
A two-socket 2U server featuring PCIe 5.0, dual AMD EPYC 9124 processors. |
Lenovo ThinkSystem SR665 Server |
A two-socket 2U server featuring PCIe 4.0, dual AMD EPYC 7003 processors. |
Verified hardware design
The solution's building blocks (shown in the following figure) uses the verified file node servers for the BeeGFS file layer and two EF600 storage systems as the block layer.
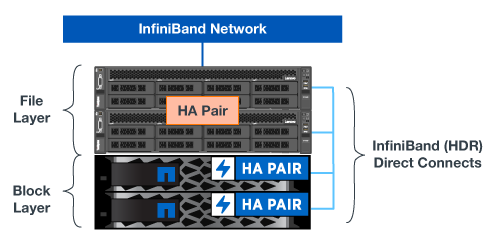
The BeeGFS on NetApp solution runs across all building blocks in the deployment. The first building block deployed must run BeeGFS management, metadata, and storage services (known as the base building block). All subsequent building blocks can be configured through software to extend metadata and storage services, or to provide storage services exclusively. This modular approach enables scaling the file system to the needs of a workload while using the same underlying hardware platforms and building block design.
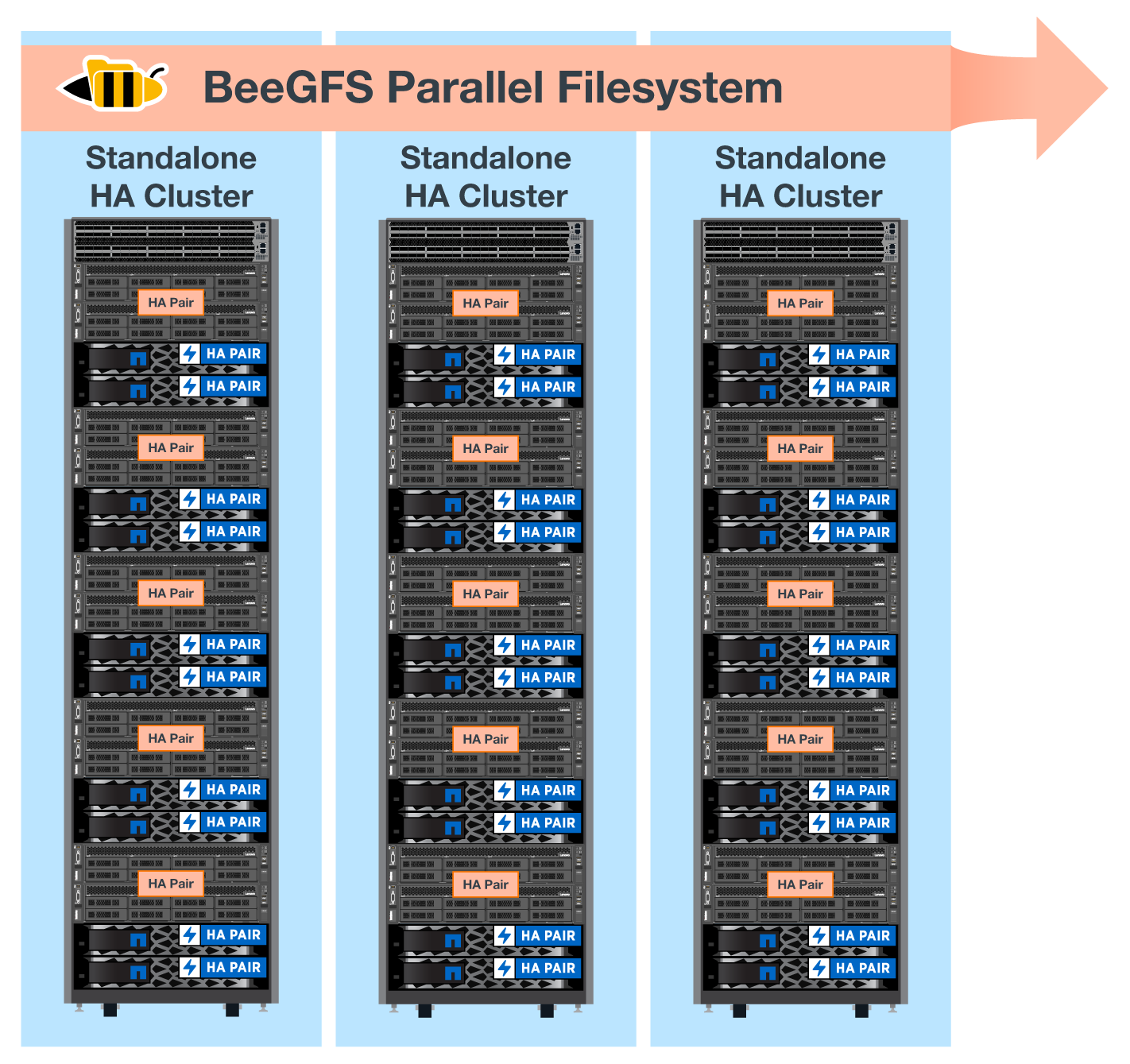
Up to five building blocks can be deployed to form a standalone Linux HA cluster. This optimizes resource management with Pacemaker and maintains efficient synchronization with Corosync. One or more of these standalone BeeGFS HA clusters are combined to create a BeeGFS file system that is accessible to clients as a single storage namespace. On the hardware side, a single 42U rack can accommodate up to five building blocks, along with two 1U InfiniBand switches for the storage/data network. See the graphic below for a visual representation.

|
A minimum of two building blocks are required to establish quorum in the failover cluster. A two-node cluster has limitations that might prevent a successful failover from occurring. You can configure a two-node cluster by incorporating a third device as a tiebreaker; however, this documentation does not describe that design. |
Ansible
BeeGFS on NetApp is delivered and deployed using Ansible automation, which is hosted on GitHub and Ansible Galaxy (the BeeGFS collection is available from Ansible Galaxy and NetApp's E-Series GitHub). Although Ansible is primarily tested with the hardware used to assemble the BeeGFS building blocks, you can configure it to run on virtually any x86-based server using a supported Linux distribution.
For more information, see Deploying BeeGFS with E-Series Storage.


