NetApp AIPod Mini - Enterprise RAG Inferencing with NetApp and Intel
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


This paper presents a validated reference design of NetApp AIPod for Enterprise RAG with technologies and combined capabilities of Intel Xeon 6 processors and NetApp data management solutions. The solution demonstrates a downstream ChatQnA application leveraging a large language model, providing accurate, contextually relevant responses to concurrent users. The responses are retrieved from an organization's internal knowledge repository through an air-gapped RAG inferencing pipeline.

Sathish Thyagarajan, Michael Oglesby, Arpita Mahajan, NetApp
Executive summary
A growing number of organizations are leveraging retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) applications and large language models (LLMs) to interpret user prompts and generate responses to increase productivity and business value. These prompts and responses can include text, code, images, or even therapeutic protein structures retrieved from an organization's internal knowledge base, data lakes, code repositories, and document repositories. This paper covers the reference design of the NetApp AIPod Mini solution, comprising NetApp AFF storage and servers with Intel Xeon 6 processors. It includes NetApp ONTAP data management software combined with Intel Advanced Matrix Extensions (Intel AMX), and Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG software built on Open Platform for Enterprise AI (OPEA). The NetApp AIPod Mini for enterprise RAG enables organizations to augment a public LLM into a private generative AI (GenAI) inferencing solution. The solution demonstrates efficient and cost-effective RAG inferencing at enterprise scale, designed to enhance reliability and provide you with better control over your proprietary information.
Intel storage partner validation
Servers powered by Intel Xeon 6 processors are built to handle demanding AI inferencing workloads, using Intel AMX for maximum performance. To enable optimal storage performance and scalability, the solution has been successfully validated using NetApp ONTAP, enabling enterprises to meet the needs of RAG applications. This validation was conducted on servers featuring Intel Xeon 6 processors. Intel and NetApp have a strong partnership focused on delivering AI solutions that are optimized, scalable, and aligned with customer business requirements.
Advantages of running RAG systems with NetApp
RAG applications involve retrieval of knowledge from companies' document repositories in various types such as PDF, text, CSV or Excel. This data is normally stored in solutions such as an S3 object storage or NFS on-premises as the source for data. NetApp has been a leader in data management, data mobility, data governance, and data security technologies across the ecosystem of edge, data center, and cloud. NetApp ONTAP data management provides enterprise-grade storage to support various types of AI workloads, including batch and real-time inferencing, and offers some of the following benefits:
-
Velocity and scalability. You can handle large datasets at high velocity for versioning with the ability to scale performance and capacity independently.
-
Data access. Multiprotocol support allows client applications to read data using S3, NFS, and SMB file-sharing protocols. ONTAP S3 NAS buckets can facilitate data access in multimodal LLM inference scenarios.
-
Reliability and confidentiality. ONTAP provides data protection, built-in NetApp Autonomous Ransomware Protection (ARP), and dynamic provisioning of storage, and it offers both software- and hardware-based encryption to enhance confidentiality and security. ONTAP is compliant with FIPS 140-2 for all SSL connections.
Target audience
This document is intended for AI decision makers, data engineers, business leaders, and departmental executives who want to take advantage of an infrastructure built to deliver enterprise RAG and GenAI solutions. Prior knowledge of AI inferencing, LLMs, Kubernetes, and networking and its components will help during the implementation phase.
Technology Requirements
Hardware
Intel® AI technologies
With Xeon 6 as a host CPU, accelerated systems benefit from high single-thread performance; higher memory bandwidth; improved reliability, availability, and serviceability (RAS); and more I/O lanes. Intel AMX accelerates inferencing for INT8 and BF16 and offers support for FP16-trained models, with up to 2,048 floating-point operations per cycle per core for INT8 and 1,024 floating-point operations per cycle per core for BF16/FP16. To deploy a RAG solution using Xeon 6 processors, a minimum RAM of 250GB and 500GB disk space is generally recommended. However, this is highly dependent on the LLM model size. For more information, refer to the Intel Xeon 6 processor product brief.
Figure 1 - Compute server with Intel Xeon 6 processors
NetApp AFF storage
The entry-level and mid-level NetApp AFF A-Series systems offer more powerful performance, density, and greater efficiency. NetApp AFF A20, AFF A30, and AFF A50 systems provide true unified storage that supports block, file, and object, based on a single OS that can seamlessly manage, protect, and mobilize data for RAG applications at the lowest cost across hybrid cloud.
Figure 2 - NetApp AFF A-Series system.
| Hardware | Quantity | Comment |
|---|---|---|
Intel Xeon 6th Gen (Granite Rapids) |
2 |
RAG inferencing nodes—with dual socket Intel Xeon 6900-series (96 core) or Intel Xeon 6700-series(64 core) processors and 250GB to 3TB RAM with DDR5(6400MHz) or MRDIMM (8800MHz). 2U server. |
Control plane server with Intel processor |
1 |
Kubernetes control plane/1U server. |
Choice of 100Gb Ethernet switch |
1 |
Data center switch. |
NetApp AFF A20 (Or AFF A30; AFF A50) |
1 |
Maximum storage capacity: 9.3PB. Note: Networking: 10/25/100 GbE ports. |
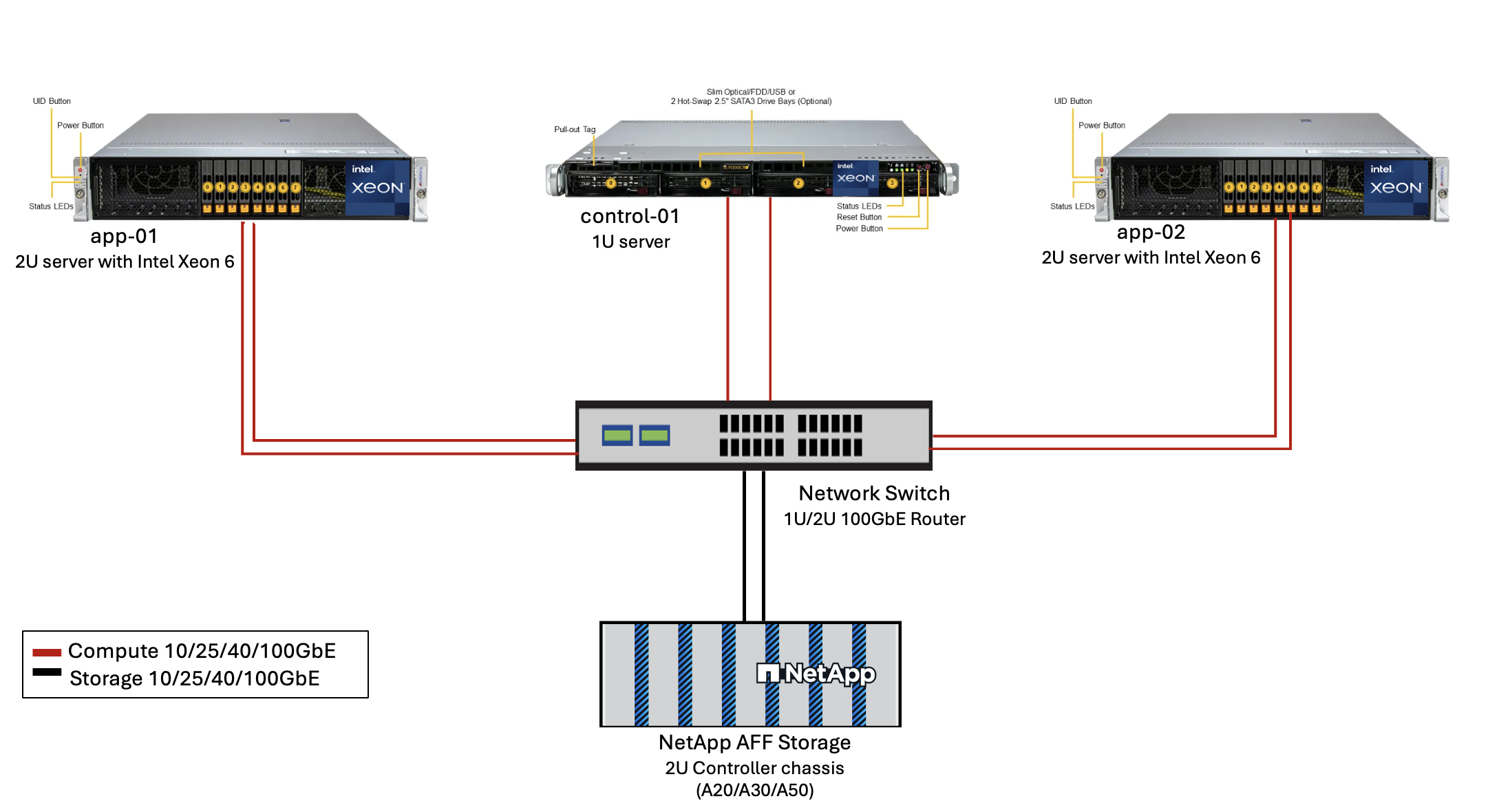
For the validation of this reference design, servers with Intel Xeon 6 processors from Supermicro (222HA-TN-OTO-37) and a 100GbE switch from Arista (7280R3A) were used.
Figure 3 - AIPod Mini Deployment Architecture
Software
Open Platform for Enterprise AI
The Open Platform for Enterprise AI (OPEA) is an open-source initiative led by Intel in collaboration with ecosystem partners. It provides a modular platform of composable building blocks designed to accelerate the development of cutting-edge generative AI systems, with a strong focus on RAG.
OPEA includes a comprehensive framework featuring LLMs, datastores, prompt engines, RAG architectural blueprints, and a four-step evaluation method that assesses generative AI systems based on performance, features, trustworthiness, and enterprise readiness.
At its core, OPEA comprises two key components:
-
GenAIComps: a service-based toolkit made up of microservice components
-
GenAIExamples: ready-to-deploy solutions like ChatQnA that demonstrate practical use cases
For more details, see the OPEA Project Documentation
Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG powered by OPEA
OPEA for Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG simplifies transforming your enterprise data into actionable insights. Powered by Intel Xeon processors, it integrates components from industry partners to offer a streamlined approach to deploying enterprise solutions. It scales seamlessly with proven orchestration frameworks, providing the flexibility and choice your enterprise needs.
Building on the foundation of OPEA, Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG extends this base with key features that enhance scalability, security, and user experience. These features include service mesh capabilities for seamless integration with modern service-based architectures, production-ready validation for pipeline reliability, and a feature-rich UI for RAG as a service, enabling easy management and monitoring of workflows. Additionally, Intel and partner support provide access to a broad ecosystem of solutions, combined with integrated Identity and Access Management (IAM) with UI and applications for secure and compliant operations. Programmable guardrails provide fine-grained control over pipeline behavior, enabling customized security and compliance settings.
NetApp ONTAP
NetApp ONTAP is the foundational technology that underpins NetApp's critical data storage solutions. ONTAP includes various data management and data protection features, such as automatic ransomware protection against cyberattacks, built-in data transport features, and storage efficiency capabilities. These benefits apply to a range of architectures, from on-premises to hybrid multicloud in NAS, SAN, object, and software-defined storage for LLM deployments. You can use an ONTAP S3 object storage server in an ONTAP cluster for deploying RAG applications, taking advantage of the storage efficiencies and security of ONTAP, provided through authorized users and client applications. For more information, refer to Learn about ONTAP S3 configuration
NetApp Trident
NetApp Trident software is an open-source and fully supported storage orchestrator for containers and Kubernetes distributions, including Red Hat OpenShift. Trident works with the entire NetApp storage portfolio, including the NetApp ONTAP and it also supports NFS and iSCSI connections. For more information, refer to NetApp Trident on Git
| Software | Version | Comment |
|---|---|---|
OPEA - Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG |
2.0 |
Enterprise RAG platform based on OPEA microservices |
Container Storage Interface (CSI driver) |
NetApp Trident 25.10 |
Enables dynamic provisioning, NetApp Snapshot copies, and volumes. |
Ubuntu |
22.04.5 |
OS on two-node cluster. |
Container orchestration |
Kubernetes 1.31.9 (Installed by Enterprise RAG infrastructure playbook) |
Environment to run RAG framework |
ONTAP |
ONTAP 9.16.1P4 or above |
Storage OS on AFF A20. |
Solution deployment
Software stack
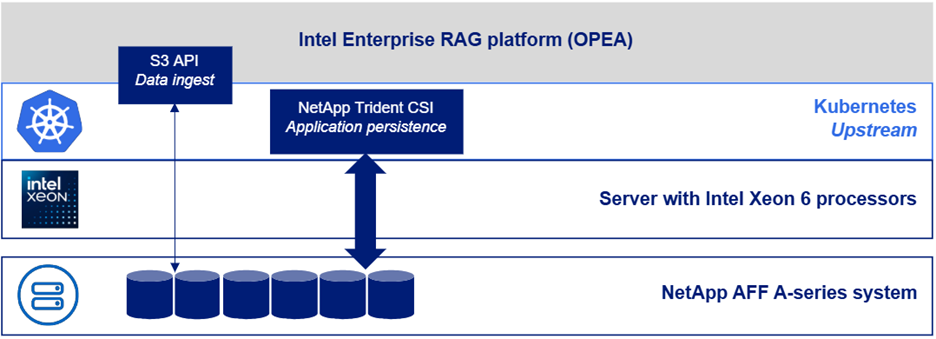
The solution is deployed on a Kubernetes cluster consisting of Intel Xeon–based app nodes. At least three nodes are required to implement basic high availability for the Kubernetes control plane. We validated the solution using the following cluster layout.
Table 3 - Kubernetes cluster layout
| Node | Role | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
Servers with Intel Xeon 6 processors and 1TB RAM |
App node, control plane node |
2 |
Generic server |
Control plane node |
1 |
The following figure depicts a "software stack view" of the solution.
Deployment steps
Deploy ONTAP storage appliance
Deploy and provision your NetApp ONTAP storage appliance. Refer to the ONTAP hardware systems documentation for details.
Configure an ONTAP SVM for NFS and S3 access
Configure an ONTAP storage virtual machine (SVM) for NFS and S3 access on a network that is accessible by your Kubernetes nodes.
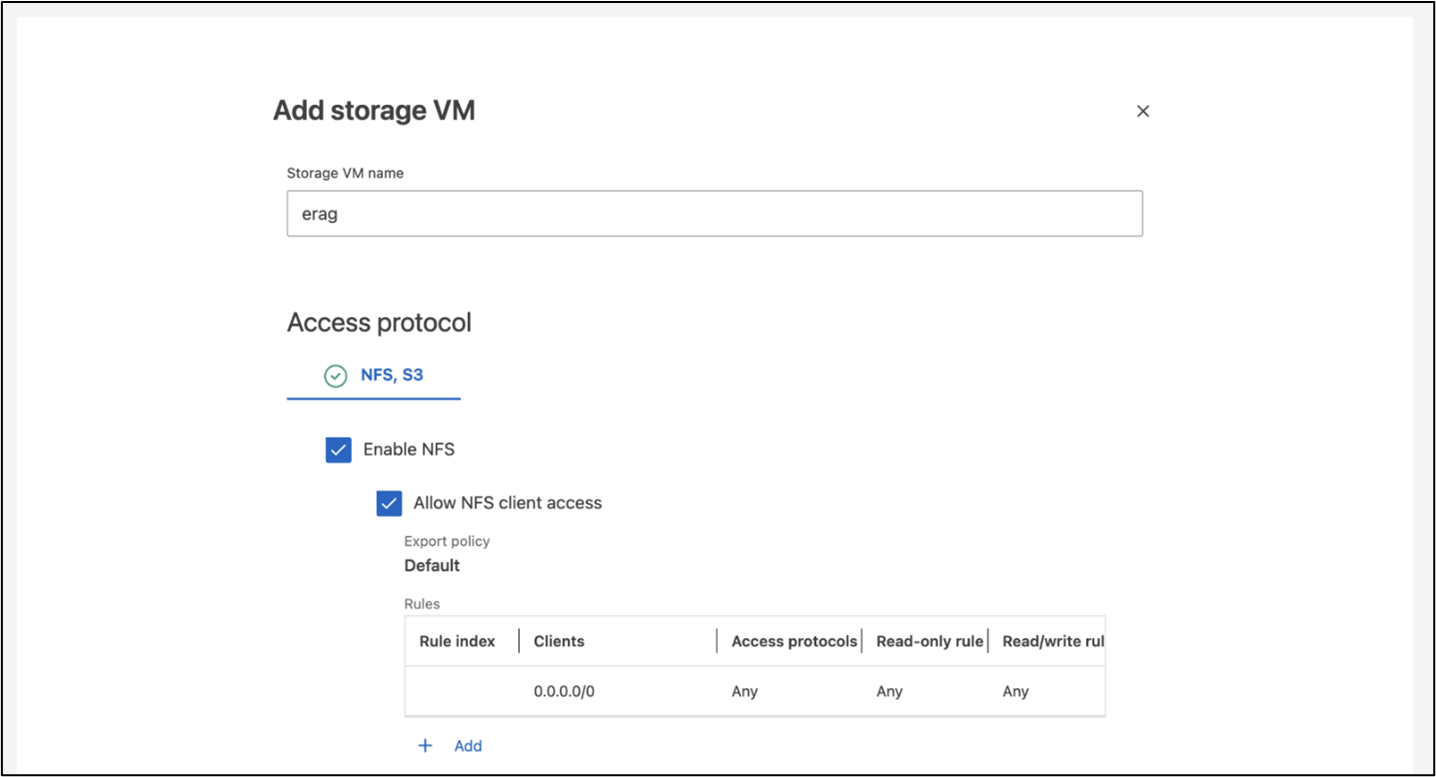
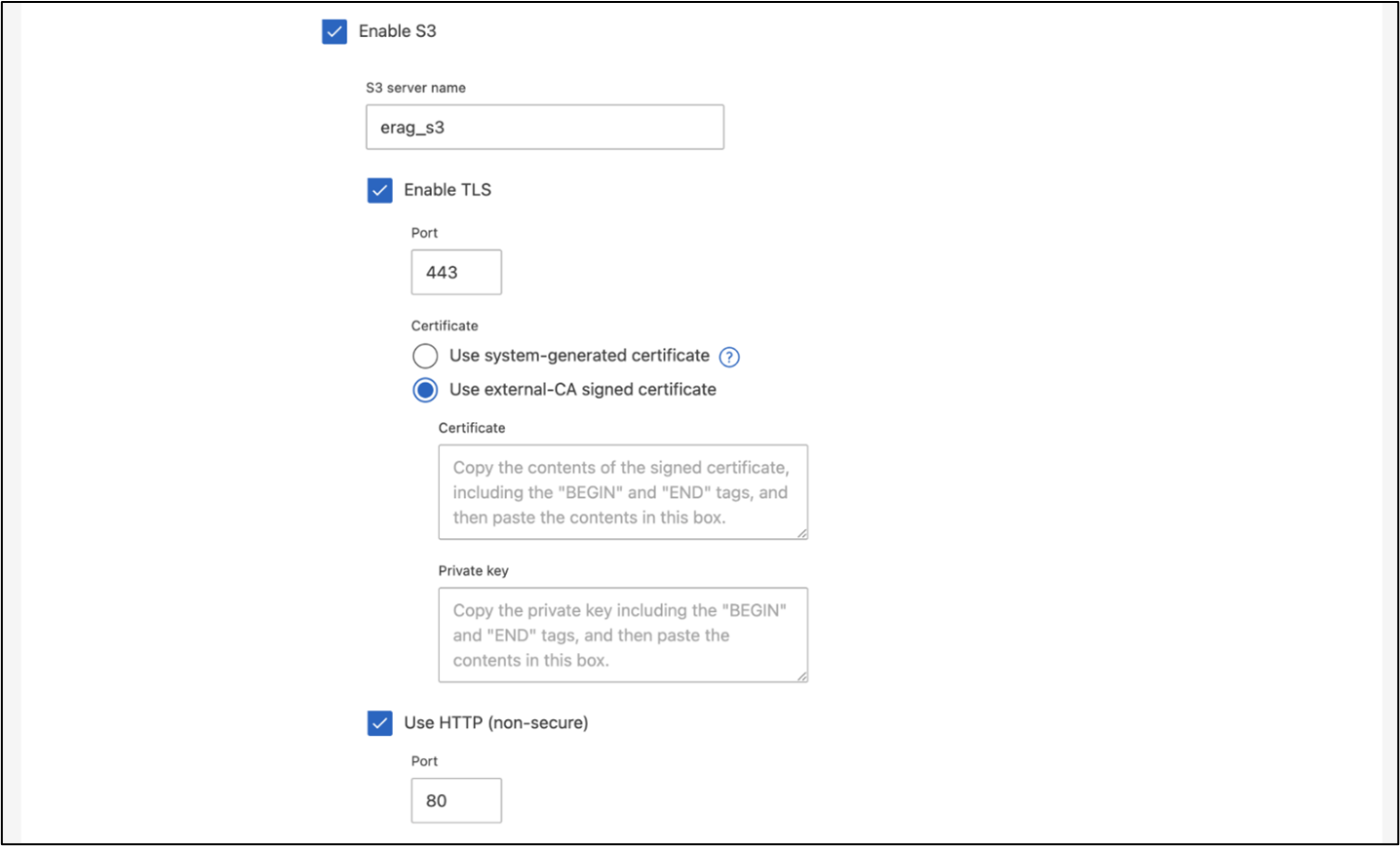
To create an SVM using ONTAP System Manager, navigate to Storage > Storage VMs, and click the + Add button. When enabling S3 access for your SVM, choose the option to use an external-CA (certificate authority) signed certificate, not a system-generated certificate. You can use either a self-signed certificate or a certificate that is signed by a publicly trusted CA. For additional details, refer to the ONTAP documentation.
The following screenshot depicts the creation of an SVM using ONTAP System Manager. Modify details as needed based on your environment.
Figure 5 - SVM creation using ONTAP System Manager.
Configure S3 permissions
Configure S3 user/group settings for the SVM that you created in the previous step. Make sure you have a user with full access to all S3 API operations for that SVM. Refer to the ONTAP S3 documentation for details.
Note: This user will be needed for the Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG application's data ingest service.
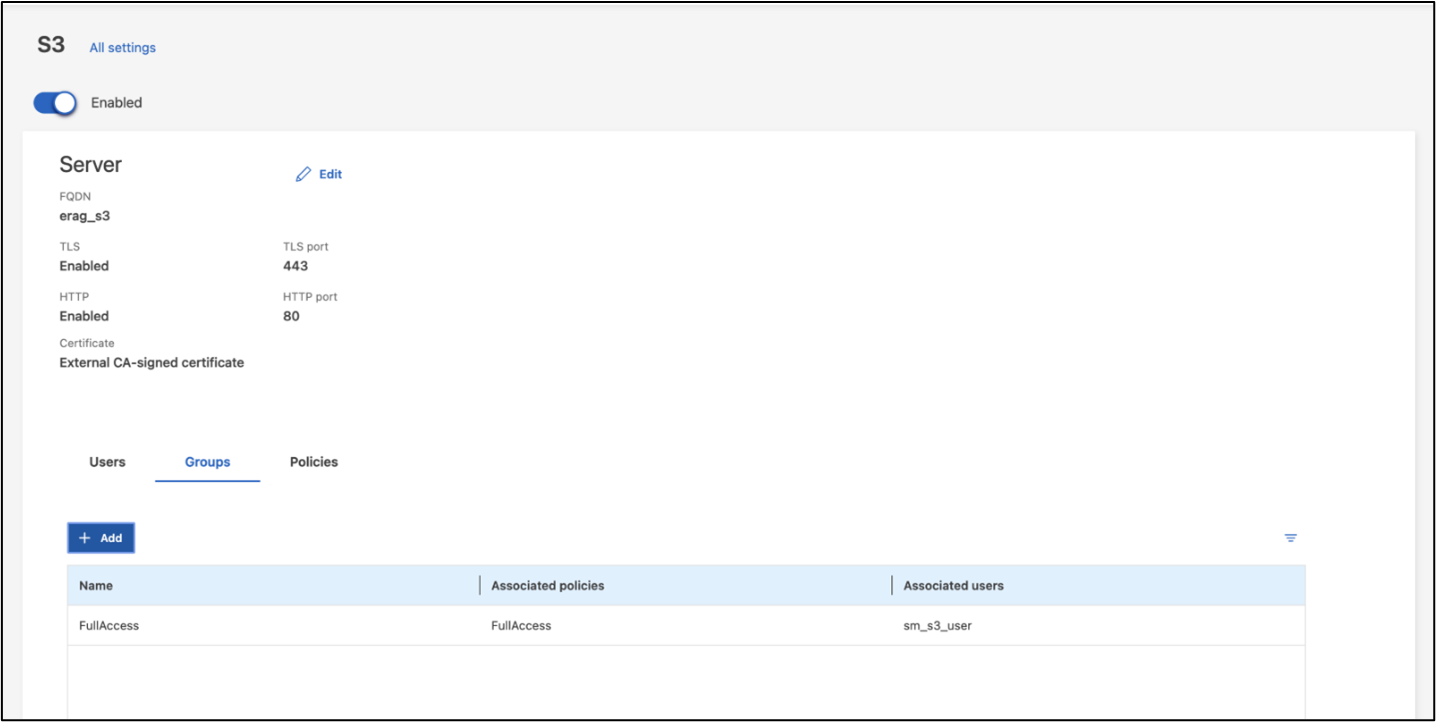
If you created your SVM using ONTAP System Manager, System Manager will have automatically created a user named sm_s3_user and a policy named FullAccess when you created your SVM, but no permissions will have been assigned to sm_s3_user.
To edit permissions for this user, navigate to Storage > Storage VMs, click the name of the SVM that you created in the previous step, click Settings, and then click the pencil icon next to "S3." To give sm_s3_user full access to all S3 API operations, create a new group that associates sm_s3_user with the FullAccess policy as depicted in the following screenshot.
Figure 6 - S3 permissions.
Create an S3 bucket
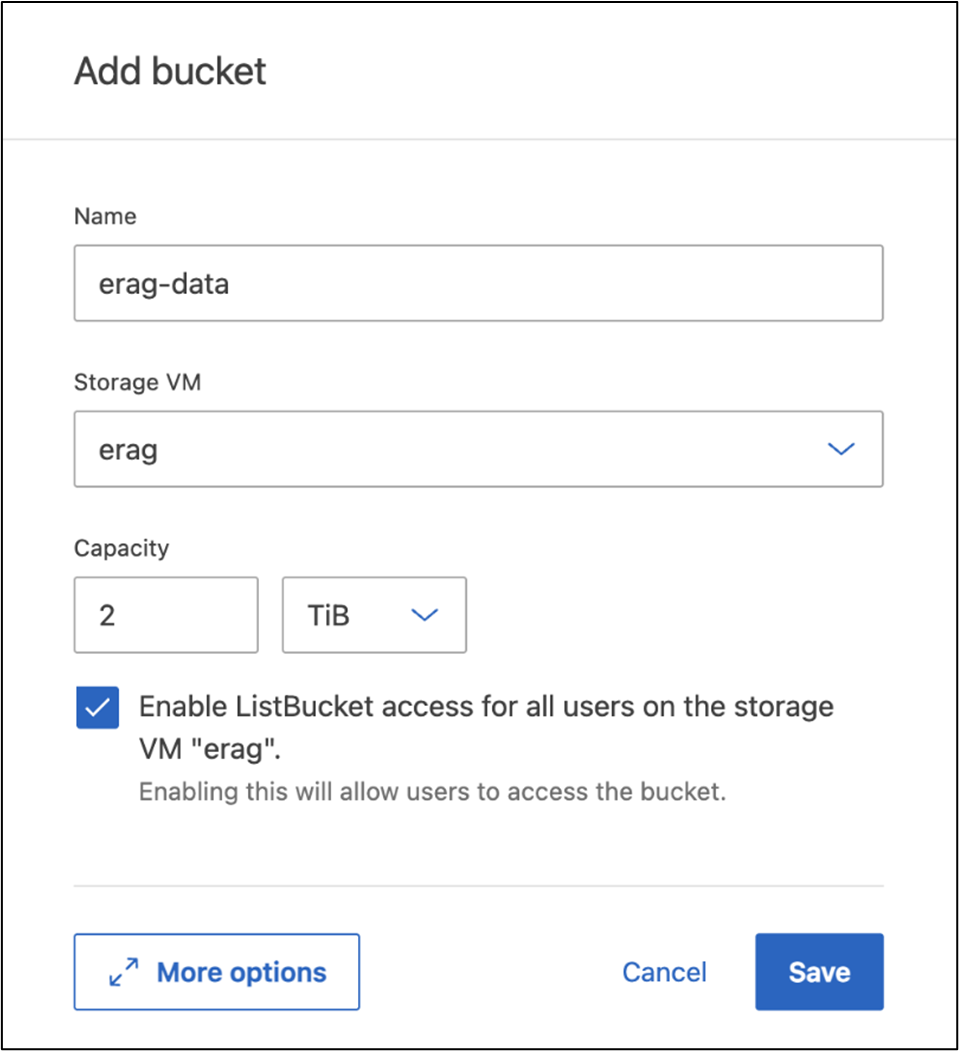
Create an S3 bucket within the SVM that you created previously.
To create an SVM using ONTAP System Manager, navigate to Storage > Buckets, and click the + Add button. For additional details, refer to the ONTAP S3 documentation.
The following screenshot depicts the creation of an S3 bucket using ONTAP System Manager.
Figure 7 - Create an S3 bucket.
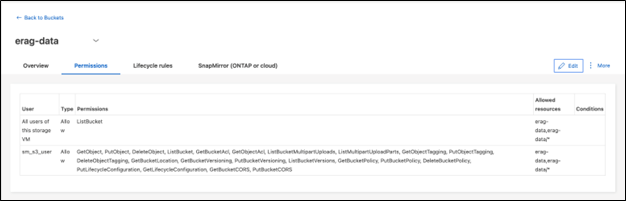
Configure S3 bucket permissions
Configure permissions for the S3 bucket that you created in the previous step. Ensure that the user you configured in a prior step has the following permissions: GetObject, PutObject, DeleteObject, ListBucket, GetBucketAcl, GetObjectAcl, ListBucketMultipartUploads, ListMultipartUploadParts, GetObjectTagging, PutObjectTagging, DeleteObjectTagging, GetBucketLocation, GetBucketVersioning, PutBucketVersioning, ListBucketVersions, GetBucketPolicy, PutBucketPolicy, DeleteBucketPolicy, PutLifecycleConfiguration, GetLifecycleConfiguration, GetBucketCORS, PutBucketCORS.
To edit S3 bucket permissions using ONTAP System Manager, navigate to Storage > Buckets, click the name of your bucket, click Permissions, and then click Edit. Refer to the ONTAP S3 documentation for additional details.
The following screenshot depicts the necessary bucket permissions in ONTAP System Manager.
Figure 8 - S3 bucket permissions.
Create bucket cross-origin resource sharing rule
Using the ONTAP CLI, create a bucket cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) rule for the bucket that you created in a previous step:
ontap::> bucket cors-rule create -vserver erag -bucket erag-data -allowed-origins *erag.com -allowed-methods GET,HEAD,PUT,DELETE,POST -allowed-headers *This rule allows OPEA for Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG web application to interact with the bucket from within a web browser.
Deploy servers
Deploy your servers and install Ubuntu 22.04 LTS on every server.
After Ubuntu is installed, install the NFS utilities on every server. To install the NFS utilities, run the following command:
apt-get update && apt-get install nfs-commonDeploy Enterprise RAG 2.0
Refer to the following document for complete, step-by-step deployment workflow:
NetApp AIPod Mini for ERAG - Deployment Steps
All pre-requisites, infrastructure preparation, configuration parameters and deployment procedures are documented in above deployment guide.
Access OPEA for Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG UI
Access the OPEA for Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG UI. Refer to the Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG deployment documentation for details.
Figure 9 - OPEA for Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG UI.
Ingest data for RAG
You can now ingest files for inclusion in RAG-based query augmentation. There are multiple options for ingesting files. Choose the appropriate option for your needs.
Note: After a file has been ingested, the OPEA for Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG application automatically checks for updates to the file and ingests the updates accordingly.
*Option 1: Upload directly to your S3 bucket
To ingest many files at once, we recommend uploading the files to your S3 bucket (the bucket that you created earlier) by using the S3 client of your choice. Popular S3 clients include the AWS CLI, the Amazon SDK for Python (Boto3), s3cmd, S3 Browser, Cyberduck, and Commander One. If the files are of a supported type, any files that you upload to your S3 bucket will be automatically ingested by the OPEA for Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG application.
Note: At the time of this writing, the following file types are supported: PDF, HTML, TXT, DOC, DOCX, ADOC, PPT, PPTX, MD, XML, JSON, JSONL, YAML, XLS, XLSX, CSV, TIFF, JPG, JPEG, PNG, and SVG.
You can use the OPEA for Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG UI to confirm that your files were properly ingested. Refer to the Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG UI documentation for details. Note that it can take some time for the application to ingest a large number of files.
*Option 2: Upload using the UI
If you need to ingest only a small number of files, you can ingest them using the OPEA for Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG UI. Refer to the Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG UI documentation for details.
Figure 10 - Data ingest UI.
Execute chat queries
You can now "chat" with the OPEA for Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG application by using the included chat UI. When responding to your queries, the application performs RAG using your ingested files. This means that the application automatically searches for relevant information within your ingested files and incorporates this information when responding to your queries.
Sizing guidance
As part of our validation effort, we conducted performance testing in coordination with Intel. This testing resulted in the sizing guidance outlined in the following table.
| Characterizations | Value | Comment |
|---|---|---|
Model size |
20 billion parameters |
Llama-8B, Llama-13B, Mistral 7B, Qwen 14B, DeepSeek Distill 8B |
Input size |
~2k tokens |
~4 pages |
Output size |
~2k tokens |
~4 pages |
Concurrent users |
32 |
"Concurrent users" refers to prompt requests that are submitting queries at the same time. |
_Note: The sizing guidance presented above is based on performance validation and test results gathered by using Intel Xeon 6 processors with 96 cores. For customers with similar I/O tokens and model size requirements we recommend using servers with Xeon 6 processors with 96 cores. For further details on sizing guide, refer to Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG Sizing Guide
Conclusion
Enterprise RAG systems and LLMs are technologies that work together to help organizations provide accurate and context-aware responses. These responses involve information retrieval based on a vast collection of private and internal enterprise data. By using RAG, APIs, vector embeddings, and high-performance storage systems to query document repositories that contain company data, the data is processed faster and securely. The NetApp AIPod Mini combines NetApp's intelligent data infrastructure with ONTAP data management capabilities and Intel Xeon 6 processors, Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG, and the OPEA software stack to help deploy high-performance RAG applications and put organizations on the path to AI leadership.
Acknowledgment
This document is authored by Sathish Thyagarajan, Michael Oglesby and Arpita Mahajan, members of the NetApp Solutions Engineering team. The authors would also like to thank the Enterprise AI product team at Intel—Ajay Mungara, Mikolaj Zyczynski, Igor Konopko, Ramakrishna Karamsetty, Michal Prostko, Anna Alberska, Maciej Cichocki, Shreejan Mistry, Nicholas Rago and Ned Fiori-as well as other team members at NetApp—Lawrence Bunka, Bobby Oommen, and Jeff Liborio, for their continued support and help during the solution validation process.
Bill of Materials
The following was the BOM used for the functional validation of this solution and can be used for reference. Any server or networking component (or even existing network with preferably 100GbE bandwidth) that aligns with the following configuration could be used.
For the App server:
| Part no. | Product description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
222HA-TN-OTO-37 |
Hyper SuperServer SYS-222HA-TN /2U |
2 |
P4X-GNR6972P-SRPL2-UC |
Intel® Xeon® 6972P Processor 96-Core 2.40GHz 480MB Cache (500W) |
4 |
RAM |
MEM-DR564MC-ER64(x16)64GB DDR5-6400 2RX4 (16Gb) ECC RDIMM |
32 |
HDS-M2N4-960G0-E1-TXD-NON-080(x2) SSD M.2 NVMe PCIe4 960GB 1DWPD TLC D, 80mm |
2 |
|
WS-1K63A-1R(x2)1U 692W/1600W redundant single output power supply. Heat dissipation of 2361 BTU/Hr with Max Temp 59 C (approx.) |
4 |
For the control server:
Part no. |
Product description |
Quantity |
511R-M-OTO-17 |
OPTIMIZED UP 1U X13SCH-SYS, CSE-813MF2TS-R0RCNBP, PWS-602A-1R |
1 |
RPL-E 6369P IP 8C/16T 3.3G 24MB 95W 1700 BO |
1 |
|
RAM |
MEM-DR516MB-EU48(x2)16GB DDR5-4800 1Rx8 (16Gb) ECC UDIMM |
1 |
HDS-M2N4-960G0-E1-TXD-NON-080(x2) SSD M.2 NVMe PCIe4 960GB 1DWPD TLC D, 80mm |
2 |
For the network switch:
Part no. |
Product description |
Quantity |
DCS-7280CR3A |
Arista 7280R3A 28x100 GbE |
1 |
NetApp AFF storage:
Part no. |
Product description |
Quantity |
AFF-A20A-100-C |
AFF A20 HA System, -C |
1 |
X800-42U-R6-C |
Jumper Crd, In-Cab, C13-C14, -C |
2 |
X97602A-C |
Power Supply,1600W, Titanium, -C |
2 |
X66211B-2-N-C |
Cable,100GbE, QSFP28-QSFP28, Cu,2m, -C |
4 |
X66240A-05-N-C |
Cable,25GbE, SFP28-SFP28, Cu,0.5m, -C |
2 |
X5532A-N-C |
Rail,4-Post, Thin, Rnd/Sq-Hole, Sm, Adj,24-32, -C |
1 |
X4024A-2-A-C |
Drive Pack 2X1.92TB, NVMe4, SED, -C |
6 |
X60130A-C |
IO Module,2PT,100GbE, -C |
2 |
X60132A-C |
IO Module,4PT,10/25GbE, -C |
2 |
SW-ONTAPB-FLASH-A20-C |
SW, ONTAP Base Package, Per TB, Flash, A20, -C |
23 |
Infra Readiness Checklist
Refer to the NetApp AIPod Mini - Infra Readiness for details.
Where to find additional information
To learn more about the information that is described in this document, review the following documents and/or websites:
OPEA Enterprise RAG deployment playbook
== Version History
| Version | Date | Document Version History |
|---|---|---|
Version 1.0 |
Sept 2025 |
Initial Release |
Version 2.0 |
Feb 2026 |
Updated with OPEA-Intel® AI for Enterprise RAG 2.0 |


