Requirements to install the NetApp Shift Toolkit
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


Verify that your environment meets the hardware, connectivity, and ONTAP storage requirements before installing the Shift Toolkit.
Hardware requirements
Ensure the Shift Toolkit server meets the following minimum hardware requirements:
-
CPU: 4 vCPUs
-
Memory: 8 GB minimum
-
Disk space: 100 GB minimum (900 MB available for installation)
Connectivity requirements
Verify the following connectivity requirements are met:
-
Shift Toolkit must be installed on a standalone Windows server (physical or virtual)
-
The hypervisor and storage environment must be configured to allow the Shift Toolkit to interact with all components
-
For Hyper-V migrations, the Shift server, ONTAP CIFS server, and Hyper-V servers must be on the same Windows Active Directory domain
-
Multiple LIFs for CIFS and NFS are supported for use with Storage Virtual Machines (SVMs) during VM conversions
-
For CIFS operations, time settings must be synchronized between the Windows domain controller and the ONTAP storage controller
ONTAP storage configurations
Configure ONTAP storage components including SVMs, qtrees, and CIFS shares to support Shift Toolkit migrations.
Create a new SVM (recommended)
Although the Shift Toolkit permits the use of an existing SVM, NetApp recommends creating a dedicated SVM for migration operations.
Creating a new SVM provides the following benefits:
-
Isolates migration operations from production workloads
-
Ensures the SVM meets Shift Toolkit requirements without modifying production configurations
-
Simplifies configuration for bi-directional migrations between VMware and Hyper-V
Use Storage vMotion to move VMs to a new designated NFSv3 datastore on the dedicated SVM without downtime. This approach ensures migrated VMs do not reside on the production SVM.
Use the ONTAP CLI, NetApp PowerShell Toolkit, or ONTAP System Manager to create the new SVM. For detailed steps, refer to the ONTAP documentation for provisioning a new SVM with both NFS and SMB protocols enabled.

|
For bi-directional migration between VMware and Hyper-V, enable both NFS and SMB protocols on the SVM and provisioned volumes. |
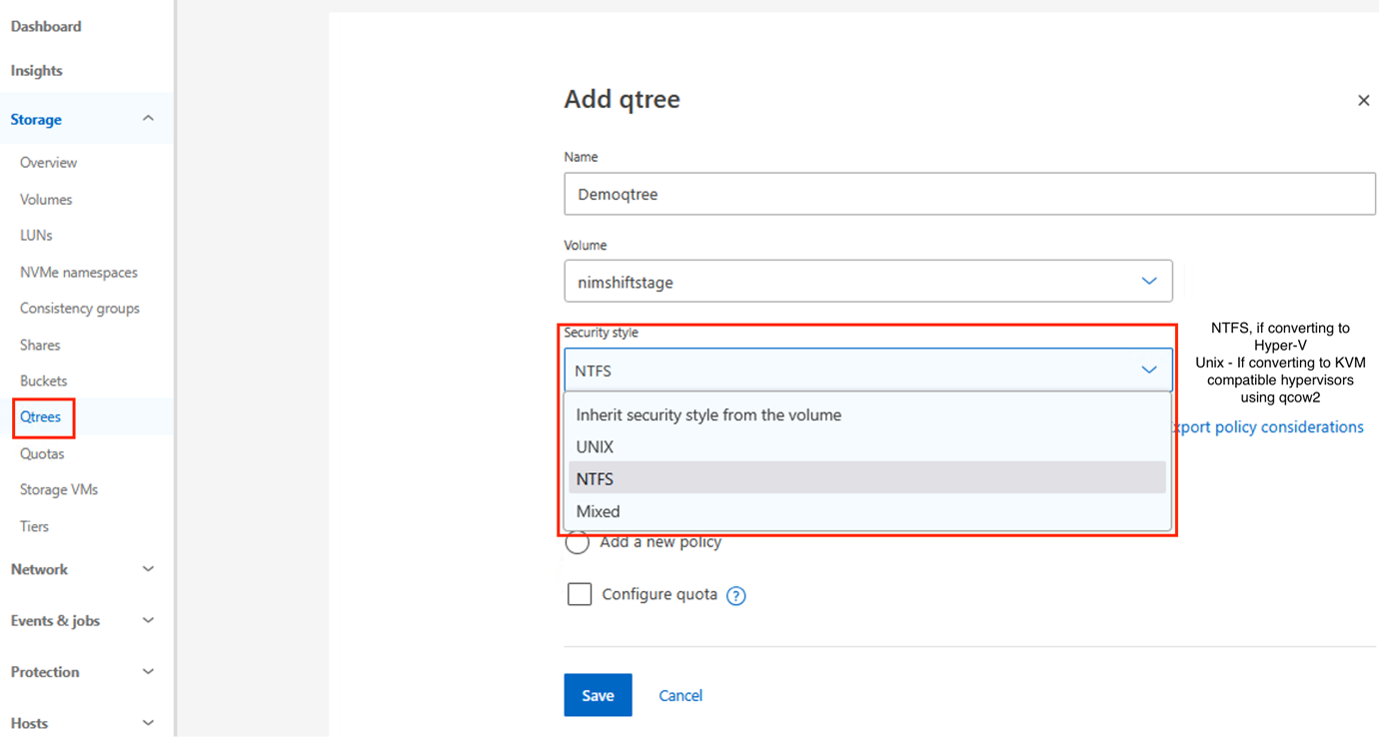
Qtree requirements
Create qtrees on the volume that will host converted VMs. Qtrees segregate and store converted disk files based on the target hypervisor.
Security style by migration type:
-
ESXi to Hyper-V: NTFS security style (stores converted VHDXs)
-
Hyper-V to ESXi: UNIX security style (stores converted VMDKs)
-
ESXi to OpenShift Virtualization (QCOW2): UNIX security style
-
ESXi to OLVM (RAW or QCOW2): UNIX security style

The Shift Toolkit does not verify qtree security styles. Create qtrees with the appropriate security style for your target hypervisor and disk format.
For detailed steps, refer to Create a qtree in the ONTAP documentation.

|
The destination path must be on the same volume as the source VM. |

|
For OpenShift Virtualization, converted QCOW2 files can optionally be placed directly on the volume without using a qtree. Use the Shift Toolkit GUI or APIs to perform this conversion. |
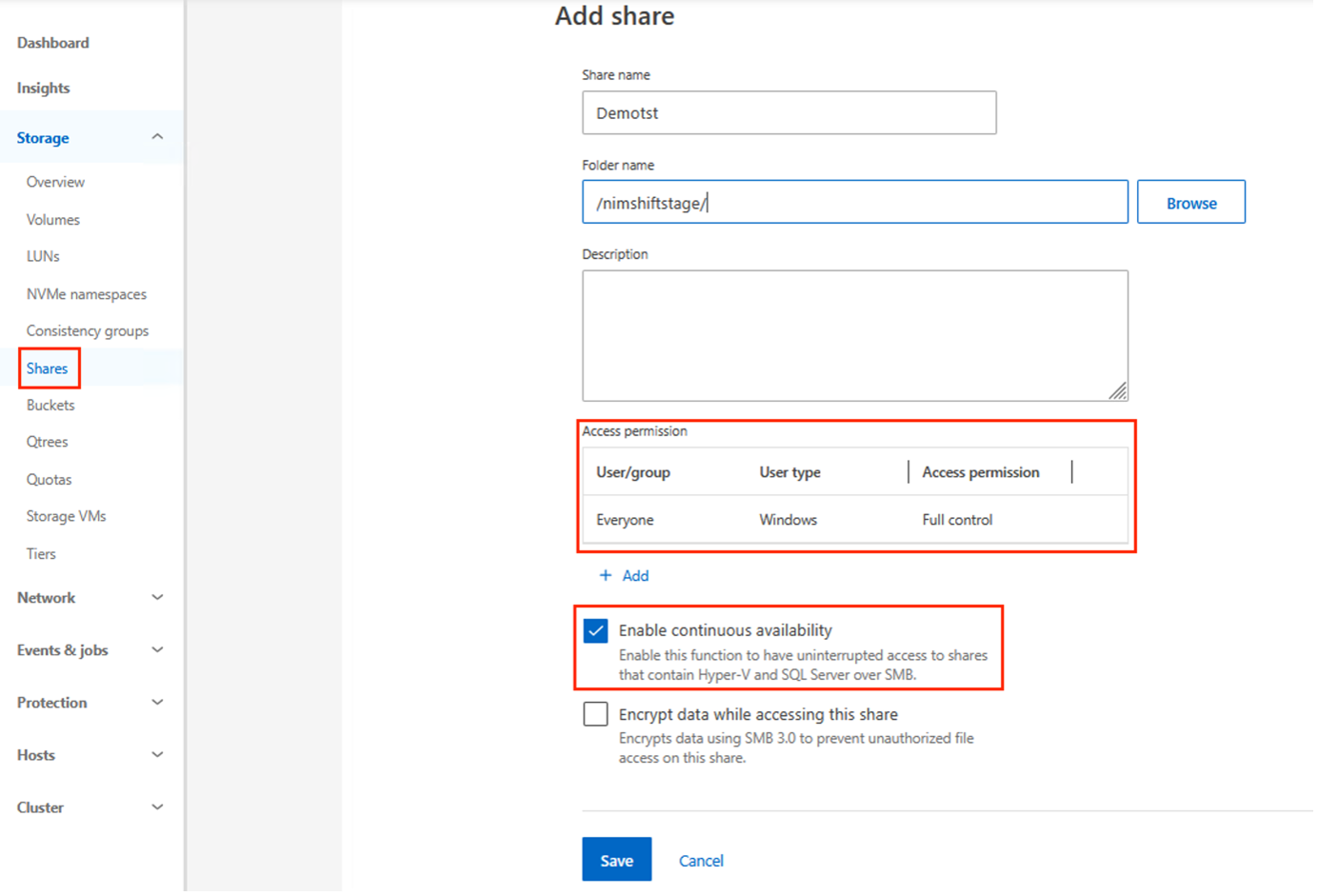
CIFS share requirements
For Hyper-V migrations, create a CIFS share for storing converted VM data. Both the NFS share (source VMs) and CIFS share (converted VMs) must reside on the same volume.
Configure the CIFS share with the following properties:
-
SMB 3.0 enabled (enabled by default)
-
Continuously available property enabled
-
Export policies for SMB disabled on the SVM
-
Kerberos and NTLMv2 authentication permitted on the domain
For detailed steps, refer to Create an SMB share in the ONTAP documentation. Select the continuous availability property along with other default properties.


|
ONTAP creates the share with the Windows default share permission of Everyone / Full Control. |


