Install or upgrade the NetApp Shift Toolkit for ONTAP storage
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


Install or upgrade the NetApp Shift Toolkit after verifying that your environment meets the preparation and prerequisite requirements.
Install the Shift Toolkit
Download and run the installer to set up the Shift Toolkit on your Windows server.
-
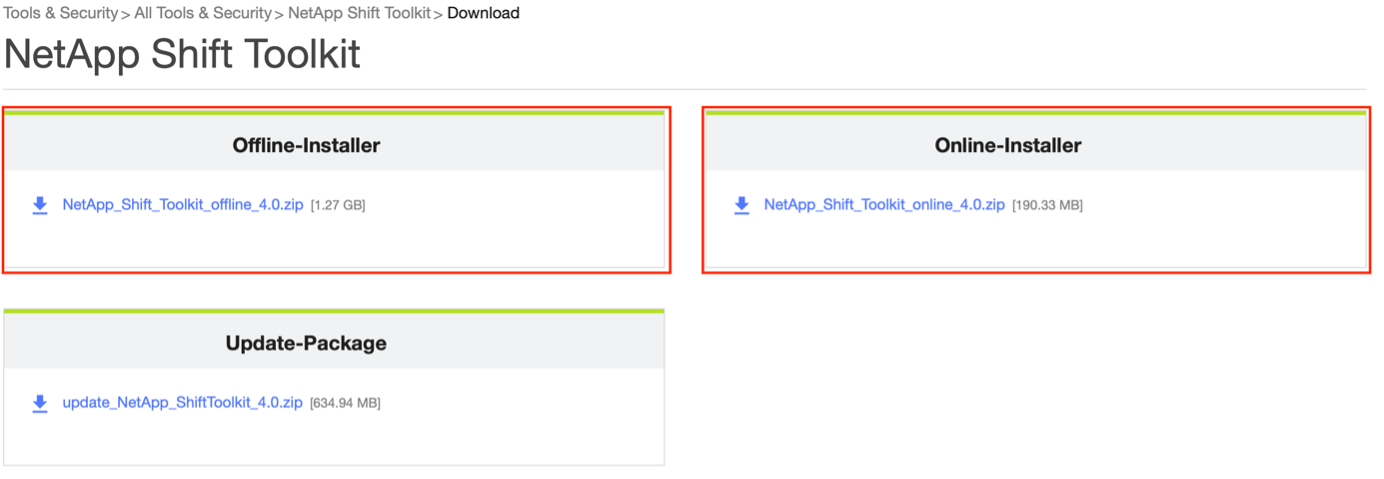
Download the Shift Toolkit package and unzip it.
Show example
-
Double-click the downloaded .exe file to initiate the Shift Toolkit installation.
Show example

All pre-checks are performed during installation. If minimum requirements are not met, appropriate error or warning messages are displayed. -
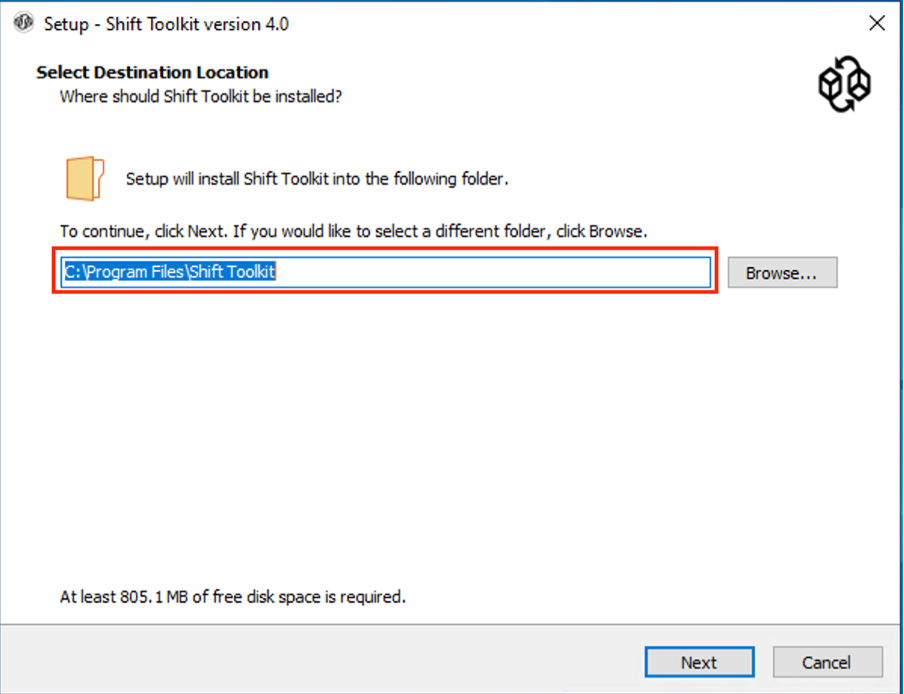
Select the installation location or use the default and click Next.
Show example
-
Select the IP address that will be used to access the Shift Toolkit UI.
Show example

If the VM has multiple NICs, the setup process allows you to select the appropriate IP address from a dropdown. -
Review the required components that will be automatically downloaded and installed, and then click Next.
These mandatory components are required for proper Shift Toolkit operation:
Show example

-
Review the Java OpenJDK GNU licensing information and click Next.
Show example

-
Keep the default setting for creating a desktop shortcut and click Next.
Show example

-
Click Install to begin the installation.
Show example

-
Wait for the installation to complete. The installer downloads and installs all required components. Click Finish when complete.
Show example
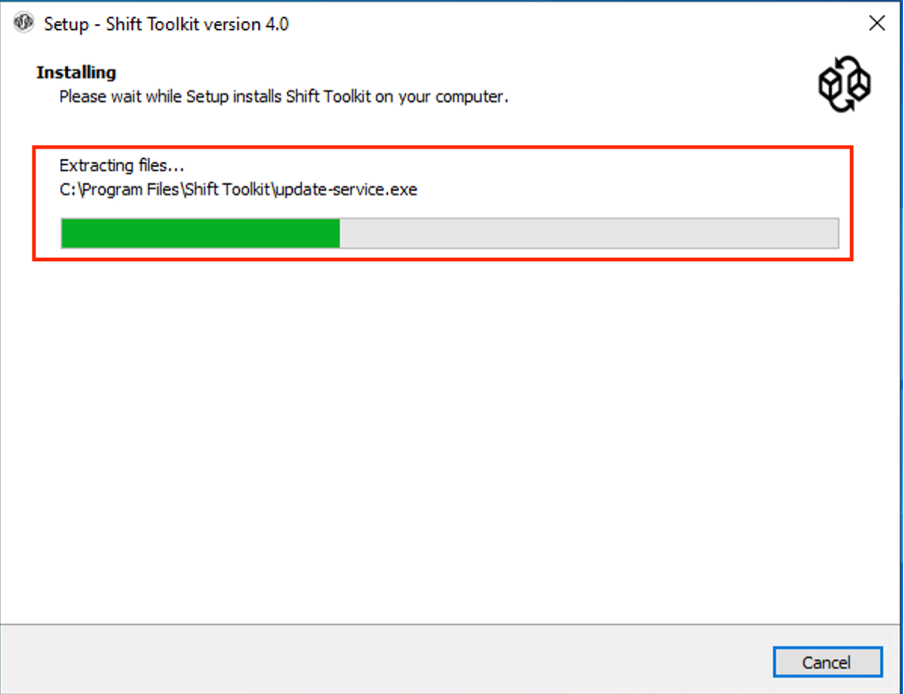
The installation can take 10-15 minutes. -
Accept the self-signed certificate prompt and click Next.
Show example
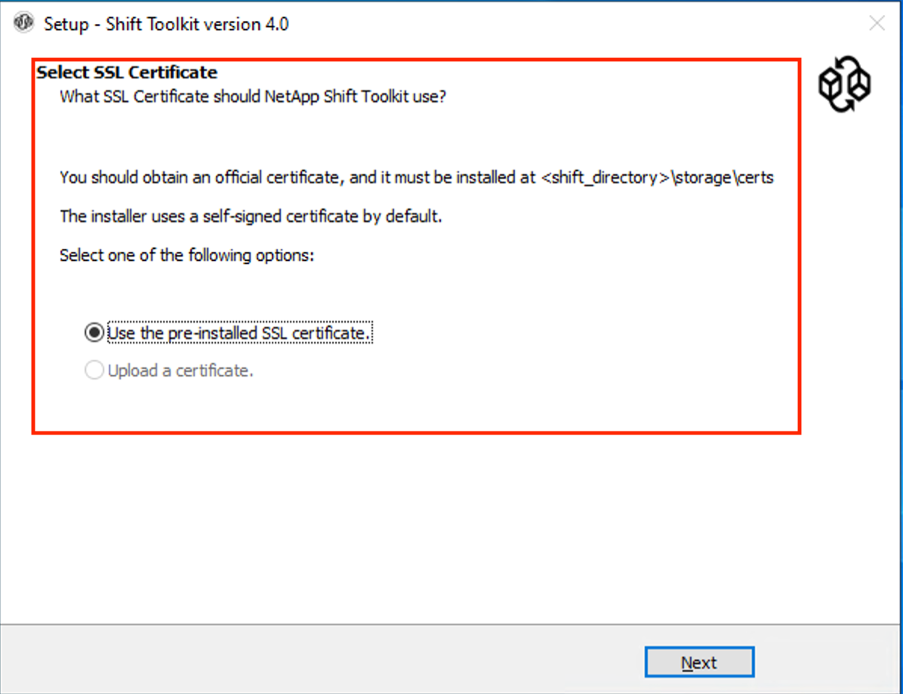
The self-signed certificate can be replaced with a third-party or CA-generated certificate. Replace the certificate in the certs folder located at <installation directory>\Storage\Certs.
The Shift Toolkit installation is complete.
Show example


|
For VMs without internet access, the offline installer performs the same steps but installs components using packages included in the executable. |
Upgrade the Shift Toolkit
Upgrades are fully automated and can be completed with a single click.
Show example

The Shift Toolkit updater service listens on port 3002 and performs the following steps:
-
Downloads the upgrade package
-
Stops the Shift Toolkit service
-
Extracts files and overwrites required files
-
Runs the update using the same IP address (retaining metadata)
-
Redirects the UI to the Shift Toolkit UI listening on port 3001
Manually download the upgrade package (filename starts with "update") from NetApp Toolchest and place it in the designated folder C:\NetApp_Shift.
Create this folder path if it doesn't exist. All other steps remain the same as the online upgrade procedure.
Show example



