Install Trident on Red Hat OpenShift cluster and create storage objects
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


Install Trident using the Red Hat Certified Trident Operator on OpenShift clusters and prepare worker nodes for block access. Create Trident backend and storage class objects for ONTAP and FSxN storage to enable dynamic volume provisioning for containers and VMs.

|
If you need to create VMs in OpenShift Virtualization, Trident must be installed and the backend objects and the storage class objects must be created in the openShift Cluster before OpenShift Virtualization is installed on the cluster (on-premises and ROSA). The default storage class and the default volume snapshot class must be set to the Trident storage and the snapshot class in the cluster. Only when this is configured, OpenShift Virtualization can make the golden images available locally for VM creation using templates. |

|
If OpenShift Virtualization operator is installed before installing Trident, you can use the following command to delete the golden images created using a different storage class and then let OpenShift Virtualization create the golden images using Trident storage class by ensuring the Trident Storage and Volume Snapshot class defaults are set. |
oc delete dv,VolumeSnapshot -n openshift-virtualization-os-images --selector=cdi.kubevirt.io/dataImportCron

|
To get sample yaml files to create trident objects for FSxN storage for ROSA clusters, and to get sample yaml file for the VolumeSnapshotClass, scroll down this page. |
Installing Trident
Installing Trident using the Red Hat Certified Operator
In this section, details of installing Trident using the Red Hat Certified Trident Operator are provided Refer to the Trident documentation for other ways to install Trident.
With the release of Trident 25.02, users of Trident in Red Hat OpenShift on premises and in the cloud and managed services like Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS can now install Trident using the Trident Certified Operator from the Operator Hub. This is significant for the OpenShift user community, as Trident was previously available only as a community operator.
The advantage of the Red Hat Certified Trident operator is that the foundation for the operator and its containers is fully supported by NetApp when used with OpenShift (whether on-premises, in the cloud, or as a managed service with ROSA). Additionally, NetApp Trident comes at no cost to the customer, so all you need to do is install it using the certified operator that has been verified to work seamlessly with Red Hat OpenShift and packaged for easy lifecycle management.
Furthermore, the Trident 25.02 operator (and future versions) offers the optional benefit of preparing the worker nodes for iSCSI. This is particularly advantageous if you plan to deploy your workloads on ROSA clusters and intend to use the iSCSI protocol with FSxN, especially for OpenShift Virtualization VM workloads. The challenge of worker node preparations for iSCSI on ROSA clusters using FSxN has been mitigated with this capability when installing Trident on the cluster.
The installation steps using the operator are the same whether you are installing it on an on-prem cluster or on ROSA.
To Install Trident using the Operator, click on Operator hub and select Certified NetApp Trident. In the Install page, the latest version is selected by default. Click on Install.
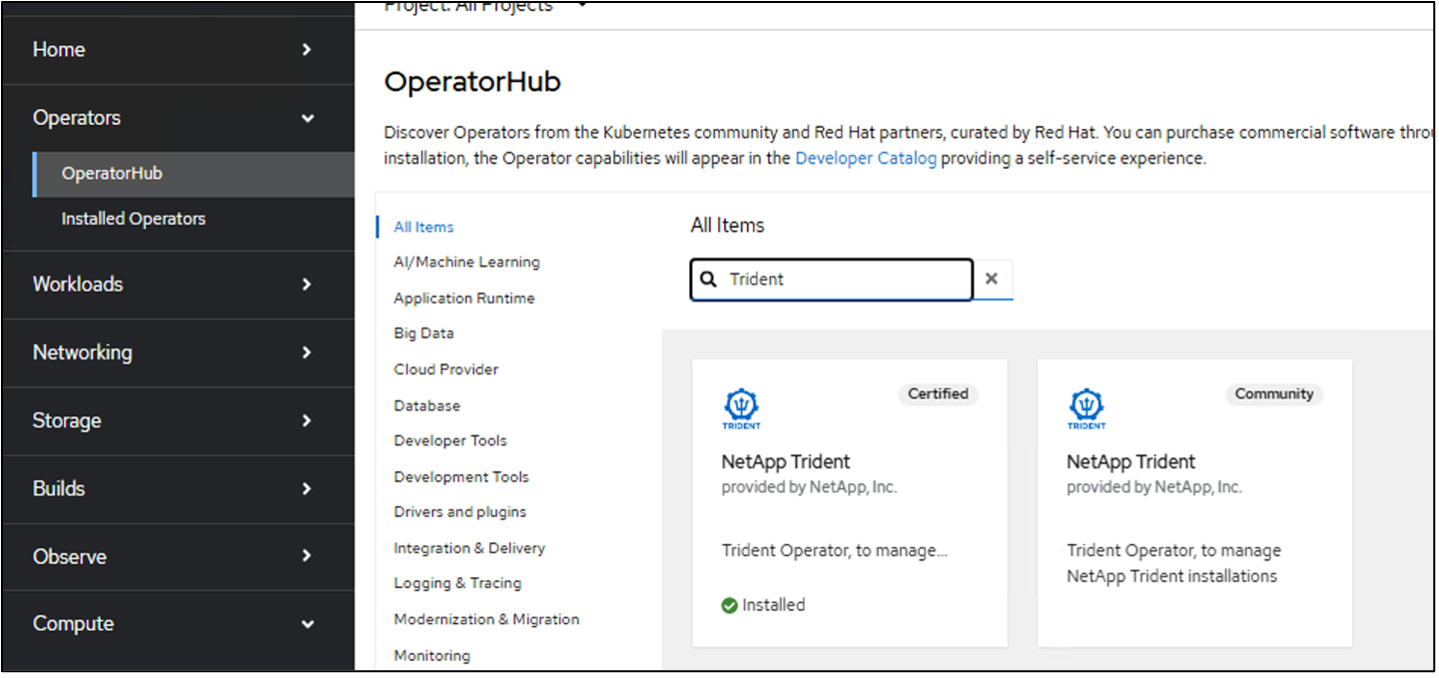
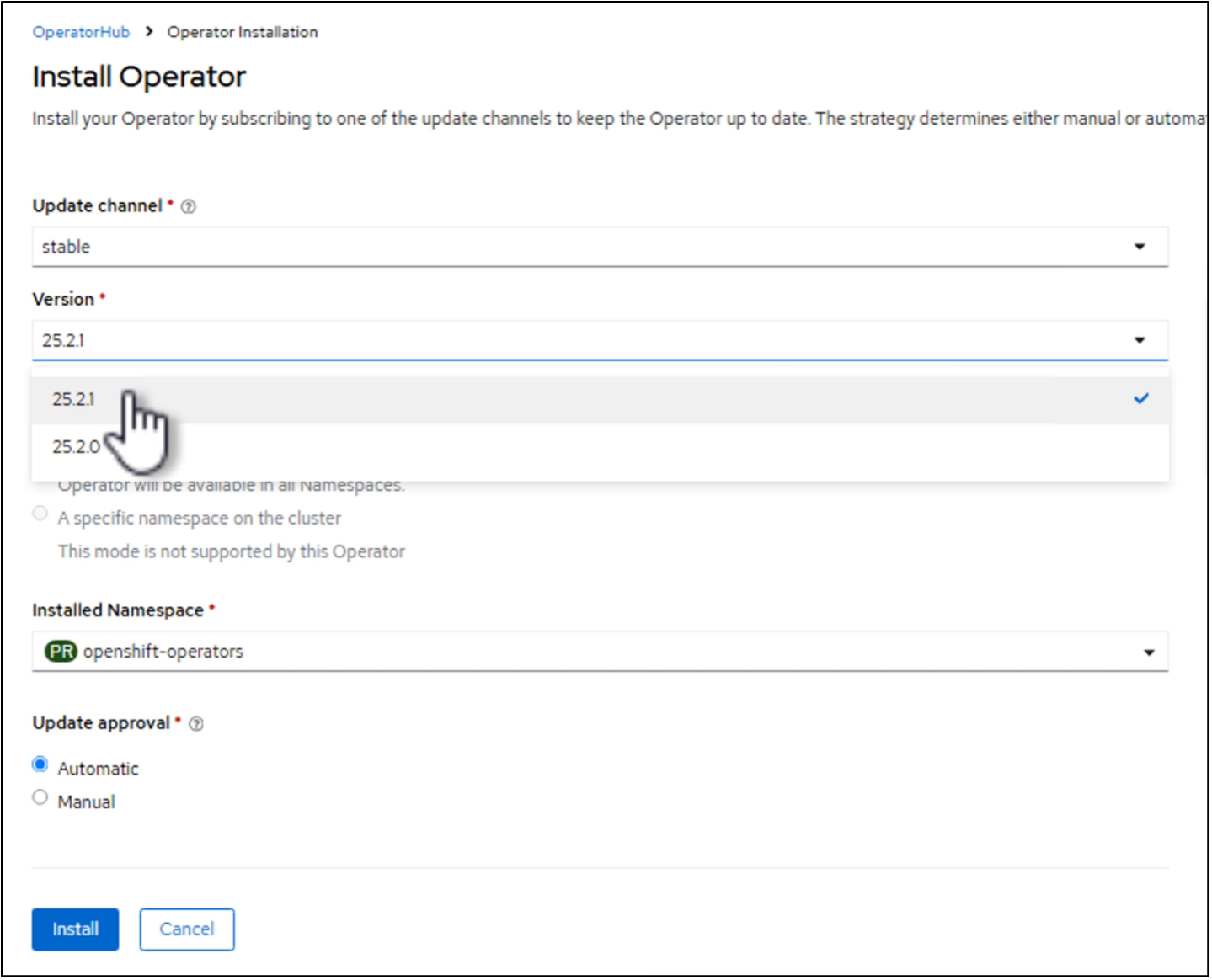
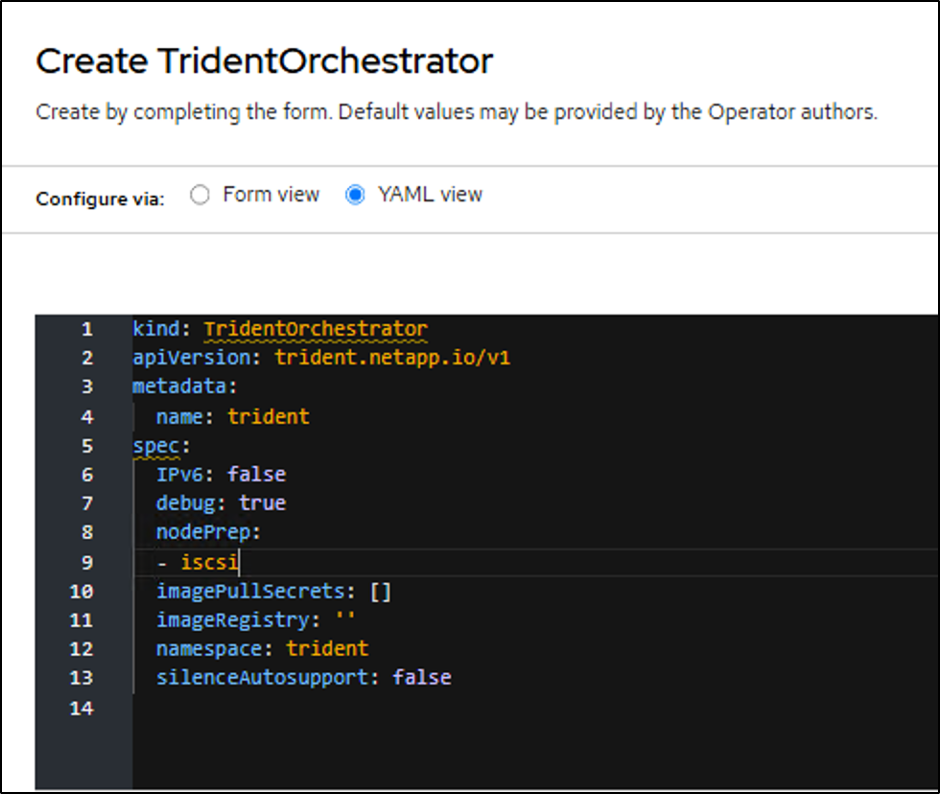
Once the operator is installed, click on view operator and then create an instance of the Trident Orchestrator. If you want to prepare the worker nodes for iSCSI storage access, go to the yaml view and modify the nodePrep parameter by adding iscsi.
You should now have all the trident pods running in your cluster.
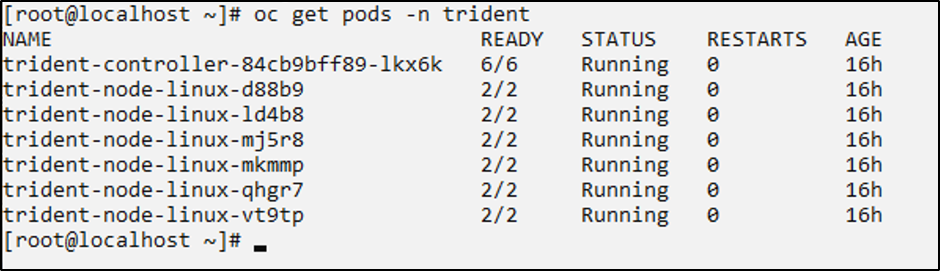
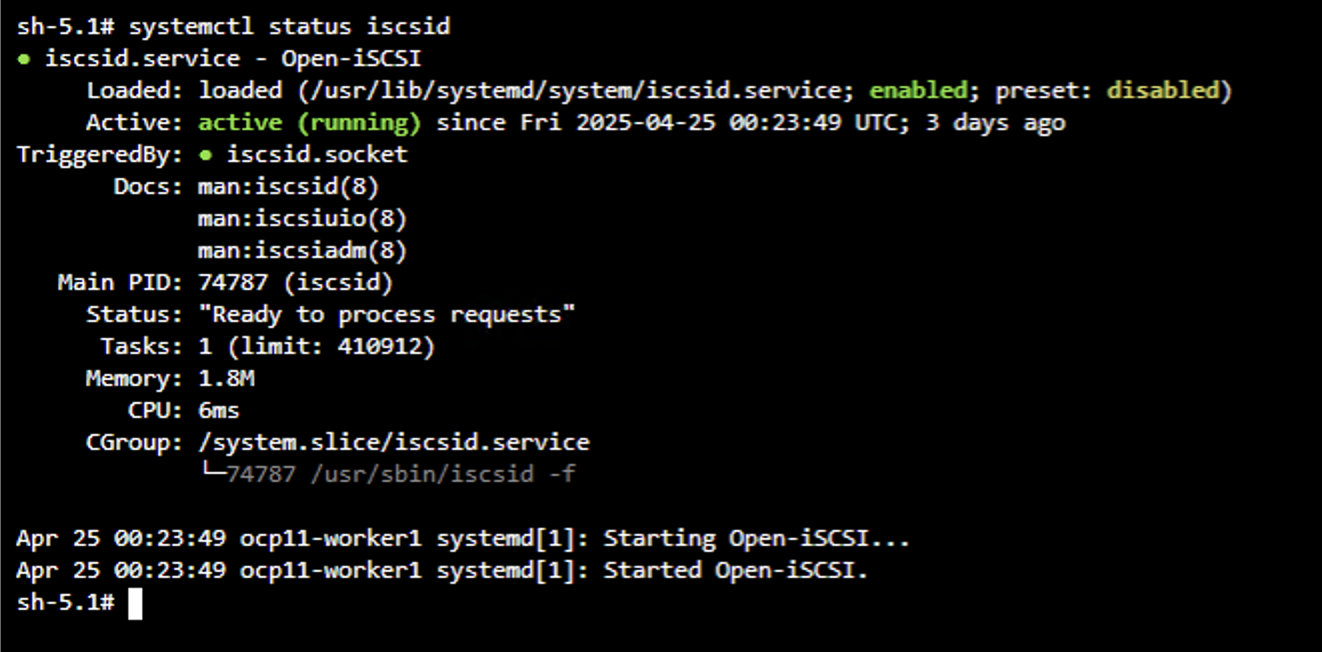
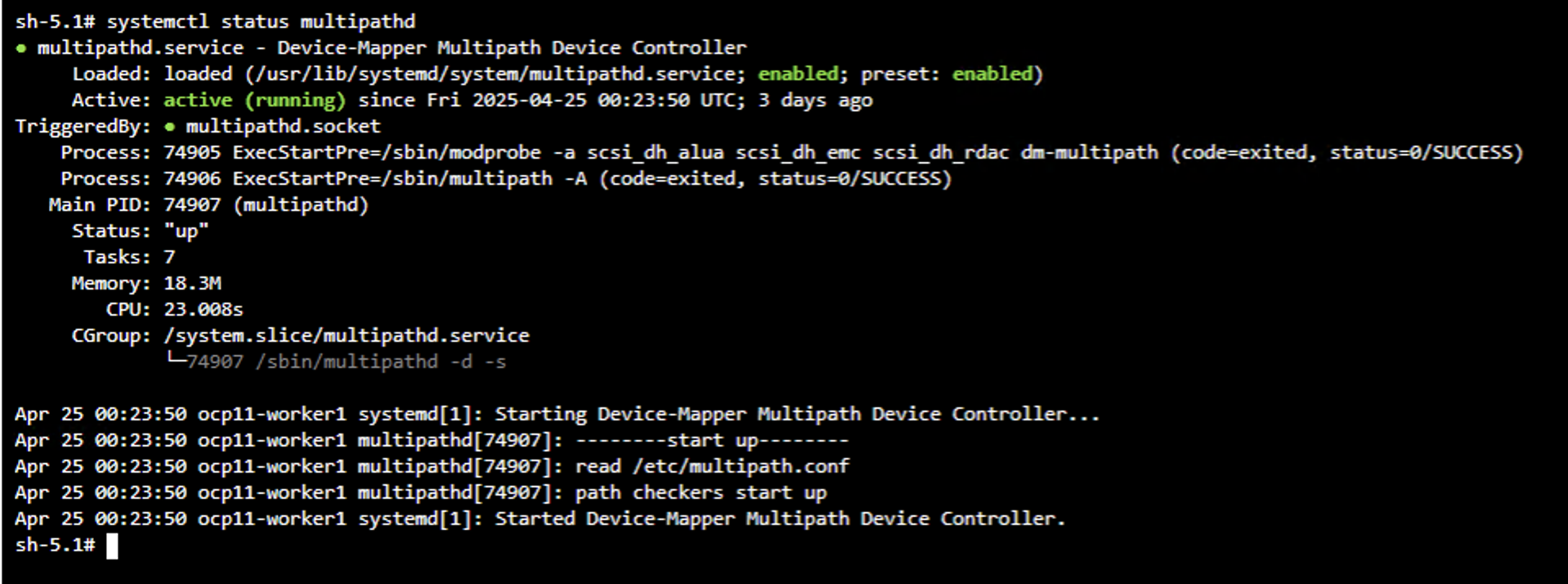
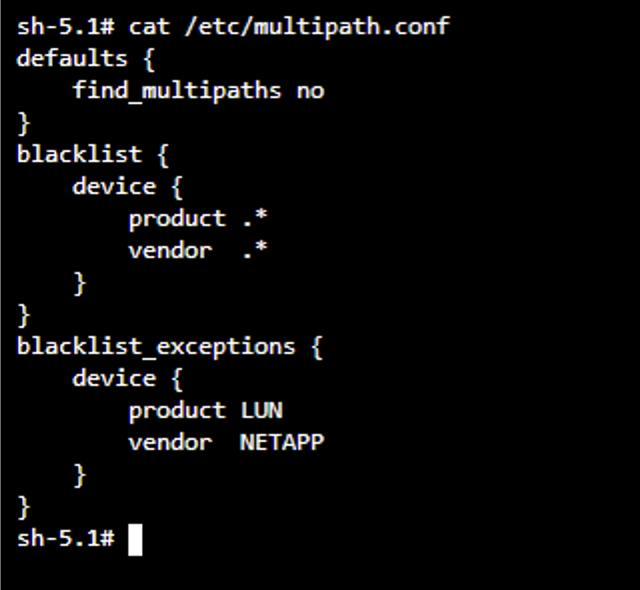
To verify that iSCSI tools have been enabled on the worker nodes of the OpenShift Cluster, log into the worker nodes and verify you see the iscsid, multipathd active and the entries in the multipath.conf file as shown.
Video Demonstration
The following video shows a demonstration of installing Trident using Red Hat Certified Trident Operator
Trident configuration for on-prem OpenShift cluster
Trident backend and storage class for NAS
cat tbc-nas.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: tbc-nas-secret
type: Opaque
stringData:
username: <cluster admin username>
password: <cluster admin password>
---
apiVersion: trident.netapp.io/v1
kind: TridentBackendConfig
metadata:
name: tbc-nas
spec:
version: 1
storageDriverName: ontap-nas
managementLIF: <cluster management lif>
backendName: tbc-nas
svm: zoneb
storagePrefix: testzoneb
defaults:
nameTemplate: "{{ .config.StoragePrefix }}_{{ .volume.Namespace }}_{{ .volume.RequestName }}"
credentials:
name: tbc-nas-secretcat sc-nas.yaml
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: sc-nas
provisioner: csi.trident.netapp.io
parameters:
backendType: "ontap-nas"
media: "ssd"
provisioningType: "thin"
snapshots: "true"
allowVolumeExpansion: trueTrident backend and storage class for iSCSI
# cat tbc-iscsi.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: backend-tbc-ontap-iscsi-secret
type: Opaque
stringData:
username: <cluster admin username>
password: <cluster admin password>
---
apiVersion: trident.netapp.io/v1
kind: TridentBackendConfig
metadata:
name: ontap-iscsi
spec:
version: 1
storageDriverName: ontap-san
managementLIF: <management LIF>
backendName: ontap-iscsi
svm: <SVM name>
credentials:
name: backend-tbc-ontap-iscsi-secret# cat sc-iscsi.yaml
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: sc-iscsi
provisioner: csi.trident.netapp.io
parameters:
backendType: "ontap-san"
media: "ssd"
provisioningType: "thin"
fsType: ext4
snapshots: "true"
allowVolumeExpansion: trueTrident backend and storage class for NVMe/TCP
# cat tbc-nvme.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: backend-tbc-ontap-nvme-secret
type: Opaque
stringData:
username: <cluster admin password>
password: <cluster admin password>
---
apiVersion: trident.netapp.io/v1
kind: TridentBackendConfig
metadata:
name: backend-tbc-ontap-nvme
spec:
version: 1
storageDriverName: ontap-san
managementLIF: <cluster management LIF>
backendName: backend-tbc-ontap-nvme
svm: <SVM name>
credentials:
name: backend-tbc-ontap-nvme-secret# cat sc-nvme.yaml
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: sc-nvme
provisioner: csi.trident.netapp.io
parameters:
backendType: "ontap-san"
media: "ssd"
provisioningType: "thin"
fsType: ext4
snapshots: "true"
allowVolumeExpansion: trueTrident backend and storage class for FC
# cat tbc-fc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: tbc-fc-secret
type: Opaque
stringData:
username: <cluster admin password>
password: <cluster admin password>
---
apiVersion: trident.netapp.io/v1
kind: TridentBackendConfig
metadata:
name: tbc-fc
spec:
version: 1
storageDriverName: ontap-san
managementLIF: <cluster mgmt lif>
backendName: tbc-fc
svm: openshift-fc
sanType: fcp
storagePrefix: demofc
defaults:
nameTemplate: "{{ .config.StoragePrefix }}_{{ .volume.Namespace }}_{{ .volume.RequestName }}"
credentials:
name: tbc-fc-secret# cat sc-fc.yaml
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: sc-fc
provisioner: csi.trident.netapp.io
parameters:
backendType: "ontap-san"
media: "ssd"
provisioningType: "thin"
fsType: ext4
snapshots: "true"
allowVolumeExpansion: trueTrident configuration for ROSA cluster using FSxN storage
Trident backend and storage class for FSxN NAS
#cat tbc-fsx-nas.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: backend-fsx-ontap-nas-secret
namespace: trident
type: Opaque
stringData:
username: <cluster admin lif>
password: <cluster admin passwd>
---
apiVersion: trident.netapp.io/v1
kind: TridentBackendConfig
metadata:
name: backend-fsx-ontap-nas
namespace: trident
spec:
version: 1
backendName: fsx-ontap
storageDriverName: ontap-nas
managementLIF: <Management DNS name>
dataLIF: <NFS DNS name>
svm: <SVM NAME>
credentials:
name: backend-fsx-ontap-nas-secret# cat sc-fsx-nas.yaml
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: trident-csi
provisioner: csi.trident.netapp.io
parameters:
backendType: "ontap-nas"
fsType: "ext4"
allowVolumeExpansion: True
reclaimPolicy: RetainTrident backend and storage class for FSxN iSCSI
# cat tbc-fsx-iscsi.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: backend-tbc-fsx-iscsi-secret
type: Opaque
stringData:
username: <cluster admin username>
password: <cluster admin password>
---
apiVersion: trident.netapp.io/v1
kind: TridentBackendConfig
metadata:
name: fsx-iscsi
spec:
version: 1
storageDriverName: ontap-san
managementLIF: <management LIF>
backendName: fsx-iscsi
svm: <SVM name>
credentials:
name: backend-tbc-ontap-iscsi-secret# cat sc-fsx-iscsi.yaml
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: sc-fsx-iscsi
provisioner: csi.trident.netapp.io
parameters:
backendType: "ontap-san"
media: "ssd"
provisioningType: "thin"
fsType: ext4
snapshots: "true"
allowVolumeExpansion: trueCreating Trident Volume Snapshot Class
Trident volume snapshot class
# cat snapshot-class.yaml
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: VolumeSnapshotClass
metadata:
name: trident-snapshotclass
driver: csi.trident.netapp.io
deletionPolicy: RetainOnce you have the required yaml files in place for the backend configuration and the storage class configuration, and the snapshot configurations, you can create the trident backend , storage class and the snapshot class objects by using the following command
oc create -f <backend-filename.yaml> -n trident
oc create -f < storageclass-filename.yaml>
oc create -f <snapshotclass-filename.yaml>Setting defaults with Trident Storage and Snapshot Class
Setting defaults with Trident Storage and Snapshot Class
You can now make the required trident storage class and the volume snapshot class as the default in the OpenShift Cluster.
As mentioned earlier, setting the default storage class and the volume snapshot class is required to allow OpenShift Virtualization to make the golden image source available to create vms from default templates.
You can set the Trident storage class and the snapshot class as default by editing the annotation from the console or patching from command line with the following.
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class:true
or
kubectl patch storageclass standard -p '{"metadata": {"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"true"}}}'
storageclass.kubevirt.io/is-default-virt-class: true
or
kubectl patch storageclass standard -p '{"metadata": {"annotations":{"storageclass.kubevirt.io/is-default-virt-class": "true"}}}'Once this is set, you can delete any pre-existing dv and VolumeSnapShot objects using the following command:
oc delete dv,VolumeSnapshot -n openshift-virtualization-os-images --selector=cdi.kubevirt.io/dataImportCron

