Set up failover and failback for VMs in Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization using Trident Protect
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


Set up disaster recovery for VMs in OpenShift Virtualization using Trident Protect. This procedure includes creating an AppVault with ONTAP S3, establishing AppMirror relationships between source and disaster recovery namespaces, scheduling replication, and executing failover and failback operations to maintain VM availability during site outages.
Prerequisites
-
Trident must be installed. Backend and storage classes must be created before OpenShift Virtualization is installed on the cluster using the OpenShift Virtualization operator.
-
Trident Protect must be installed to implement failover and failback operations for the OpenShift VMs. Refer to the instructions here to install Trident Protect
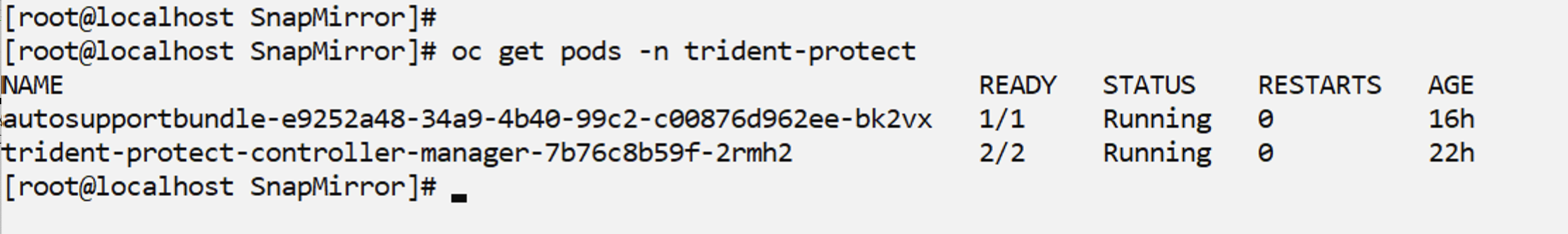
A VM must be available in OpenShift Virtualization. For details about deploying a new VM, or migrating an existing VM into OpenShift Virtualization, see the appropriate section in the documentation.
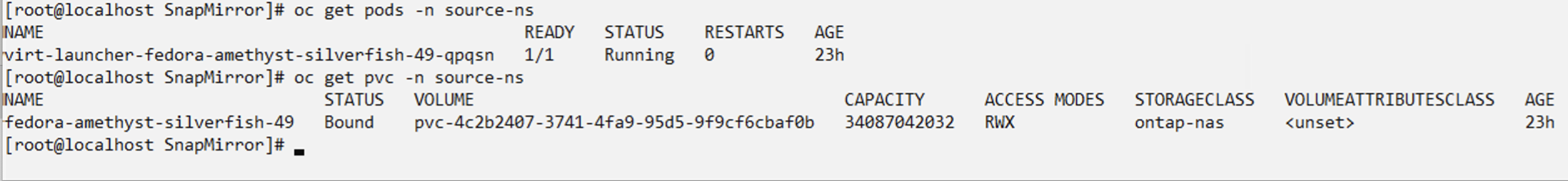
Create App Vault using ONTAP S3
This section shows how to set up an app vault in trident protect using ontap S3 Object storage.
Use oc commands and the yaml files shown below to create a secret and the appvault custom resource for ontap s3. Ensure that you create them in the trident protect namespace.
oc create -f app-vault-secret.yaml -n trident-protect
oc create -f app-vault.yaml -n trident-protectapiVersion: v1
# You can provide the keys either as stringData or base 64 encoded data
stringData:
accessKeyID: "<access key id as obtained from ONTAP>"
secretAccessKey: "<secret access key as obtained from ONTAP>"
#data:
#accessKeyID: <base 64 encoded value of access key>
#secretAccessKey: <base 64 encoded value of secret access key>
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: appvault-secret
namespace: trident-protect
type: OpaqueapiVersion: protect.trident.netapp.io/v1
kind: AppVault
metadata:
name: ontap-s3-appvault
namespace: trident-protect
spec:
providerConfig:
azure:
accountName: ""
bucketName: ""
endpoint: ""
gcp:
bucketName: ""
projectID: ""
s3:
bucketName: trident-protect
endpoint: <data lif to use to access S3>
secure: "false"
skipCertValidation: "true"
providerCredentials:
accessKeyID:
valueFromSecret:
key: accessKeyID
name: appvault-secret
secretAccessKey:
valueFromSecret:
key: secretAccessKey
name: appvault-secret
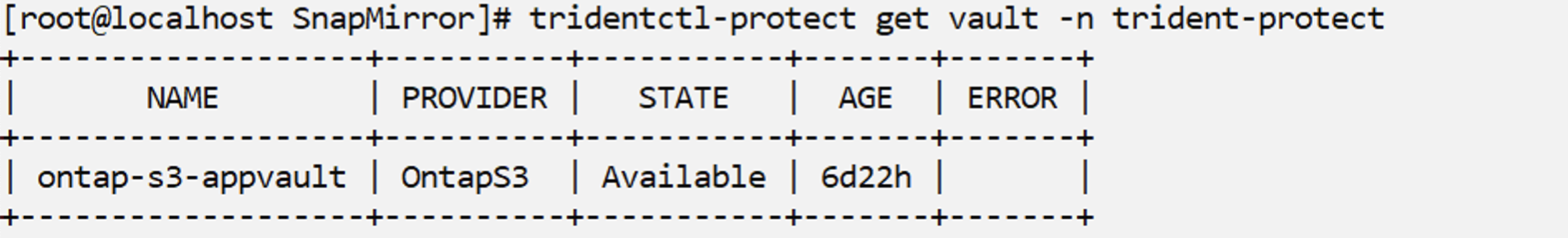
providerType: OntapS3Ensure that ontap S3 vault is created and is in the Available state
Create a Trident Protect app for the VM
Create an app custom resource in the namespace where the VM is located.

tridentctl-protect create app source-vm -n source-ns --namespaces source-ns
Create a Trident Protect app for the Disaster Recovery VM in a new namespace
oc create ns dr-ns
tridentctl-protect create app dr-vm -n dr-ns --namespaces dr-ns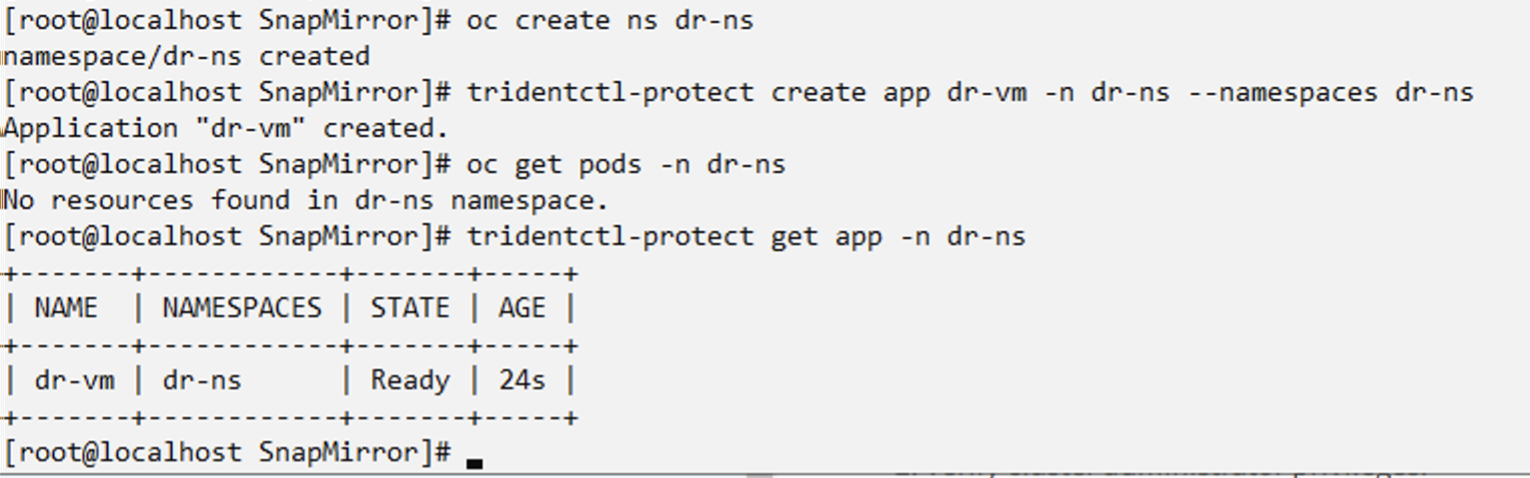
Create an AppMirror Schedule in the source namespace
Create a schedule for AppMirror using the yaml as shown. This will create snapshots using the schedule (every 5 minutes) and retain 2 snapshots
oc create -f appmirror-schedule.yaml -n source-nsapiVersion: protect.trident.netapp.io/v1
kind: Schedule
metadata:
name: appmirror-sched1
spec:
appVaultRef: ontap-s3-appvault
applicationRef: source-vm
backupRetention: "0"
enabled: true
granularity: Custom
recurrenceRule: |-
DTSTART:20240901T000200Z
RRULE:FREQ=MINUTELY;INTERVAL=5
snapshotRetention: "2"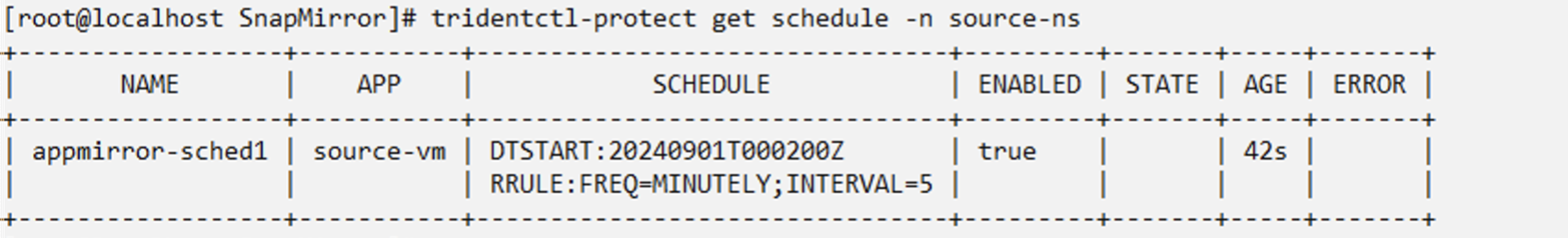
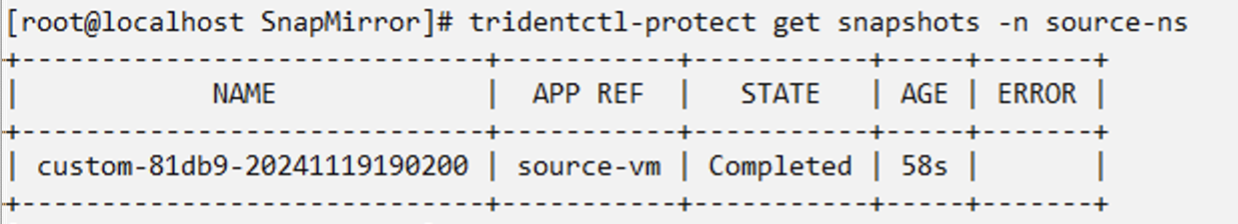
Create an appMirror relationship in the DR namespace
Create an Appmirror relationship in the Disaster Recovery namespace. Set the desiredState to Established.
apiVersion: protect.trident.netapp.io/v1
kind: AppMirrorRelationship
metadata:
name: amr1
spec:
desiredState: Established
destinationAppVaultRef: ontap-s3-appvault
destinationApplicationRef: dr-vm
namespaceMapping:
- destination: dr-ns
source: source-ns
recurrenceRule: |-
DTSTART:20240901T000200Z
RRULE:FREQ=MINUTELY;INTERVAL=5
sourceAppVaultRef: ontap-s3-appvault
sourceApplicationName: source-vm
sourceApplicationUID: "<application UID of the source VM>"
storageClassName: "ontap-nas"

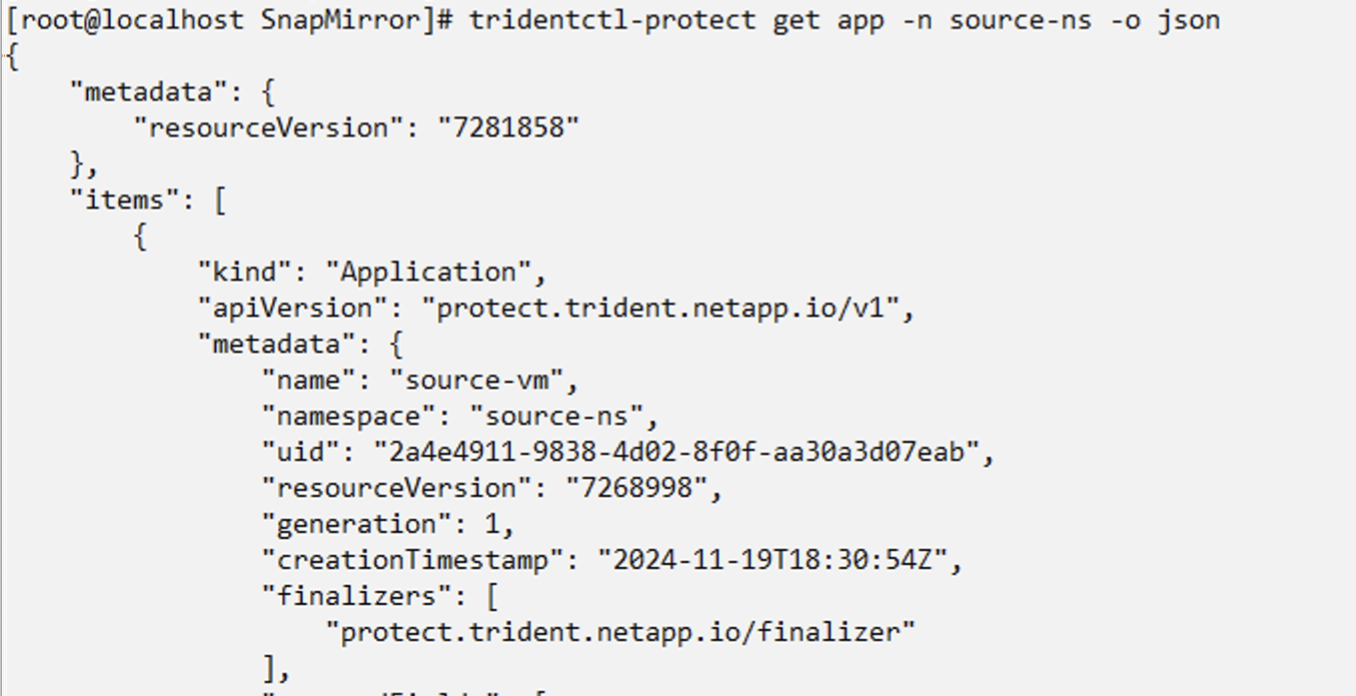
|
You can get the application UID of the source VM from the json output of the source app as shown below |

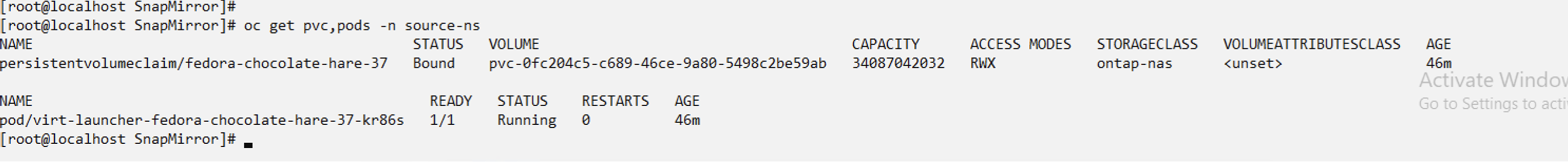
When the AppMirror relationship is established, the most recent snapshot is transferred to the destination namespace. The PVC is created for the VM in the dr namespace, however, the VM pod is not yet created in the dr namespace.
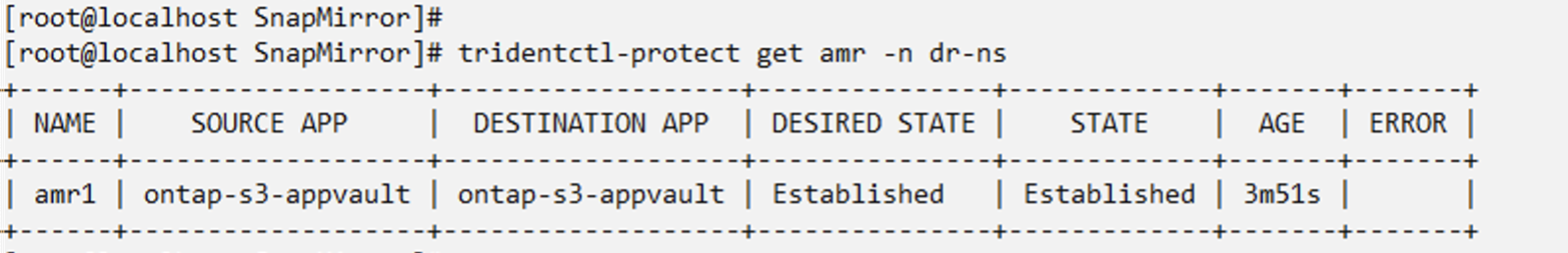
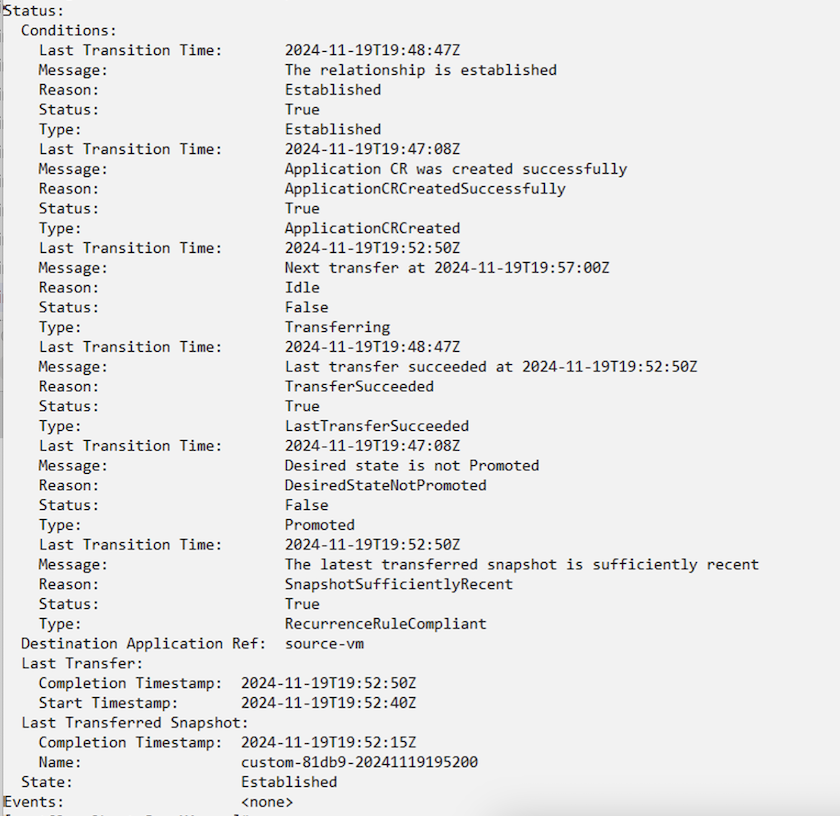

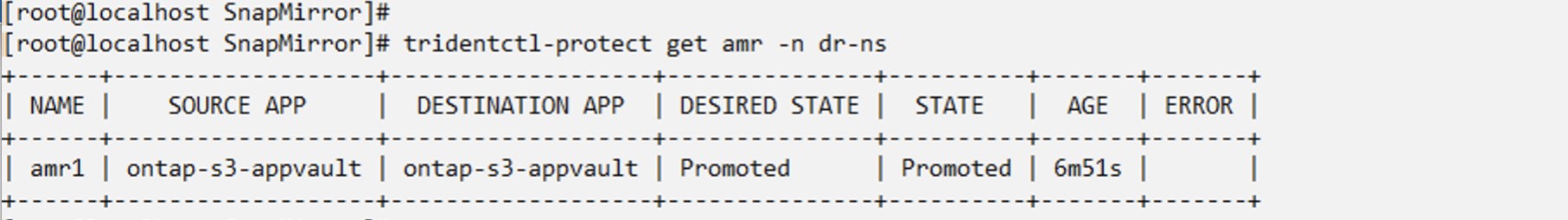
Promote the relationship to Failover
Change the desired state of the relationship to "Promoted" to create the VM in the DR namespace. The VM is still running in the source namespace.
oc patch amr amr1 -n dr-ns --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"desiredState":"Promoted"}}'

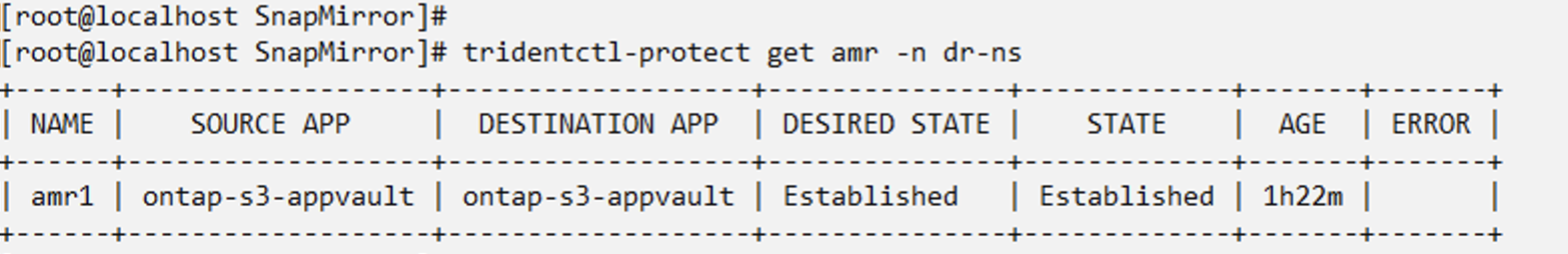
Establish the relationship again to Failback
Change the desired state of the relationship to "Established". The VM is deleted in the DR namespace. The pvc still exists in the DR namespace. The VM is still running in the source namespace. The original relationship from source namespace to DR ns is established. .
oc patch amr amr1 -n dr-ns --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"desiredState":"Established"}}'

Video Demonstration
The following video shows a demonstration of implementing a Disaster Recovery Scenario for an OpenShift VM using Trident Protect


