Creating a cyber vault with ONTAP
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


The steps below will assist with the creation of a cyber vault with ONTAP.
-
The source cluster must be running ONTAP 9 or later.
-
The source and destination aggregates must be 64-bit.
-
The source and destination volumes must be created in peered clusters with peered SVMs. For more information, see Cluster Peering.
-
If volume autogrow is disabled, the free space on the destination volume must be at least five percent more than the used space on the source volume.
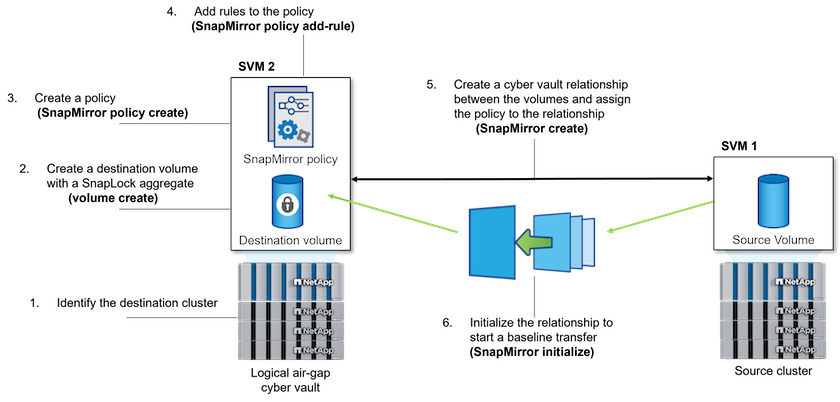
The following illustration shows the procedure for initializing a SnapLock Compliance vault relationship:
-
Identify the destination array to become the cyber vault to receive the air-gapped data.
-
On the destination array, to prepare the cyber vault, install the ONTAP One license, initialize the Compliance Clock, and, if you are using an ONTAP release earlier than 9.10.1, create a SnapLock Compliance aggregate.
-
On the destination array, create a SnapLock Compliance destination volume of type DP:
volume create -vserver SVM_name -volume volume_name -aggregate aggregate_name -snaplock-type compliance|enterprise -type DP -size size -
Beginning with ONTAP 9.10.1, SnapLock and non-SnapLock volumes can exist on the same aggregate; therefore, you are no longer required to create a separate SnapLock aggregate if you are using ONTAP 9.10.1. You use the volume
-snaplock-typeoption to specify a Compliance type. In ONTAP releases earlier than ONTAP 9.10.1, the SnapLock mode, Compliance is inherited from the aggregate. Version-flexible destination volumes are not supported. The language setting of the destination volume must match the language setting of the source volume.The following command creates a 2 GB SnapLock Compliance volume named
dstvolBinSVM2on the aggregatenode01_aggr:cluster2::> volume create -vserver SVM2 -volume dstvolB -aggregate node01_aggr -snaplock-type compliance -type DP -size 2GB -
On the destination cluster, to create the air-gap, set the default retention period, as described in Set the default retention period.
A SnapLock volume that is a vault destination has a default retention period assigned to it. The value for this period is initially set to a minimum of 0 years and maximum of 100 years (Beginning with ONTAP 9.10.1. For earlier ONTAP releases, the value is 0 - 70.) for SnapLock Compliance volumes. Each NetApp Snapshot copy is committed with this default retention period at first. The default-retention-period must be changed. The retention period can be extended later, if needed, but never shortened. For more information, see Set retention time overview.Service providers should consider customer's contract end dates when determining retention period. For example, if the cyber vault retention period is 30 days and the customer's contract ends before the retention period expires, data in the cyber vault can not be deleted until the retention period expires. -
Create a new replication relationship between the non-SnapLock source and the new SnapLock destination you created in Step 3.
This example creates a new SnapMirror relationship with destination SnapLock volume dstvolB using a policy of XDPDefault to vault Snapshot copies labeled daily and weekly on an hourly schedule:
cluster2::> snapmirror create -source-path SVM1:srcvolA -destination-path SVM2:dstvolB -vserver SVM2 -policy XDPDefault -schedule hourlyCreate a custom replication policy or a custom schedule if the available defaults are not suitable.
-
On the destination SVM, initialize the SnapVault relationship created in Step 5:
snapmirror initialize -destination-path destination_path -
The following command initializes the relationship between the source volume srcvolA on SVM1 and the destination volume dstvolB on SVM2:
cluster2::> snapmirror initialize -destination-path SVM2:dstvolB -
After the relationship is initialized and idle, use the snapshot show command on the destination to verify the SnapLock expiry time applied to the replicated Snapshot copies.
This example lists the Snapshot copies on volume dstvolB that have the SnapMirror label and the SnapLock expiration date:
cluster2::> snapshot show -vserver SVM2 -volume dstvolB -fields snapmirror-label, snaplock-expiry-time



