Phases of copy-free transition
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


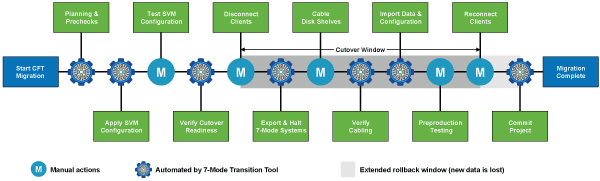
Copy-free transition using the 7-Mode Transition Tool consists of the following phases: planning, SVM provisioning, exporting and halting, cabling, importing, preproduction testing, starting production, and committing. You should understand the phases to manage the transition effectively.
Copy-free transition is a disruptive operation. Therefore, you must plan for the downtime for the applications and workload running on the 7-Mode storage systems.
In most cases, the storage cutover time can be 3 through 8 hours. Cutover time includes the time taken by the tool to perform two automated operations—the export and halt operation and the import operation—as well as the time taken for manually cabling the disk shelves to the new controllers. The export and halt operation and the import operation together can up to 2 hours.

|
For scaled configurations, the export and halt operation and the import operation together can take more than 2 hours. 7-Mode Transition Tool detects such conditions and provides a warning. |
Cabling of the disk shelves can take from 1 hour through 6 hours. This cutover time guidance does not include the time for the required preproduction testing and assumes an error-free transition without unexpected failures such as disk failure.
Planning the project
You can plan the following details about the source and target of a copy-free transition project:
-
7-Mode HA pair and vFiler unit details
-
Target cluster nodes and mapping of source controllers to target nodes
-
7-Mode controller or vFiler unit to SVM mapping
-
IP addresses to transition (new LIFs or existing 7-Mode IP addresses) and the IPspaces and broadcast domains on the SVM
The 7-Mode Transition Tool does not support the transition of FC and iSCSI LIFs. These LIFs must be manually configured on the SVMs before transition.
In this phase, prechecks are run to verify whether the 7-Mode HA pair is ready to be migrated to clustered Data ONTAP. The 7-Mode Transition Tool also verifies that the cluster is configured properly and can support the transition.
You must resolve any errors before continuing with the transition. Although the tool allows you to continue without resolving warnings, it is a best practice to address any warnings before continuing with the transition. You can run the prechecks multiple times to verify that all the errors have been resolved.
SVM provisioning
After planning your transition project, you must perform some manual tasks, such as adding licenses, creating the CIFS server, and creating SAN LIFs, to prepare the cluster and SVMs for transition.
You can then apply the configurations on the SVMs by using the tool. All the 7-Mode controller or vFiler unit level configurations are transitioned to the mapped SVM. Volume and LUN configurations are not transitioned during this phase; they are transitioned in the import phase.
At the end of this phase, you should manually verify the configurations applied to SVMs and make the necessary changes.
Exporting storage configurations and halting 7-Mode systems
This phase starts the cutover window for copy-free transition. Client access must be manually disconnected. However, all the NAS and SAN services must be up and running on the 7-Mode HA pair. This is because the 7-Mode Transition Tool requires all services to be up and running for collecting the volume-level configurations from the 7-Mode systems.
The tool performs the following operations in the export phase:
-
Collects all volume and storage configurations
-
Creates a Snapshot copy of each transitioning aggregate
This Snapshot copy is used for rolling back to 7-Mode, if required.
-
Boots the 7-Mode controllers in maintenance mode
-
Removes disk ownership from the disks attached to the 7-Mode controllers
-
Disables disk autoassignment on the target cluster nodes
Cabling the 7-Mode disk shelves
You must perform the tasks in this phase manually. You must ensure that the disk shelf IDs are unique across the 7-Mode controllers and target cluster nodes.

|
If there are duplicate shelf IDs, you must change the disk shelf IDs and power cycle the disk shelves. |
You must disconnect all the 7-Mode disk shelves and hot-add them to the target cluster nodes. After the disk shelves are connected to the target cluster nodes, you must power cycle the disk shelves.
It is a best practice to manually verify the cabling by using Config Advisor. Config Advisor is a configuration validation and health check tool for NetApp systems. It can be deployed at both secure sites and non-secure sites for data collection and system analysis.
You can then verify the cabling by using the 7-Mode Transition Tool to proceed with the transition. The 7-Mode Transition Tool performs only a subset of the cabling checks that are performed by Config Advisor.
Importing 7-Mode data and configurations
All the storage objects (aggregates, volumes, and LUNs) and the associated configurations are transitioned during this phase.
The tool performs the following operations in the import phase:
-
7-Mode disks are assigned to the mapped target cluster nodes.
-
All 7-Mode aggregates, volumes, and LUNs are converted to the clustered Data ONTAP format.
-
LIFs are configured on the SVMs in the administrative up state.
-
All volume-level and LUN-level configurations are applied.
Preproduction testing
You must manually test all the transitioned aggregates, volumes, and configurations that are applied to the target SVMs during this phase. You must also perform all manual tasks for completing your configuration—for example, configuring hosts and performing host remediation for SAN hosts.
You cannot perform certain operations on the transitioned aggregates or volumes during this phase. There are also certain operations that are not recommended during the testing phase. This is to ensure a successful rollback operation in case you decide to roll back to 7-Mode.
You must also manually test all applications and workloads thoroughly before starting data access in a production environment.

|
The aggregates might run out of space because of the aggregate Snapshot copies and the write operations that are performed during the testing. If the free physical space is less than 5% of the total space, the aggregates are taken offline. You must regularly monitor the free physical space available in the transitioned aggregates to avoid space issues. |
Starting production
After testing all workloads and applications, you can start client access to the transitioned data in the production environment. This stage of transition—where production is started but the project is not yet committed—is the final stage of transition when you can decide to roll back to 7-Mode. You must not prolong this phase because of the following reasons:
-
The probability of running out of space in the transitioned aggregates increases as new data is written to the volumes.
-
Any new data written to the volumes during this stage will not be available after rollback.
Committing the project
In this final stage of transition, the aggregate-level Snapshot copies that were created during the export phase are deleted.
You cannot roll back to 7-Mode after you commit the 7-Mode aggregates and complete the transition.
Related information


