Configure Windows Server 2012 R2 for FCP and iSCSI with ONTAP storage
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


The Windows Host Utilities enable you to connect Windows hosts to virtual disks (LUNs) on a NetApp SAN. Install the Windows Host Utilities on a Windows Server 2012 R2 host to help you manage FCP and iSCSI protocol operations with ONTAP LUNs.
Step 1: Optionally, enable SAN booting
You can boot the Windows OS using a local boot or a SAN boot. NetApp recommends using a SAN boot to simplify deployment and improve scalability..
If you choose to use SAN booting, it must be supported by your configuration.
Use the Interoperability Matrix Tool to verify that your Windows OS, host bus adapter (HBA), HBA firmware, HBA boot BIOS, and ONTAP version support SAN booting.
-
Enable SAN booting in the server BIOS for the ports to which the SAN boot LUN is mapped.
For information on how to enable the HBA BIOS, see your vendor-specific documentation.
-
Verify that the configuration was successful by rebooting the host and verifying that the OS is up and running.
Perform a local boot by installing the Windows OS on the local hard disk, for example, on an SSD, SATA, or RAID.
Step 2: Install Windows hotfixes
NetApp recommends installing the latest cumulative update available from the Microsoft Update Catalog on the host server.
-
Download the hotfixes from the Microsoft Update Catalog 2012 R2.

|
You need to contact Microsoft support for the hotfixes that aren't available for download from the Microsoft Update Catalog. |
-
Follow the instructions provided by Microsoft to install the hotfixes.

|
Many hotfixes require a Windows host reboot. You can wait to reboot the host until after you install or upgrade the Host Utilities. |
Step 3: Install the Windows Host Utilities
The Windows Host Utilities are a set of software programs with documentation that enable you to connect host computers to virtual disks (LUNs) on a NetApp SAN. NetApp recommends downloading and installing the latest Windows Host Utilities to support ONTAP LUN management and help technical support collect configuration data.
For Windows Host Utilities configuration and installation information, see the Windows Host Utilities documentation and select the installation procedure for your Windows Host Utilities version.
Step 4: Confirm the multipath configuration for your host
Install the Microsoft Multipath I/O (MPIO) software and enable multipathing if your Windows host has more than one path to the storage system.
On a Windows system, the two main components in an MPIO solution are the device-specific module (DSM) and the Windows MPIO. MPIO presents one disk to the Windows OS for all paths and the DSM manages path failovers.

|
If you don't install the MPIO software, the Windows OS might see each path as a separate disk. This can lead to data corruption. |

|
Windows XP or Windows Vista running in a Hyper-V virtual machine doesn't support MPIO. |
-
Install the MPIO software and enable multipathing.
-
When you select MPIO on systems using FC, the Host Utilities installer sets the required timeout values for Emulex and QLogic FC HBAs.
Emulex FCThe timeout values for Emulex FC HBAs:
Property type Property value LinkTimeOut
1
NodeTimeOut
10
QLogic FCThe timeout values for QLogic FC HBAs:
Property type Property value LinkDownTimeOut
1
PortDownRetryCount
10
-
Verify the path status for your ONTAP LUNs:
Depending on your SAN configuration, the host uses ASA, AFF, or FAS configurations to access ONTAP LUNs. These configurations shouldn't require more than four paths to access a single ONTAP LUN. More than four paths can cause problems during storage failure.
The following example outputs show the correct settings for ONTAP LUNs for an ASA, AFF, or FAS configuration.
ASA configurationAn ASA configuration should have one group of Active/Optimized paths with single priorities. The controller services the paths and sends I/O on all active paths.
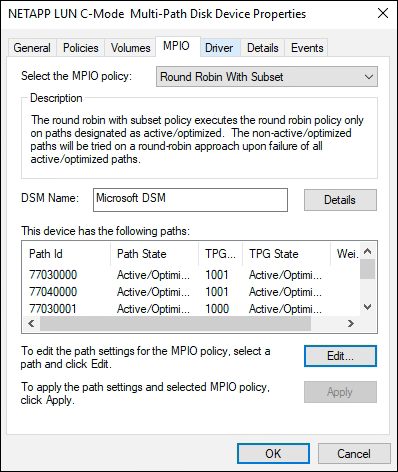 AFF or FAS configuration
AFF or FAS configurationAn AFF or FAS configuration should have two groups of paths with different priorities. The paths with higher priorities are Active/Optimized and are serviced by the controller where the aggregate is located. The paths with lower priorities are serviced from a different controller. They are active but non-optimized and are only used when optimized paths aren't available.
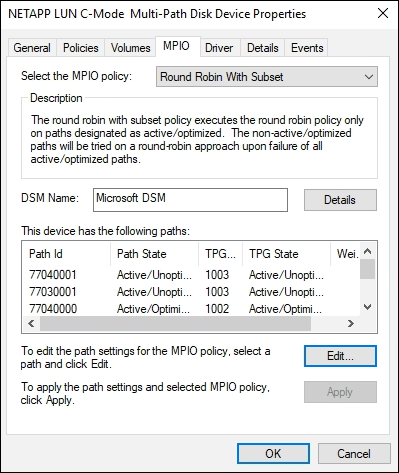
Step 5: Review the Known issues
There are no known issues.


