ARL upgrade workflow
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


Before you upgrade the nodes using ARL, you must understand how the procedure works. In this document, the procedure is broken down into several stages.
Upgrade the node pair
To upgrade the node pair, you must prepare the original nodes and then perform a series of steps on both the original and new nodes. You can then decommission the original nodes.
ARL upgrade sequence overview
During the procedure, you upgrade the original controller hardware with the replacement controller hardware, one controller at a time, taking advantage of the HA pair configuration to relocate the ownership of non-root aggregates. All non-root aggregates must undergo two relocations to reach their final destination, which is the correct upgraded node.
Each aggregate has a home owner and current owner. The home owner is the actual owner of the aggregate, and the current owner is the temporary owner.
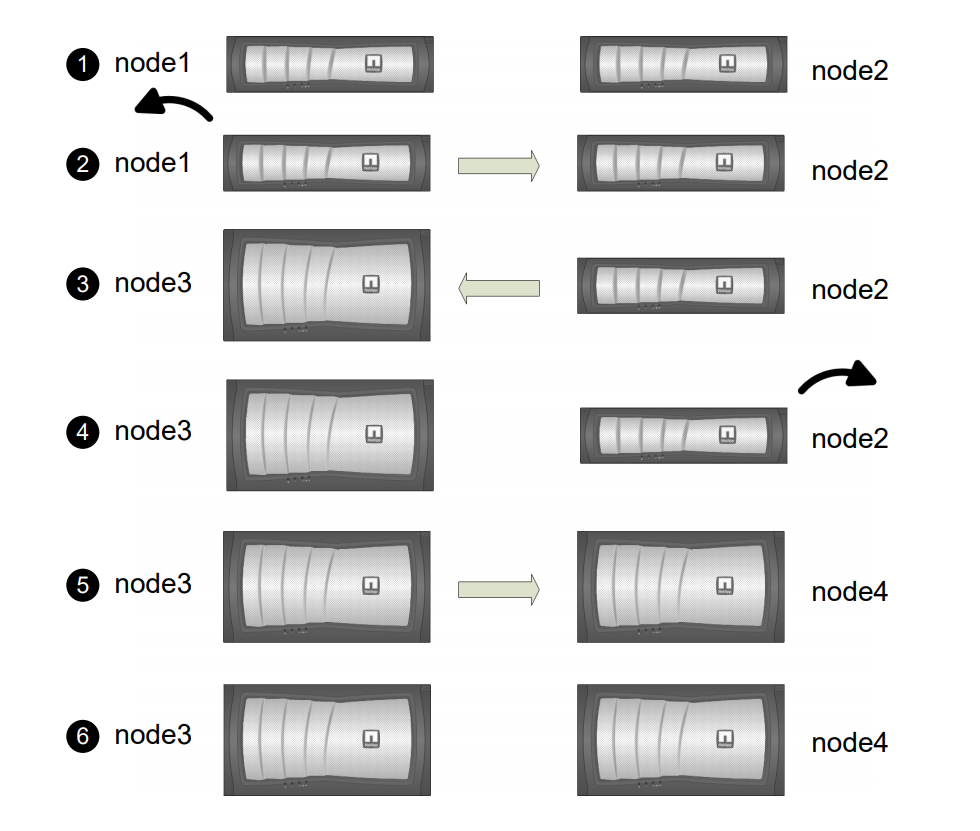
The following illustration shows the stages of the procedure. The thick, light gray arrows represent the relocation of aggregates and the movement of LIFs, and the thinner black arrows represent the removal of the original nodes. The smaller controller images represent the original nodes, and the larger controller images represent the new nodes.
The following table describes the high-level tasks you perform during each stage and the state of aggregate ownership at the end of the stage. Detailed steps are provided later in the procedure:
| Stage | Steps | ||
|---|---|---|---|
During Stage 1, if required, you confirm that internal disk drives do not contain root aggregates or data aggregates, prepare the nodes for the upgrade, and run a series of prechecks. If required, you rekey disks for Storage Encryption and prepare to netboot the new controllers. Aggregate ownership at the end of Stage 1:
|
|||
During Stage 2, you relocate non-root aggregates from node1 to node2 and move non-SAN data LIFs owned by node1 to node2, including failed or vetoed aggregates. You also record the necessary node1 information for use later in the procedure and retire node1. Aggregate ownership at the end of Stage 2:
|
|||
During Stage 3, you install and boot node3, map the cluster and node-management ports from node1 to node3, and move data LIFs and SAN LIFs belonging to node1 from node2 to node3. You also relocate all aggregates from node2 to node3, and move the data LIFs and SAN LIFs owned by node2 to node3. Aggregate ownership at the end of Stage 3:
|
|||
During Stage 4, you record the necessary node2 information for use later in the procedure and then retire node2. |
|||
During Stage 5, you install and boot node4, map the cluster and node-management ports from node2 to node4, and move data LIFs and SAN LIFs belonging to node2 from node3 to node4. You also relocate node2 aggregates from node3 to node4 and move the data LIFs and SAN LIFs owned by node2 to node3. Aggregate ownership at the end of Stage 5:
|
|||
During Stage 6, you confirm that the new nodes are set up correctly and set up Storage Encryption or NetApp Volume Encryption if the new nodes are encryption-enabled. You should also decommission the old nodes resume SnapMirror operations.
No changes occur in aggregate ownership. |