Configure Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) for ONTAP S3 buckets
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


Beginning with ONTAP 9.16.1, you can configure Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) to allow client web applications from different domains to access your ONTAP buckets. This provides secure access to the bucket objects using a web browser.
CORS is a framework built on HTTP that allows scripts defined in one web page to access resources at a server in a different domain. The framework is used to securely bypass the same-origin policy which is an early foundation for web security. The key concepts and terminology are described below.
An origin precisely defines the location and identity of a resource. It's represented as a combination of the following values:
-
URI scheme (protocol)
-
Host name (domain name or IP address)
-
Port number
Here's a simple example of an origin: https://www.mycompany.com:8001. When an origin is used with CORS, it identifies the client making the request.
The same-origin policy (SOP) is a security concept and restriction applied to browser-based scripts. The policy allows scripts initially loaded from a web page to access data in another page as long as both pages are in the same origin. This limitation prevents malicious scripts from accessing data in the pages of a different origin.
There are several general use cases for CORS. Most involve well-defined instances of cross-domain access, such as AJAX requests, loading fonts, stylesheets, and scripts as well as cross-domain authentication. CORS can also be implemented as part of a single-page application (SPA).
CORS is implemented using headers that are inserted into the HTTP requests and responses. For example, there are several response headers that implement access control and indicate what operations, including methods and headers, are allowed. The presence of the Origin header in an HTTP request defines it as a cross domain request. The origin value is used by the CORS server to locate a valid CORS configuration.
This is an optional request to initially determine if a server supports CORS, including the specific methods and headers. Based on the response, the CORS request can be completed or not.
A bucket is a container of objects stored and accessed based on a well-defined namespace. There are two types of ONTAP buckets:
-
NAS buckets which are accessible through the NAS and S3 protocols
-
S3 buckets which are only accessible through the S3 protocol
CORS implementation in ONTAP
CORS is enabled by default with ONTAP 9.16.1 and later releases. You need to configure CORS at each SVM where it will be active.

|
There is no administrative option to disable CORS for an ONTAP cluster. However, you can effectively disable it by not defining any rules or deleting all the existing rules. |
Possible use cases
The ONTAP CORS implementation enables several possible topologies for cross domain resource access, including:
-
ONTAP S3 buckets (within the same or different SVM or cluster)
-
ONTAP NAS buckets (within the same or different SVM or cluster)
-
ONTAP S3 and NAS buckets (within the same or different SVM or cluster)
-
ONTAP buckets and external vendor buckets
-
Buckets in different timezones
High-level view
The following illustrates at a high-level how CORS enables access to the ONTAP S3 buckets.
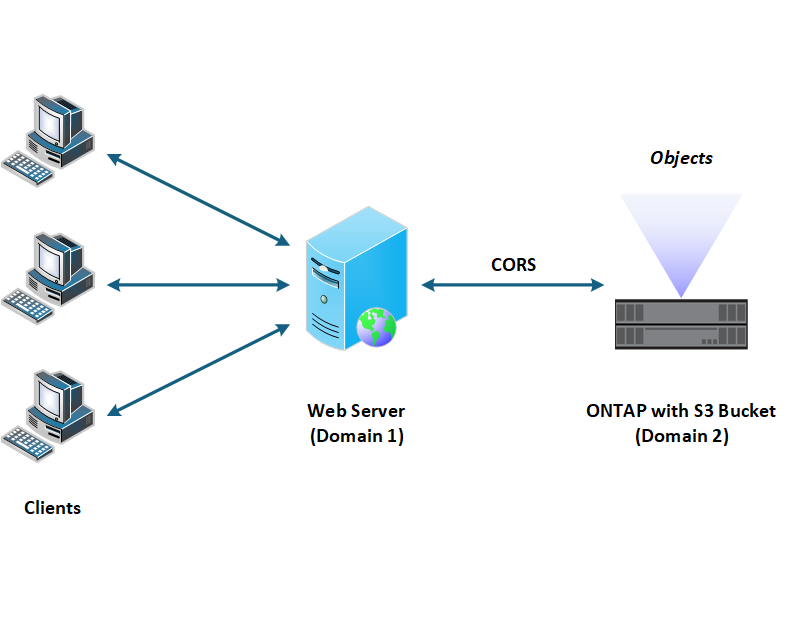
Defining CORS rules
You need to define CORS rules in ONTAP to activate and use the feature.
Configuration actions
There are three primary configuration rule actions supported in ONTAP:
-
Show
-
Create
-
Delete
A CORS rule defined in ONTAP has several properties, including the SVM and bucket as well as the allowed origins, methods, and headers.
Administration options
You have several options available when administering CORS at your ONTAP cluster.
You can configure CORS using the command line interface. See Administering CORS using the CLI for more information.
You can configure CORS using the ONTAP REST API. No new endpoints have been added to support the CORS feature. Instead you can use the following existing endpoint:
/api/protocols/s3/services/{svm.uuid}/buckets/{bucket.uuid}
Learn more in the ONTAP automation documentation.
You can use the S3 API to create and delete a CORS configuration on an ONTAP bucket. An S3 client administrator requires sufficient privileges, including:
-
Access or secret key credentials
-
Policy configured on the bucket to allow access through s3api
Upgrading and reverting
If you plan on using CORS to access the ONTAP S3 buckets, you should be aware of several administrative issues.
The CORS feature is supported when all nodes are upgraded to 9.16.1. In mixed mode clusters, the feature will only be available when the effective cluster version (ECV) is 9.16.1 or later.
From the user perspective, all CORS configuration should be removed before cluster revert can proceed. Internally, the operation will delete all the CORS databases. You'll be asked to run a command to clear and revert those data structures.
Administering CORS using the CLI
You can use the ONTAP CLI to administer CORS rules. The primary operations are described below. You need to be at the ONTAP admin privilege level to issue the CORS commands.
Create
You can define a CORS rule using the vserver object-store-server bucket cors-rule create command. Learn more about vserver object-store-server bucket cors-rule create in the ONTAP command reference.
The parameters used to create a rule are described below.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Specifies the name of the SVM (vserver) hosting the object store server bucket where the rule is created. |
|
The name of the bucket at the object store server for which the rule is created. |
|
An optional parameter indicating the index of the object store server bucket where the rule is created. |
|
A unique identifier for the object store server bucket rule. |
|
A list of the origins where cross-origin requests are allowed to originate from. |
|
A list of the HTTP methods allowed in a cross-origin request. |
|
A list of the HTTP headers allowed in the cross-origin requests. |
|
A list of the extra headers send in the CORS responses that customers can access from their applications. |
|
An optional parameter specifying the amount of time your browser should cache a pre-flight response for a specific resource. |
vserver object-store-server bucket cors-rule create -vserver vs1 -bucket bucket1 -allowed-origins www.myexample.com -allowed-methods GET,DELETE
Show
You can use the command vserver object-store-server bucket cors-rule show to display a list of the current rules and their contents. Learn more about vserver object-store-server bucket cors-rule show in the ONTAP command reference.

|
Including the parameter -instance expands the data presented for each of the rules. You can also specify which fields you want.
|
server object-store-server bucket cors-rule show -instance
Delete
You can use the delete command to remove an instance of a CORS rule. You need the index value of the rule and so this is operation is performed in two steps:
-
Issue a
showcommand to display the rule and retrieve its index. -
Issue the delete using the index value.
vserver object-store-server bucket cors-rule delete -vserver vs1 -bucket bucket1 -index 1
Modify
There is no CLI command available to modify an existing CORS rule. To modify a rule, you need to do the following:
-
Delete the existing rule.
-
Create a new rule with the desired options.


