Verifying object integrity
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


The StorageGRID system verifies the integrity of object data on Storage Nodes, checking for both corrupt and missing objects.
There are two verification processes: background verification and foreground verification. They work together to ensure data integrity. Background verification runs automatically, and continuously checks the correctness of object data. Foreground verification can be triggered by a user, to more quickly verify the existence (although not the correctness) of objects.
What background verification is
The background verification process automatically and continuously checks Storage Nodes for corrupt copies of object data, and automatically attempts to repair any issues that it finds.
Background verification checks the integrity of replicated objects and erasure-coded objects, as follows:
-
Replicated objects: If the background verification process finds a replicated object that is corrupt, the corrupt copy is removed from its location and quarantined elsewhere on the Storage Node. Then, a new uncorrupted copy is generated and placed to satisfy the active ILM policy. The new copy might not be placed on the Storage Node that was used for the original copy.

|
Corrupt object data is quarantined rather than deleted from the system, so that it can still be accessed. For more information on accessing quarantined object data, contact technical support. |
-
Erasure-coded objects: If the background verification process detects that a fragment of an erasure-coded object is corrupt, StorageGRID automatically attempts to rebuild the missing fragment in place on the same Storage Node, using the remaining data and parity fragments. If the corrupted fragment cannot be rebuilt, the Corrupt Copies Detected (ECOR) attribute is incremented by one, and an attempt is made to retrieve another copy of the object. If retrieval is successful, an ILM evaluation is performed to create a replacement copy of the erasure-coded object.
The background verification process checks objects on Storage Nodes only. It does not check objects on Archive Nodes or in a Cloud Storage Pool. Objects must be older than four days to qualify for background verification.
Background verification runs at a continuous rate that is designed not to interfere with ordinary system activities. Background verification cannot be stopped. However you can increase the background verification rate to more quickly verify the contents of a Storage Node if you suspect a problem.
Alerts and alarms (legacy) related to background verification
If the system detects a corrupt object that it cannot correct automatically (because the corruption prevents the object from being identified), the Unidentified corrupt object detected alert is triggered.
If background verification cannot replace a corrupted object because it cannot locate another copy, the Objects lost alert and the LOST (Lost Objects) legacy alarm are triggered.
Changing the background verification rate
You can change the rate at which background verification checks replicated object data on a Storage Node if you have concerns about data integrity.
-
You must be signed in to the Grid Manager using a supported browser.
-
You must have specific access permissions.
You can change the Verification Rate for background verification on a Storage Node:
-
Adaptive: Default setting. The task is designed to verify at a maximum of 4 MB/s or 10 objects/s (whichever is exceeded first).
-
High: Storage verification proceeds quickly, at a rate that can slow ordinary system activities.
Use the High verification rate only when you suspect that a hardware or software fault might have corrupted object data. After the High priority background verification completes, the Verification Rate automatically resets to Adaptive.
-
Select Support > Tools > Grid Topology.
-
Select Storage Node > LDR > Verification.
-
Select Configuration > Main.
-
Go to LDR > Verification > Configuration > Main.
-
Under Background Verification, select Verification Rate > High or Verification Rate > Adaptive.

|
Setting the Verification Rate to High triggers the VPRI (Verification Rate) legacy alarm at the Notice level. |
-
Click Apply Changes.
-
Monitor the results of background verification for replicated objects.
-
Go to Nodes > Storage Node > Objects.
-
In the Verification section, monitor the values for Corrupt Objects and Corrupt Objects Unidentified.
If background verification finds corrupt replicated object data, the Corrupt Objects metric is incremented, and StorageGRID attempts to extract the object identifier from the data, as follows:
-
If the object identifier can be extracted, StorageGRID automatically creates a new copy of the object data. The new copy can be made anywhere in the StorageGRID system that satisfies the active ILM policy.
-
If the object identifier cannot be extracted (because it has been corrupted), the Corrupt Objects Unidentified metric is incremented, and the Unidentified corrupt object detected alert is triggered.
-
-
If corrupt replicated object data is found, contact technical support to determine the root cause of the corruption.
-
-
Monitor the results of background verification for erasure-coded objects.
If background verification finds corrupt fragments of erasure-coded object data, the Corrupt Fragments Detected attribute is incremented. StorageGRID recovers by rebuilding the corrupt fragment in place on the same Storage Node.
-
Select Support > Tools > Grid Topology.
-
Select Storage Node > LDR > Erasure Coding.
-
In the Verification Results table, monitor the Corrupt Fragments Detected (ECCD) attribute.
-
-
After corrupt objects have been automatically restored by the StorageGRID system, reset the count of corrupt objects.
-
Select Support > Tools > Grid Topology.
-
Select Storage Node > LDR > Verification > Configuration.
-
Select Reset Corrupt Object Count.
-
Click Apply Changes.
-
-
If you are confident that quarantined objects are not required, you can delete them.

|
If the Objects lost alert or the LOST (Lost Objects) legacy alarm was triggered, technical support might want to access quarantined objects to help debug the underlying issue or to attempt data recovery. |
-
Select Support > Tools > Grid Topology.
-
Select Storage Node > LDR > Verification > Configuration.
-
Select Delete Quarantined Objects.
-
Click Apply Changes.
What foreground verification is
Foreground verification is a user-initiated process that checks if all expected object data exists on a Storage Node. Foreground verification is used to verify the integrity of a storage device.
Foreground verification is a faster alternative to background verification that checks the existence, but not the integrity, of object data on a Storage Node. If foreground verification finds that many items are missing, there might be an issue with all or part of a storage device associated with the Storage Node.
Foreground verification checks both replicated object data and erasure-coded object data, as follows:
-
Replicated objects: If a copy of replicated object data is found to be missing, StorageGRID automatically attempts to replace the copy from copies stored elsewhere in the system. The Storage Node runs an existing copy through an ILM evaluation, which will determine that the current ILM policy is no longer being met for this object because the missing copy no longer exists at the expected location. A new copy is generated and placed to satisfy the system's active ILM policy. This new copy might not be placed in the same location that the missing copy was stored.
-
Erasure-coded objects: If a fragment of an erasure-coded object is found to be missing, StorageGRID automatically attempts to rebuild the missing fragment in place on the same Storage Node using the remaining fragments. If the missing fragment cannot be rebuilt (because too many fragments have been lost), the Corrupt Copies Detected (ECOR) attribute is incremented by one. ILM then attempts to find another copy of the object, which it can use to generate a new erasure-coded copy.
If foreground verification identifies an issue with erasure coding on a storage volume, the foreground verification task pauses with an error message that identifies the affected volume. You must perform a recovery procedure for any affected storage volumes.
If no other copies of a missing replicated object or a corrupted erasure-coded object can be found in the grid, the Objects lost alert and the LOST (Lost Objects) legacy alarm are triggered.
Running foreground verification
Foreground verification enables you to verify the existence of data on a Storage Node. Missing object data might indicate that an issue exists with the underlying storage device.
-
You have ensured that the following grid tasks are not running:
-
Grid Expansion: Add Server (GEXP), when adding a Storage Node
-
Storage Node Decommissioning (LDCM) on the same Storage Node If these grid tasks are running, wait for them to complete or release their lock.
-
-
You have ensured that the storage is online. (Select Support > Tools > Grid Topology. Then, select Storage Node > LDR > Storage > Overview > Main. Ensure that Storage State - Current is Online.)
-
You have ensured that the following recovery procedures are not running on the same Storage Node:
-
Recovery of a failed storage volume
-
Recovery of a Storage Node with a failed system drive Foreground verification does not provide useful information while recovery procedures are in progress.
-
Foreground verification checks for both missing replicated object data and missing erasure-coded object data:
-
If foreground verification finds large amounts of missing object data, there is likely an issue with the Storage Node's storage that needs to be investigated and addressed.
-
If foreground verification finds a serious storage error associated with erasure-coded data, it will notify you. You must perform storage volume recovery to repair the error.
You can configure foreground verification to check all of a Storage Node's object stores or only specific object stores.
If foreground verification finds missing object data, the StorageGRID system attempts to replace it. If a replacement copy cannot be made, the LOST (Lost Objects) alarm might be triggered.
Foreground verification generates an LDR Foreground Verification grid task that, depending on the number of objects stored on a Storage Node, can take days or weeks to complete. It is possible to select multiple Storage Nodes at the same time; however, these grid tasks are not run simultaneously. Instead, they are queued and run one after the other until completion. When foreground verification is in progress on a Storage Node, you cannot start another foreground verification task on that same Storage Node even though the option to verify additional volumes might appear to be available for the Storage Node.
If a Storage Node other than the one where foreground verification is being run goes offline, the grid task continues to run until the % Complete attribute reaches 99.99 percent. The % Complete attribute then falls back to 50 percent and waits for the Storage Node to return to online status. When the Storage Node's state returns to online, the LDR Foreground Verification grid task continues until it completes.
-
Select Storage Node > LDR > Verification.
-
Select Configuration > Main.
-
Under Foreground Verification, select the check box for each storage volume ID you want to verify.
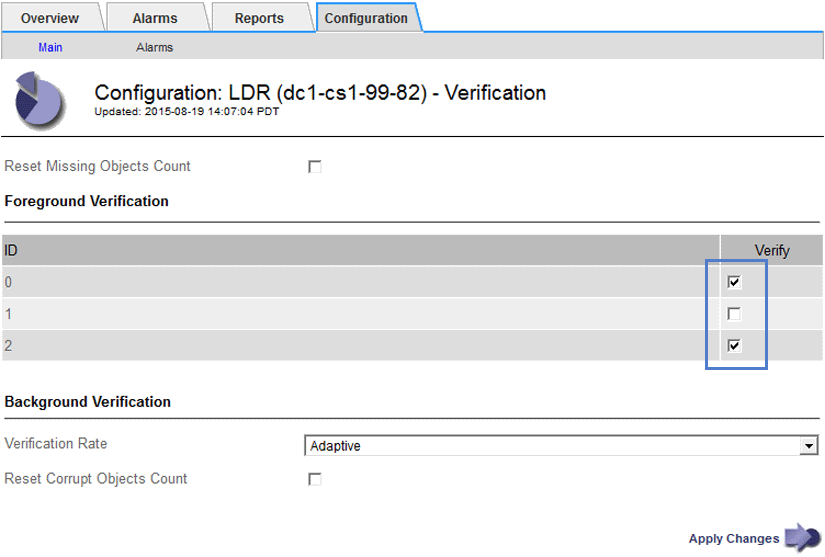
-
Click Apply Changes.
Wait until the page auto-refreshes and reloads before you leave the page. Once refreshed, object stores become unavailable for selection on that Storage Node.
An LDR Foreground Verification grid task is generated and runs until it completes, pauses, or is aborted.
-
Monitor missing objects or missing fragments:
-
Select Storage Node > LDR > Verification.
-
On the Overview tab under Verification Results, note the value of Missing Objects Detected.
Note: The same value is reported as Lost Objects on the Nodes page. Go to Nodes > Storage Node, and select the Objects tab.
If the number of Missing Objects Detected is large (if there are a hundreds of missing objects), there is likely an issue with the Storage Node's storage. Contact technical support.
-
Select Storage Node > LDR > Erasure Coding.
-
On the Overview tab under Verification Results, note the value of Missing Fragments Detected.
If the number of Missing Fragments Detected is large (if there are a hundreds of missing fragments), there is likely an issue with the Storage Node's storage. Contact technical support.
If foreground verification does not detect a significant number of missing replicated object copies or a significant number of missing fragments, then the storage is operating normally.
-
-
Monitor the completion of the foreground verification grid task:
-
Select Support > Tools > Grid Topology. Then select site > Admin Node > CMN > Grid Task > Overview > Main.
-
Verify that the foreground verification grid task is progressing without errors.
Note: A notice-level alarm is triggered on grid task status (SCAS) if the foreground verification grid task pauses.
-
If the grid task pauses with a
critical storage error, recover the affected volume and then run foreground verification on the remaining volumes to check for additional errors.Attention: If the foreground verification grid task pauses with the message
Encountered a critical storage error in volume volID, you must perform the procedure for recovering a failed storage volume. See the recovery and maintenance instructions.
-
If you still have concerns about data integrity, go to LDR > Verification > Configuration > Main and increase the background Verification Rate. Background verification checks the correctness of all stored object data and repairs any issues that it finds. Finding and repairing potential issues as quickly as possible reduces the risk of data loss.


