TR-4871 - Commvault Complete Backup and Recovery and NetApp StorageGRID
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


Solution Overview
Commvault and NetApp have partnered to create a joint data protection solution combining Commvault Complete Backup and Recovery for NetApp software with NetApp StorageGRID software for cloud storage. Many organizations want to migrate their storage to the cloud, scale their systems, and automate their policy for long-term retention of data. Commvault Complete Backup and Recovery and NetApp StorageGRID provide unique, easy-to-use solutions that work together to help you meet demands of rapid data growth and increasing regulations around the world. Cloud-based object storage is known for its resilience, ability to scale, and operational and cost efficiencies that make it a natural choice as a target for your backup. Commvault and NetApp jointly certified their combined solution in 2014 and since then have engineered deeper integration between their two solutions. Customers of all types around the world have adopted the Commvault Complete Backup and Recovery and StorageGRID combined solution.
When you implement Commvault Complete Backup and Recovery software with cloud storage, you have two backup options:
-
Back up to a primary disk target and also back up an auxiliary copy to cloud storage.
-
Back up to cloud storage as the primary target.
In the past, cloud or object storage was considered to be too low-performing to be used for primary backup. The use of a primary disk target allowed customers to have faster backup and restore processes and to keep an auxiliary copy on the cloud as a cold backup. StorageGRID represents the next generation of object storage. StorageGRID is capable of high performance and massive throughput as well as performance and flexibility beyond what other object-storage vendors offer.
Table 1 lists the benefits of each backup option with StorageGRID.
Table 1) Primary backup to disk plus an auxiliary copy, versus primary backup to StorageGRID.
| Primary Backup to Disk and an Auxiliary Copy to StorageGRID | Primary Backup to StorageGRID | |
|---|---|---|
Performance |
Fastest recovery time, using live mount or live recovery: best for Tier0/Tier1 workloads. |
Cannot be used for live mount or live recovery operations. Ideal for streaming restore operation and for long-term retention. |
Deployment architecture |
Uses all flash or a spinning disk as a first backup landing tier. StorageGRID is used as a secondary tier. |
Simplifies the deployment by using StorageGRID as the all-inclusive backup target. |
Advanced features (live restore) |
Supported |
Not supported |
Target audience
This document is intended for data administrators and architects using Commvault and StorageGRID backup and recovery solutions.
Solution technology
The tested solution combines Commvault and NetApp solutions to make a powerful joint solution.
Commvault Complete Backup and Recovery software is an enterprise-level, integrated data and information management solution, built from the ground up on a single platform and with a unified code base. All of its functions share back-end technologies, bringing the unparalleled advantages and benefits of a fully integrated approach to protecting, managing, and accessing your data. The software contains modules to protect, archive, analyze, replicate, and search your data. The modules share a common set of back-end services and advanced capabilities that seamlessly interact with each other. The solution addresses all aspects of data management in your enterprise, while providing infinite scalability and unprecedented control of data and information.
Key features of the Commvault software platform include:
-
A complete data protection solution supporting all major operating systems, applications, and databases on virtual and physical servers, NAS systems, cloud-based infrastructures, and mobile devices.
-
Simplified management through a single console: You can view, manage, and access all functions and all data and information across the enterprise.
-
Multiple protection methods including data backup and archiving, snapshot management, data replication, and content indexing for e-discovery.
-
Efficient storage management using deduplication for disk and cloud storage.
-
Integration with NetApp storage arrays such as AFF, FAS, NetApp HCI, and E-Series arrays and NetApp SolidFire® scale-out storage systems. Integration also with NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP software to automate the creation of indexed, application-aware NetApp Snapshot™ copies across the NetApp storage portfolio.
-
Complete virtual infrastructure management that supports leading on-premises virtual hypervisors and public cloud hyperscaler platforms.
-
Advanced security capabilities to limit access to critical data, provide granular management capabilities, and provide single-sign-on access for Active Directory users.
-
Policy-based data management that allows you to manage your data based on business needs—not physical location.
-
A cutting-edge end-user experience, empowering your users to protect, find, and recover their own data.
-
API-driven automation, allowing you to use third-party tools like vRealize Automation or Service Now to manage your data protection and recovery operations.
For details on supported workloads, visit https://www.commvault.com/supported-technologies.
NetApp StorageGRID as a Commvault cloud tier is an enterprise hybrid-cloud object-storage solution. You can deploy it across many sites, either on a purpose-built appliance or as a software-defined deployment. StorageGRID enables you to establish data management policies that determine how data is stored and protected. StorageGRID collects the information you need to develop and enforce policies. It examines a wide range of characteristics and needs, including performance, durability, availability, geographic location, longevity, and cost. Data is fully maintained and protected as it moves between locations and as it ages.
The StorageGRID intelligent policy engine helps you choose either of the following options:
-
To use erasure coding to back up data across multiple sites for resilience.
-
To copy objects to remote sites to minimize WAN latency and cost.
When StorageGRID stores an object, you access it as one object, regardless of where it is or how many copies exist. This behavior is crucial for disaster recovery, because with it, even if one backup copy of your data is corrupted, StorageGRID is able to restore your data.
Retaining backup data in your primary storage can be expensive. When you use NetApp StorageGRID, you free up space on your primary storage by migrating inactive backup data into StorageGRID while you benefit from the numerous capabilities of StorageGRID. The value of backup data changes over time, as does the cost of storing it. StorageGRID can minimize the cost of your primary storage while increasing the durability of your data.
Solution Setup
In the lab setup, the StorageGRID environment consisted of four NetApp StorageGRID SG5712 appliances, one virtual primary Admin node and one virtual Gateway node. The SG5712 appliance is the entry level option—a baseline configuration. Choosing higher performance appliance options such as the NetApp StorageGRID SG5760 or SG6060 can provide significant performance benefits. Consult your NetApp StorageGRID solution architect for sizing assistance.
For its data protection policy, StorageGRID uses an integrated lifecycle management (ILM) policy to manage and protect data. ILM rules are evaluated in a policy from top to bottom. We implemented the ILM policy shown in Table 2.
Table 2) StorageGRID ILM policy.
| ILM Rule | Qualifiers | Ingest Behavior |
|---|---|---|
Erasure Coding 2+1 |
Objects over 200KB |
Balanced |
2 Copy |
All objects |
Dual Commit |
The ILM 2 Copy rule is the default rule. The Erasure Coding 2+1 rule was applied for this testing to any object 200KB or larger. The default rule was applied to objects smaller than 200KB. Application of the rules in this way is a StorageGRID best practice.
For technical details about this test environment, read the Solution Design and Best Practices section in the NetApp Scale-out Data Protection with Commvault technical report.
Sizing
Consult your NetApp data protection specialists for specific sizing for your environment. NetApp data protection specialists can use the Commvault Total Backup Storage Calculator tool to estimate the backup infrastructure requirements. The tool requires Commvault Partner Portal access. Sign up for access, if needed.
Commvault Sizing Inputs
The following tasks can be used to perform discovery for sizing of the data protection solution:
-
Identify the system or application/database workloads and corresponding front-end capacity (in terabytes [TB]) that will need to be protected.
-
Identify the VM/file workload and similar front-end capacity (TB) that will need to be protected.
-
Identify short-term and long-term retention requirements.
-
Identify the daily % change rate for the datasets/workloads identified.
-
Identify projected data growth over the next 12, 24, and 36 months.
-
Define the RTO and RPO for data protection/recovery according to business needs.
When this information is available, the backup infrastructure sizing can be done resulting in a breakdown of required storage capacities.
StorageGRID Sizing Guidance
Before you perform NetApp StorageGRID sizing, consider these aspects of your workload:
-
Usable capacity
-
WORM mode
-
Average object size
-
Performance requirements
-
ILM policy applied
The amount of usable capacity needs to accommodate the size of the backup workload you have tiered to StorageGRID and the retention schedule.
Will WORM mode be enabled or not? With WORM enabled in Commvault, this will configure object lock on StorageGRID. This will increase the object storage capacity required. The amount of capacity required will vary based on the retention duration and number of object changes with each backup.
Average object size is an input parameter that helps with sizing for performance in a StorageGRID environment. The average object sizes used for a Commvault workload depend on the type of backup.
Table 3 lists average object sizes by type of backup and describes what the restore process reads from the object store.
Table 3) Commvault workload object size and restore behavior.
| Backup Type | Average Object Size | Restore Behavior |
|---|---|---|
Make an auxiliary copy in StorageGRID |
32MB |
Full read of 32MB object |
Direct the backup to StorageGRID (deduplication enabled) |
8MB |
1MB random-range read |
Direct the backup to StorageGRID (deduplication disabled) |
32MB |
Full read of 32MB object |
In addition, understanding your performance requirements for full backups and incremental backups helps you determine sizing for the StorageGRID storage nodes. StorageGRID information lifecycle management (ILM) policy data protection methods determine the capacity needed to store Commvault backups and affect the sizing of the grid.
StorageGRID ILM replication is one of two mechanisms used by StorageGRID to store object data. When StorageGRID assigns objects to an ILM rule that replicates data, the system creates exact copies of the objects’ data and stores the copies on storage nodes.
Erasure coding is the second method used by StorageGRID to store object data. When StorageGRID assigns objects to an ILM rule that is configured to create erasure-coded copies, it slices object data into data fragments. It then computes additional parity fragments and stores each fragment on a different storage node. When an object is accessed, it is reassembled using the stored fragments. If a data fragment or a parity fragment becomes corrupt or is lost, the erasure-coding algorithm can re-create that fragment using a subset of the remaining data and parity fragments.
The two mechanisms require different amounts of storage, as these examples demonstrate:
-
If you store two replicated copies, your storage overhead doubles.
-
If you store a 2+1 erasure-coded copy, your storage overhead increases by 1.5 times.
For the solution tested, an entry-level StorageGRID deployment on a single site was used:
-
Admin node: VMware virtual machine (VM)
-
Load balancer: VMware VM
-
Storage nodes: 4x SG5712 with 4TB drives
-
Primary Admin node and Gateway node: VMware VMs with the minimum production workload requirements

|
StorageGRID also supports third-party load balancers. |
StorageGRID is typically deployed in two or more sites with data protection policies that replicate data to protect against node and site-level failures. By backing up your data to StorageGRID, your data is protected by multiple copies or by erasure coding that separates and reassembles data dependably through an algorithm.
You can use the sizing tool Fusion to size your grid.
Scaling
You can expand a NetApp StorageGRID system by adding storage to storage nodes, adding new grid nodes to an existing site, or adding a new data center site. You can perform expansions without interrupting the operation of your current system.
StorageGRID scales performance by using either higher performance nodes for storage nodes or the physical appliance which runs the load balancer and the admin nodes or by simply adding additional nodes.

|
For more information about expanding the StorageGRID system, see StorageGRID 11.9 Expansion Guide. |
StorageGRID Hardware Specifications
Table 4 describes the NetApp StorageGRID hardware used in this testing. The StorageGRID SG5712 appliance with 10Gbps networking is the entry-level option and represents a baseline configuration. Optionally the SG5712 can be configured for 25Gbps networking.
Choosing higher-performance appliance options such as the NetApp StorageGRID SG5760, SG6060, or all flash SGF6112 appliances can provide significant performance benefits. Consult your NetApp StorageGRID solution architect for sizing assistance.
Table 4) SG5712 hardware specifications.
| Hardware | Quantity | Disk | Usable Capacity | Network |
|---|---|---|---|---|
StorageGRID SG5712 appliances |
4 |
48 x 4TB (near-line SAS HDD) |
136TB |
10Gbps |
Commvault and StorageGRID Software Requirements
Tables 5 and 6 list the software requirements for the Commvault and NetApp StorageGRID software installed on VMware software for our testing. Four MediaAgent data transmission managers and one CommServe server were installed. In the test, 10Gbps networking was implemented for the VMware infrastructure.
Table 5) Commvault software total system requirements.
| Component | Quantity | Datastore | Size | Total | Total Required IOPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CommServe Server |
1 |
OS |
500GB |
500GB |
n/a |
SQL |
500GB |
500GB |
n/a |
||
MediaAgent |
4 |
Virtual CPU (vCPU) |
16 |
64 |
n/a |
RAM |
128GB |
512 |
n/a |
||
OS |
500GB |
2TB |
n/a |
||
Index Cache |
2TB |
8TB |
200+ |
||
DDB |
2TB |
8TB |
200-80,000K |
In the test environment, one virtual primary Admin node and one virtual Gateway node were deployed on VMware on a NetApp E-Series E2812 storage array. Each node was on a separate server with the minimum production environment requirements described in Table 6:
Table 6) Requirements for StorageGRID virtual Admin nodes and Gateway nodes.
| Node type | Quantity | vCPU | RAM | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Gateway node |
1 |
8 |
24GB |
100GB LUN for the OS |
Admin node |
1 |
8 |
24GB |
100GB LUN for the OS 200GB LUN for Admin node tables 200GB LUN for the Admin node audit log |
Running a Data Protection Job with Commvault Complete Backup and Recovery and NetApp StorageGRID
To configure NetApp StorageGRID with Commvault Complete Backup and Recovery for NetApp, the following steps were performed to add StorageGRID as a cloud library within the Commvault software.
Configure Commvault with NetApp StorageGRID
-
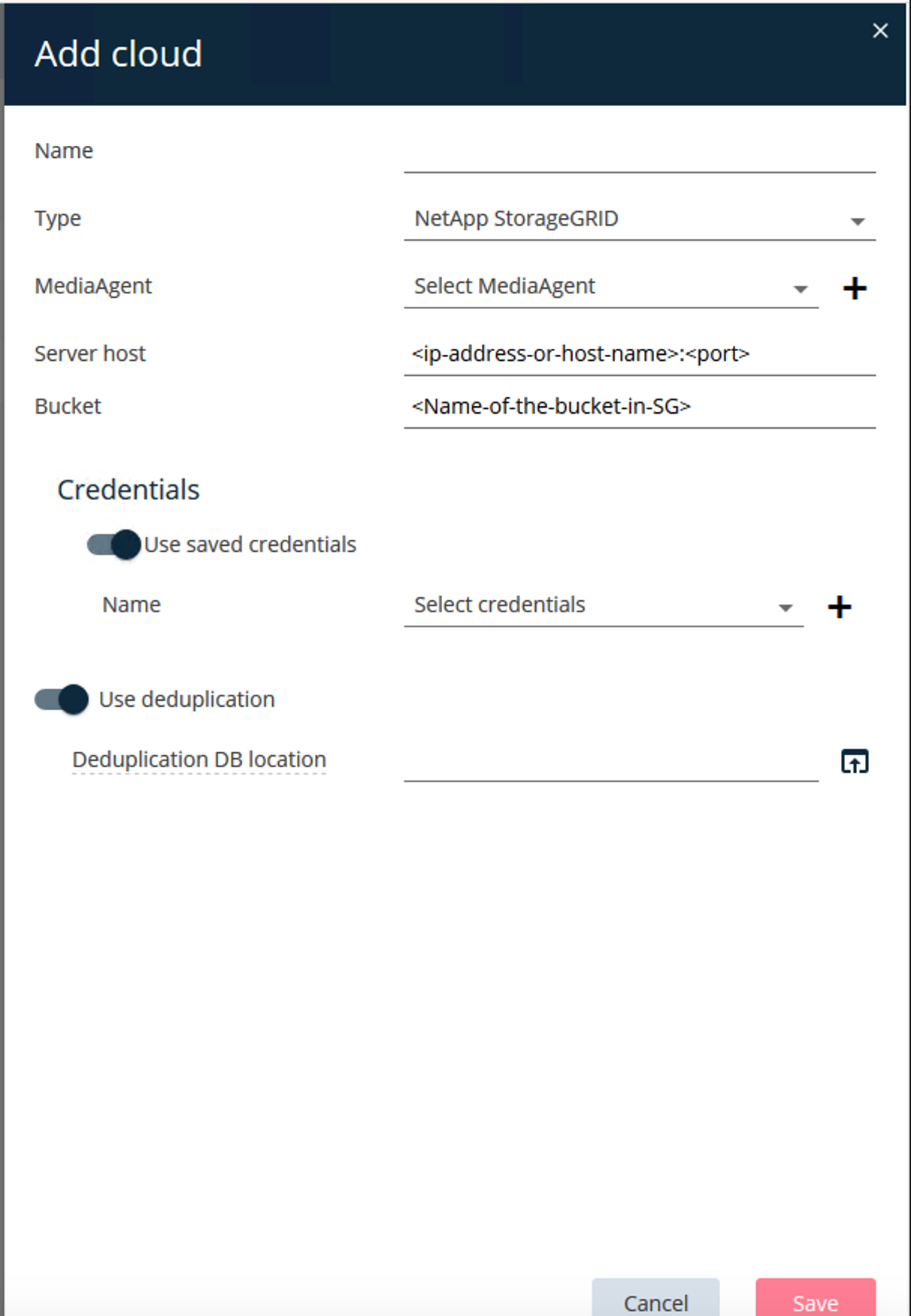
Log in to the Commvault Command Center. On the left panel, click Storage > Cloud > Add to see and respond to the Add Cloud dialog box:
-
For Type, select NetApp StorageGRID.
-
For MediaAgent, select all that are associated with the cloud library.
-
For Server Host, enter the IP address or the host name of the StorageGRID endpoint and the port number.
Follow the steps in StorageGRID documentation on how to configure a load balancer endpoint (port). Make sure you have an HTTPS port with a self-signed certificate and the IP address or the domain name of the StorageGRID endpoint.
-
If you want to use deduplication, turn on this option and provide the path to the deduplication database location.
-
Click Save.
Create a Backup Plan with NetApp StorageGRID as the Primary Target
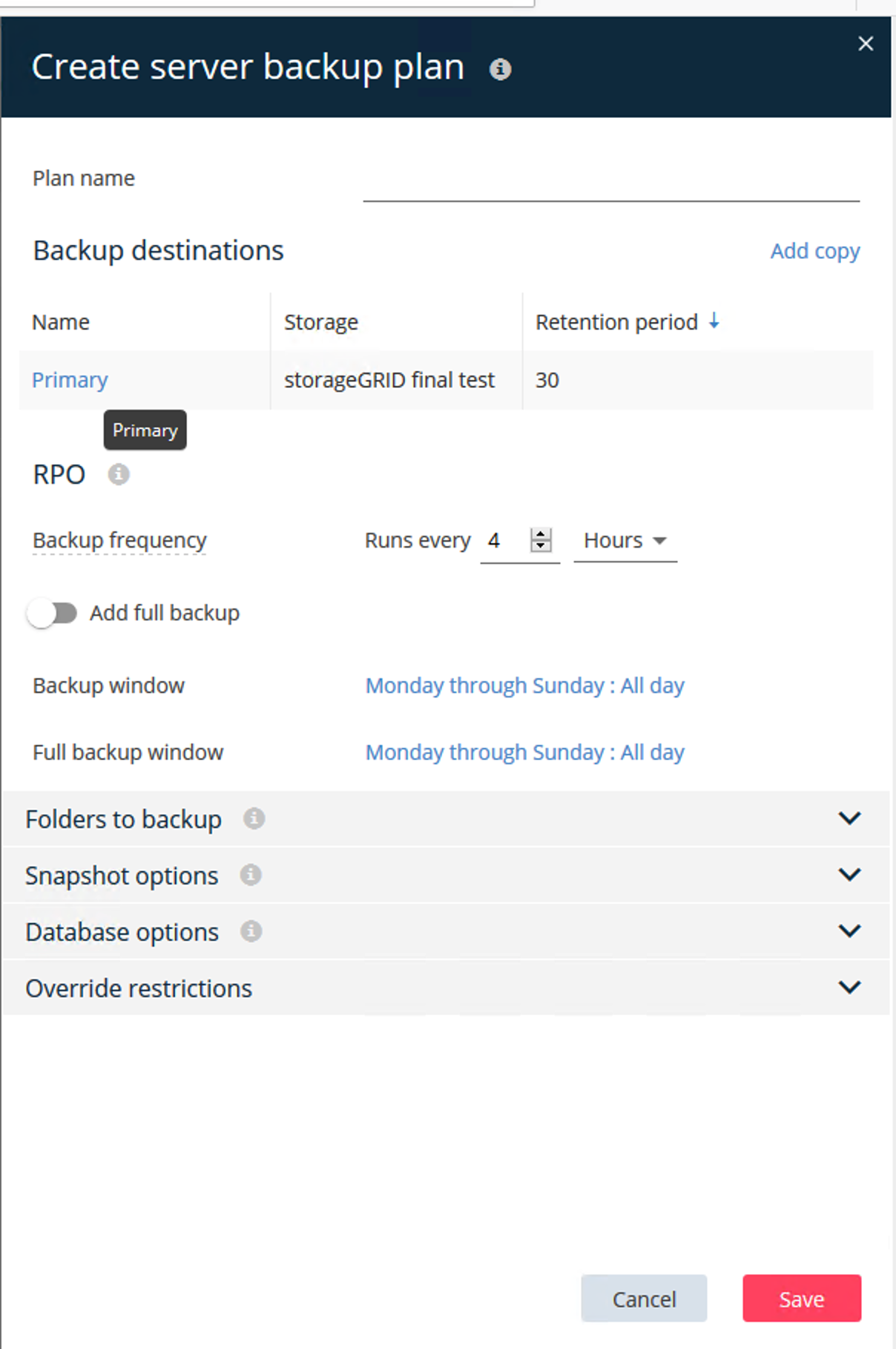
-
On the left panel, select Manage > Plans to see and respond to the Create Server Backup Plan dialog box.
-
Enter a plan name.
-
Select the StorageGRID Simple Storage Service (S3) storage backup destination that you created earlier.
-
Enter the backup retention period and recovery point objective (RPO) that you want.
-
Click Save.
Start a Backup Job to Protect Your Workloads Using Commvault Software and StorageGRID
To start a backup job from Commvault Complete Backup and Recovery to StorageGRID, follow these steps:
-
On the Commvault Command Center, navigate to Protect > Virtualization.
-
Add a VMware vCenter Server hypervisor.
-
Click the hypervisor that you just added.
-
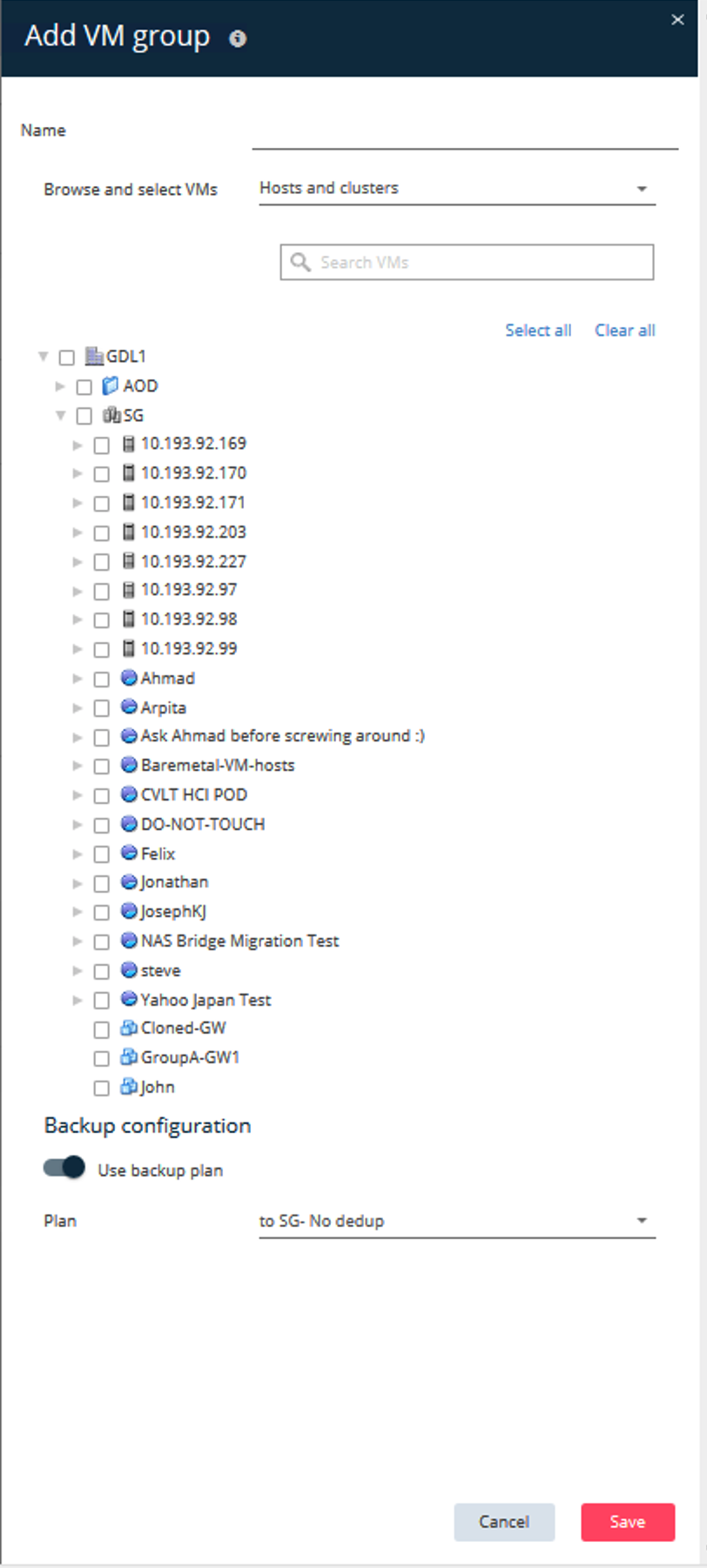
Click Add VM group to respond to the Add VM Group dialog box so that you can see the vCenter environment that you plan to protect.
-
Select a datastore, a VM, or a collection of VMs, and enter a name for it.
-
Select the backup plan that you created in the previous task.
-
Click Save to see the VM group you created.
-
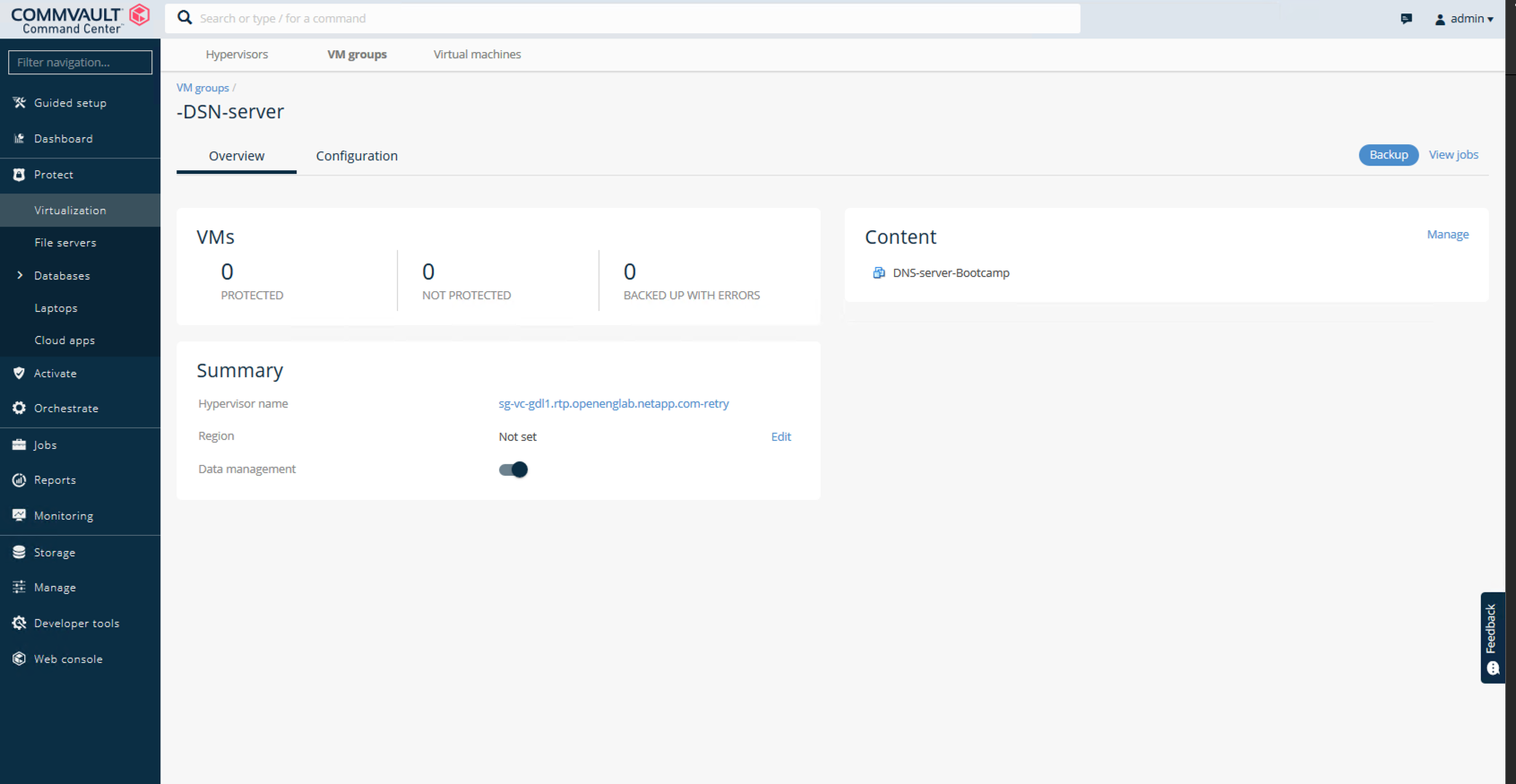
In the upper-right corner of the VM group window, select Backup:
-
Select Full as the backup level, (optionally) request an email when the backup is finished, then click OK to have your backup job start:

-
Navigate to the job summary page to view the job metrics:
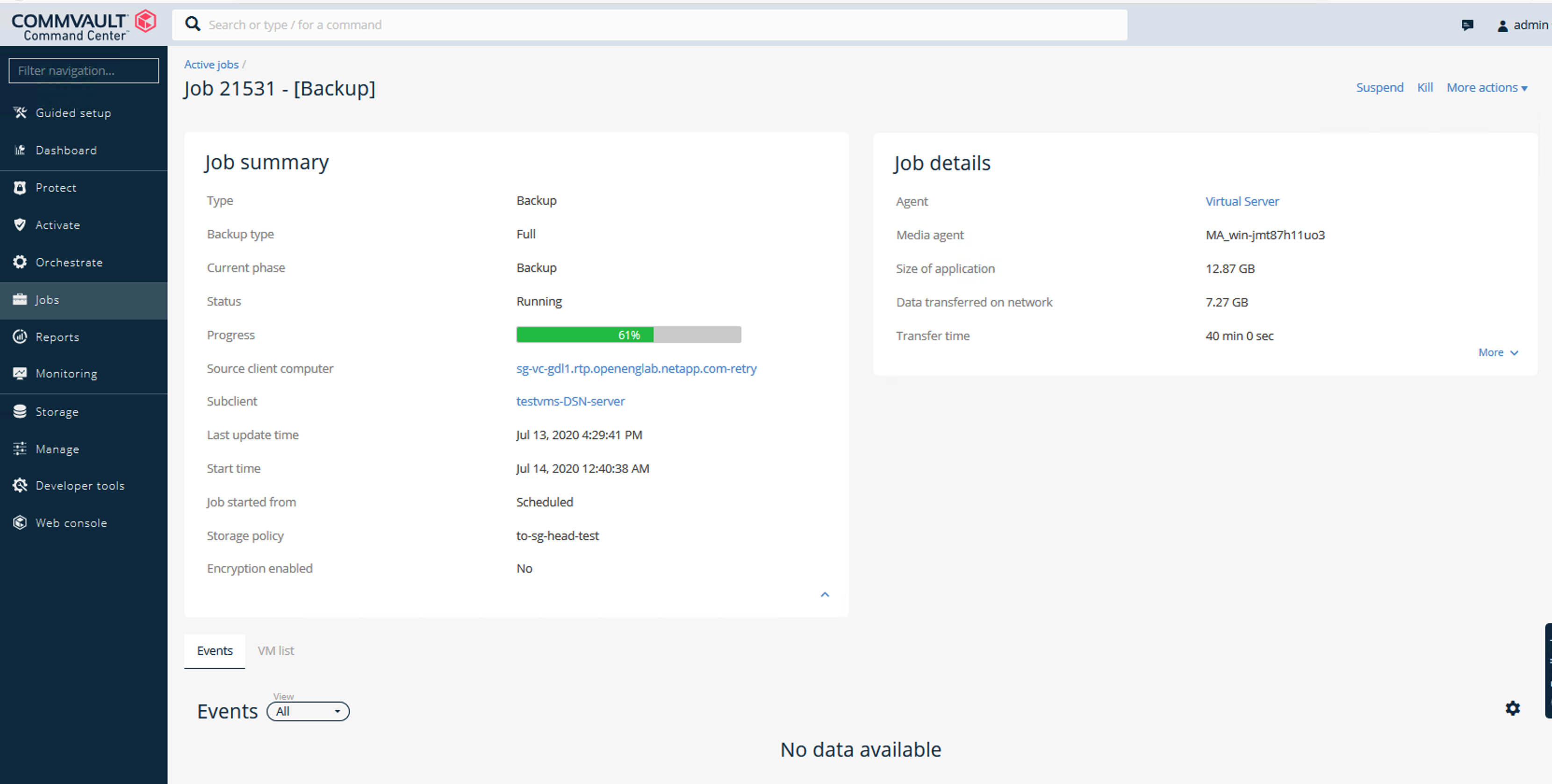
Baseline Performance Tests
Table 7 shows the results from our baseline performance tests. In the Aux Copy operation, four Commvault MediaAgents backed up data to a NetApp AFF A300 system and an auxiliary copy was created on NetApp StorageGRID. For details on the test setup environment, read the Solution Design and Best Practices section in the NetApp Scale-out Data Protection with Commvault technical report.
The tests were performed with 100 VMs and 1000 VMs, both tests with a 50/50 mix of Windows and CentOS VMs.
Table 7) Baseline performance tests.
| Operation | Backup Speed | Restore Speed |
|---|---|---|
Aux Copy |
2 TB/hour |
1.27 TB/hour |
Direct to and from object (Deduplication On) |
2.2 TB/hour |
1.22 TB/hour |
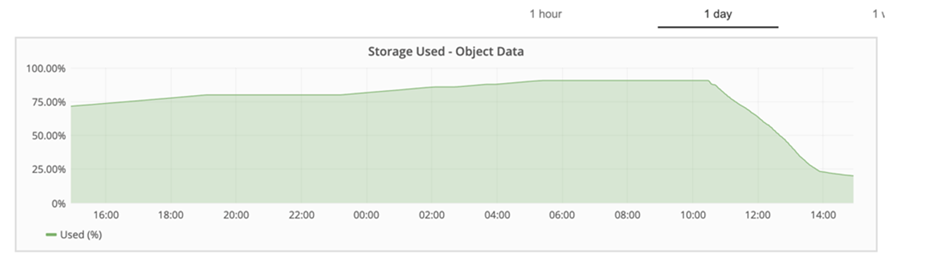
To test age-off performance, 2.5 million objects were deleted. As shown in Figures 2 and 3, the delete run was completed in less than 3 hours and freed up more than 80TB of space. The delete run started at 10:30 AM.
Figure 1) Deletion of 2.5 million (80TB) objects in less than 3 hours.
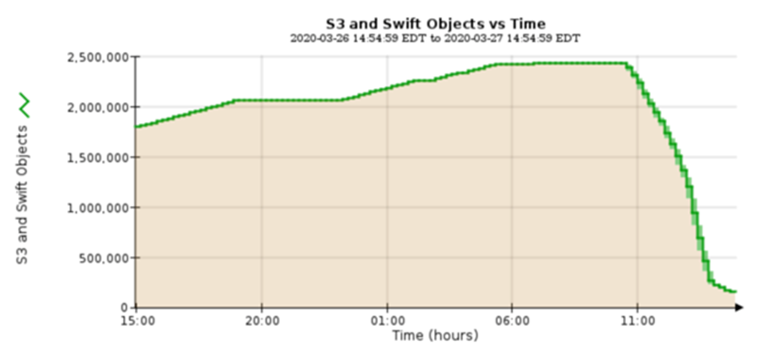
Figure 2) Freeing up 80TB of storage in less than 3 hours.
Bucket Consistency Level Recommendation
NetApp StorageGRID allows the end user to select the consistency level for operations performed on the objects in Simple Storage Service (S3) buckets.
Commvault MediaAgents are the data movers in a Commvault environment. In most cases, MediaAgents are configured to write locally into a primary StorageGRID site. For this reason, a high consistency level within a local primary site is recommended. Use the following guidelines when you set the consistency level on Commvault buckets created in StorageGRID.

|
If you have a Commvault version earlier than 11.0.0 - Service Pack 16, consider upgrading Commvault to the newest version. If that is not an option, be sure to follow the guidelines for your version. |
-
Commvault versions earlier than 11.0.0 - Service Pack 16.* In versions earlier than 11.0.0 - Service Pack 16, Commvault performs S3 HEAD and GET operations on non-existent objects as part of restore and pruning process. Set the bucket consistency level to Strong-site to achieve the optimal consistency level for Commvault backups to StorageGRID.
-
Commvault versions 11.0.0 - Service Pack 16 and later.* In versions 11.0.0 - Service Pack 16 and later, the number of S3 HEAD and GET operations performed on non-existent objects are minimized. Set the default bucket consistency level to Read-after-new-write to ensure high consistency level in the Commvault and StorageGRID environment.
Where to Find Additional Information
To learn more about the information that is described in this document, review the following documents and/or websites:
-
StorageGRID 11.9 Documentation Center
https://docs.netapp.com/us-en/storagegrid-119/ -
NetApp Product Documentation
https://docs.netapp.com -
Commvault documentation
https://documentation.commvault.com/2024/essential/index.html

