Networking requirements for Cloud Volumes ONTAP in Google Cloud
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


Set up your Google Cloud networking so Cloud Volumes ONTAP systems can operate properly.
If you want to deploy an HA pair, you should learn how HA pairs work in Google Cloud.
Requirements for Cloud Volumes ONTAP
The following requirements must be met in Google Cloud.
Requirements specific to single node systems
If you want to deploy a single node system, ensure that your networking meets the following requirements.
One VPC
One Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is required for a single node system.
Private IP addresses
BlueXP allocates 3 or 4 private IP addresses to a single node system in Google Cloud.
You can skip creation of the storage VM (SVM) management LIF if you deploy Cloud Volumes ONTAP using the API and specify the following flag:
skipSvmManagementLif: true

|
A LIF is an IP address associated with a physical port. A storage VM (SVM) management LIF is required for management tools like SnapCenter. |
Requirements specific to HA pairs
If you want to deploy an HA pair, ensure that your networking meets the following requirements.
One or multiple zones
You can ensure the high availability of your data by deploying an HA configuration across multiple or in a single zone. BlueXP will prompt you to choose multiple zones or a single zone when you create the HA pair.
-
Multiple zones (recommended)
Deploying an HA configuration across three zones ensures continuous data availability if a failure occurs within a zone. Note that write performance is slightly lower compared to using a single zone, but it's minimal.
-
Single zone
When deployed in a single zone, a Cloud Volumes ONTAP HA configuration uses a spread placement policy. This policy ensures that an HA configuration is protected from a single point of failure within the zone, without having to use separate zones to achieve fault isolation.
This deployment model does lower your costs because there are no data egress charges between zones.
Four Virtual Private Clouds
Four Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) are required for an HA configuration. Four VPCs are required because Google Cloud requires that each network interface resides in a separate VPC network.
BlueXP will prompt you to choose four VPCs when you create the HA pair:
-
VPC-0 for inbound connections to the data and nodes
-
VPC-1, VPC-2, and VPC-3 for internal communication between the nodes and the HA mediator
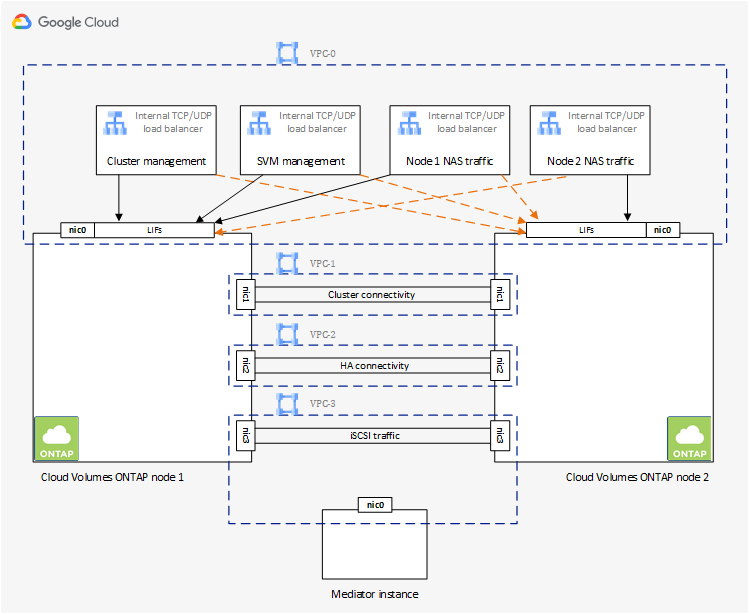
Subnets
A private subnet is required for each VPC.
If you place the Connector in VPC-0, then you will need to enable Private Google Access on the subnet to access the APIs and to enable data tiering.
The subnets in these VPCs must have distinct CIDR ranges. They can't have overlapping CIDR ranges.
Private IP addresses
BlueXP automatically allocates the required number of private IP addresses to Cloud Volumes ONTAP in Google Cloud. You need to make sure that your networking has enough private addresses available.
The number of LIFs that BlueXP allocates for Cloud Volumes ONTAP depends on whether you deploy a single node system or an HA pair. A LIF is an IP address associated with a physical port. An SVM management LIF is required for management tools like SnapCenter.
-
Single node
BlueXP allocates 4 IP addresses to a single node system:-
Node management LIF
-
Cluster management LIF
-
iSCSI data LIF
An iSCSI LIF provides client access over the iSCSI protocol and is used by the system for other important networking workflows. These LIFs are required and should not be deleted. -
NAS LIF
You can skip creation of the storage VM (SVM) management LIF if you deploy Cloud Volumes ONTAP using the API and specify the following flag:
skipSvmManagementLif: true
-
-
HA pair
BlueXP allocates 12-13 IP addresses to an HA pair:-
2 Node management LIFs (e0a)
-
1 Cluster management LIF (e0a)
-
2 iSCSI LIFs (e0a)
An iSCSI LIF provides client access over the iSCSI protocol and is used by the system for other important networking workflows. These LIFs are required and should not be deleted. -
1 or 2 NAS LIFs (e0a)
-
2 Cluster LIFs (e0b)
-
2 HA Interconnect IP addresses (e0c)
-
2 RSM iSCSI IP addresses (e0d)
You can skip creation of the storage VM (SVM) management LIF if you deploy Cloud Volumes ONTAP using the API and specify the following flag:
skipSvmManagementLif: true
-
Internal load balancers
BlueXP automatically creates four Google Cloud internal load balancers (TCP/UDP) that manage incoming traffic to the Cloud Volumes ONTAP HA pair. No setup is required from your end. We've listed this as a requirement simply to inform you of the network traffic and to mitigate any security concerns.
One load balancer is for cluster management, one is for storage VM (SVM) management, one is for NAS traffic to node 1, and the last is for NAS traffic to node 2.
The setup for each load balancer is as follows:
-
One shared private IP address
-
One global health check
By default, the ports used by the health check are 63001, 63002, and 63003.
-
One regional TCP backend service
-
One regional UDP backend service
-
One TCP forwarding rule
-
One UDP forwarding rule
-
Global access is disabled
Even though global access is disabled by default, enabling it post deployment is supported. We disabled it because cross region traffic will have significantly higher latencies. We wanted to ensure that you didn't have a negative experience due to accidental cross region mounts. Enabling this option is specific to your business needs.
Shared VPCs
Cloud Volumes ONTAP and the Connector are supported in a Google Cloud shared VPC and also in standalone VPCs.
For a single node system, the VPC can be either a shared VPC or a standalone VPC.
For an HA pair, four VPCs are required. Each of those VPCs can be either shared or standalone. For example, VPC-0 could be a shared VPC, while VPC-1, VPC-2, and VPC-3 could be standalone VPCs.
A shared VPC enables you to configure and centrally manage virtual networks across multiple projects. You can set up shared VPC networks in the host project and deploy the Connector and Cloud Volumes ONTAP virtual machine instances in a service project. Google Cloud documentation: Shared VPC overview.
Packet mirroring in VPCs
Packet mirroring must be disabled in the Google Cloud VPC in which you deploy Cloud Volumes ONTAP. Cloud Volumes ONTAP can't operate properly if packet mirroring is enabled.
Outbound internet access
Cloud Volumes ONTAP requires outbound internet access for NetApp AutoSupport, which proactively monitors the health of your system and sends messages to NetApp technical support.
Routing and firewall policies must allow HTTP/HTTPS traffic to the following endpoints so Cloud Volumes ONTAP can send AutoSupport messages:
-
https://support.netapp.com/aods/asupmessage
-
https://support.netapp.com/asupprod/post/1.0/postAsup
If an outbound internet connection isn't available to send AutoSupport messages, BlueXP automatically configures your Cloud Volumes ONTAP systems to use the Connector as a proxy server. The only requirement is to ensure that the Connector's firewall allows inbound connections over port 3128. You'll need to open this port after you deploy the Connector.
If you defined strict outbound rules for Cloud Volumes ONTAP, then you'll also need to ensure that the Cloud Volumes ONTAP firewall allows outbound connections over port 3128.
After you've verified that outbound internet access is available, you can test AutoSupport to ensure that it can send messages. For instructions, refer to ONTAP docs: Set up AutoSupport.

|
If you're using an HA pair, the HA mediator doesn't require outbound internet access. |
If BlueXP notifies you that AutoSupport messages can't be sent, troubleshoot your AutoSupport configuration.
- Firewall rules
-
You don't need to create firewall rules because BlueXP does that for you. If you need to use your own, refer to the firewall rules listed below.
Note that two sets of firewall rules are required for an HA configuration:
-
One set of rules for HA components in VPC-0. These rules enable data access to Cloud Volumes ONTAP. Learn more.
-
Another set of rules for HA components in VPC-1, VPC-2, and VPC-3. These rules are open for inbound & outbound communication between the HA components. Learn more.
-
If you want to tier cold data to a Google Cloud Storage bucket, the subnet in which Cloud Volumes ONTAP resides must be configured for Private Google Access (if you're using an HA pair, this is the subnet in VPC-0). For instructions, refer to Google Cloud documentation: Configuring Private Google Access.
For additional steps required to set up data tiering in BlueXP, see Tiering cold data to low-cost object storage.
Connections to ONTAP systems in other networks
To replicate data between a Cloud Volumes ONTAP system in Google Cloud and ONTAP systems in other networks, you must have a VPN connection between the VPC and the other network—for example, your corporate network.
For instructions, refer to Google Cloud documentation: Cloud VPN overview.
Firewall rules
BlueXP creates Google Cloud firewall rules that include the inbound and outbound rules that Cloud Volumes ONTAP needs to operate successfully. You might want to refer to the ports for testing purposes or if you prefer your to use own firewall rules.
The firewall rules for Cloud Volumes ONTAP requires both inbound and outbound rules. If you're deploying an HA configuration, these are the firewall rules for Cloud Volumes ONTAP in VPC-0.
Note that two sets of firewall rules are required for an HA configuration:
-
One set of rules for HA components in VPC-0. These rules enable data access to Cloud Volumes ONTAP.
-
Another set of rules for HA components in VPC-1, VPC-2, and VPC-3. These rules are open for inbound & outbound communication between the HA components. Learn more.

|
Looking for information about the Connector? View firewall rules for the Connector |
Inbound rules
When you create a working environment, you can choose the source filter for the predefined firewall policy during deployment:
-
Selected VPC only: the source filter for inbound traffic is the subnet range of the VPC for the Cloud Volumes ONTAP system and the subnet range of the VPC where the Connector resides. This is the recommended option.
-
All VPCs: the source filter for inbound traffic is the 0.0.0.0/0 IP range.
If you use your own firewall policy, ensure that you add all networks that need to communicate with Cloud Volumes ONTAP, but also ensure to add both address ranges to allow the internal Google Load Balancer to function correctly. These addresses are 130.211.0.0/22 and 35.191.0.0/16. For more information, refer to Google Cloud documentation: Load Balancer Firewall Rules.
| Protocol | Port | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
All ICMP |
All |
Pinging the instance |
HTTP |
80 |
HTTP access to the System Manager web console using the IP address of the cluster management LIF |
HTTPS |
443 |
Connectivity with the Connector and HTTPS access to the System Manager web console using the IP address of the cluster management LIF |
SSH |
22 |
SSH access to the IP address of the cluster management LIF or a node management LIF |
TCP |
111 |
Remote procedure call for NFS |
TCP |
139 |
NetBIOS service session for CIFS |
TCP |
161-162 |
Simple network management protocol |
TCP |
445 |
Microsoft SMB/CIFS over TCP with NetBIOS framing |
TCP |
635 |
NFS mount |
TCP |
749 |
Kerberos |
TCP |
2049 |
NFS server daemon |
TCP |
3260 |
iSCSI access through the iSCSI data LIF |
TCP |
4045 |
NFS lock daemon |
TCP |
4046 |
Network status monitor for NFS |
TCP |
10000 |
Backup using NDMP |
TCP |
11104 |
Management of intercluster communication sessions for SnapMirror |
TCP |
11105 |
SnapMirror data transfer using intercluster LIFs |
TCP |
63001-63050 |
Load balance probe ports to determine which node is healthy (required for HA pairs only) |
UDP |
111 |
Remote procedure call for NFS |
UDP |
161-162 |
Simple network management protocol |
UDP |
635 |
NFS mount |
UDP |
2049 |
NFS server daemon |
UDP |
4045 |
NFS lock daemon |
UDP |
4046 |
Network status monitor for NFS |
UDP |
4049 |
NFS rquotad protocol |
Outbound rules
The predefined security group for Cloud Volumes ONTAP opens all outbound traffic. If that is acceptable, follow the basic outbound rules. If you need more rigid rules, use the advanced outbound rules.
Basic outbound rules
The predefined security group for Cloud Volumes ONTAP includes the following outbound rules.
| Protocol | Port | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
All ICMP |
All |
All outbound traffic |
All TCP |
All |
All outbound traffic |
All UDP |
All |
All outbound traffic |
Advanced outbound rules
If you need rigid rules for outbound traffic, you can use the following information to open only those ports that are required for outbound communication by Cloud Volumes ONTAP.

|
The source is the interface (IP address) on the Cloud Volumes ONTAP system. |
| Service | Protocol | Port | Source | Destination | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Active Directory |
TCP |
88 |
Node management LIF |
Active Directory forest |
Kerberos V authentication |
UDP |
137 |
Node management LIF |
Active Directory forest |
NetBIOS name service |
|
UDP |
138 |
Node management LIF |
Active Directory forest |
NetBIOS datagram service |
|
TCP |
139 |
Node management LIF |
Active Directory forest |
NetBIOS service session |
|
TCP & UDP |
389 |
Node management LIF |
Active Directory forest |
LDAP |
|
TCP |
445 |
Node management LIF |
Active Directory forest |
Microsoft SMB/CIFS over TCP with NetBIOS framing |
|
TCP |
464 |
Node management LIF |
Active Directory forest |
Kerberos V change & set password (SET_CHANGE) |
|
UDP |
464 |
Node management LIF |
Active Directory forest |
Kerberos key administration |
|
TCP |
749 |
Node management LIF |
Active Directory forest |
Kerberos V change & set Password (RPCSEC_GSS) |
|
TCP |
88 |
Data LIF (NFS, CIFS, iSCSI) |
Active Directory forest |
Kerberos V authentication |
|
UDP |
137 |
Data LIF (NFS, CIFS) |
Active Directory forest |
NetBIOS name service |
|
UDP |
138 |
Data LIF (NFS, CIFS) |
Active Directory forest |
NetBIOS datagram service |
|
TCP |
139 |
Data LIF (NFS, CIFS) |
Active Directory forest |
NetBIOS service session |
|
TCP & UDP |
389 |
Data LIF (NFS, CIFS) |
Active Directory forest |
LDAP |
|
TCP |
445 |
Data LIF (NFS, CIFS) |
Active Directory forest |
Microsoft SMB/CIFS over TCP with NetBIOS framing |
|
TCP |
464 |
Data LIF (NFS, CIFS) |
Active Directory forest |
Kerberos V change & set password (SET_CHANGE) |
|
UDP |
464 |
Data LIF (NFS, CIFS) |
Active Directory forest |
Kerberos key administration |
|
TCP |
749 |
Data LIF (NFS, CIFS) |
Active Directory forest |
Kerberos V change & set password (RPCSEC_GSS) |
|
AutoSupport |
HTTPS |
443 |
Node management LIF |
support.netapp.com |
AutoSupport (HTTPS is the default) |
HTTP |
80 |
Node management LIF |
support.netapp.com |
AutoSupport (only if the transport protocol is changed from HTTPS to HTTP) |
|
TCP |
3128 |
Node management LIF |
Connector |
Sending AutoSupport messages through a proxy server on the Connector, if an outbound internet connection isn't available |
|
Cluster |
All traffic |
All traffic |
All LIFs on one node |
All LIFs on the other node |
Intercluster communications (Cloud Volumes ONTAP HA only) |
Configuration backups |
HTTP |
80 |
Node management LIF |
http://<connector-IP-address>/occm/offboxconfig |
Send configuration backups to the Connector. Learn about configuration backup files. |
DHCP |
UDP |
68 |
Node management LIF |
DHCP |
DHCP client for first-time setup |
DHCPS |
UDP |
67 |
Node management LIF |
DHCP |
DHCP server |
DNS |
UDP |
53 |
Node management LIF and data LIF (NFS, CIFS) |
DNS |
DNS |
NDMP |
TCP |
18600–18699 |
Node management LIF |
Destination servers |
NDMP copy |
SMTP |
TCP |
25 |
Node management LIF |
Mail server |
SMTP alerts, can be used for AutoSupport |
SNMP |
TCP |
161 |
Node management LIF |
Monitor server |
Monitoring by SNMP traps |
UDP |
161 |
Node management LIF |
Monitor server |
Monitoring by SNMP traps |
|
TCP |
162 |
Node management LIF |
Monitor server |
Monitoring by SNMP traps |
|
UDP |
162 |
Node management LIF |
Monitor server |
Monitoring by SNMP traps |
|
SnapMirror |
TCP |
11104 |
Intercluster LIF |
ONTAP intercluster LIFs |
Management of intercluster communication sessions for SnapMirror |
TCP |
11105 |
Intercluster LIF |
ONTAP intercluster LIFs |
SnapMirror data transfer |
|
Syslog |
UDP |
514 |
Node management LIF |
Syslog server |
Syslog forward messages |
Rules for VPC-1, VPC-2, and VPC-3
In Google Cloud, an HA configuration is deployed across four VPCs. The firewall rules needed for the HA configuration in VPC-0 are listed above for Cloud Volumes ONTAP.
Meanwhile, the predefined firewall rules that BlueXP creates for instances in VPC-1, VPC-2, and VPC-3 enables ingress communication over all protocols and ports. These rules enable communication between HA nodes.
Communication from the HA nodes to the HA mediator takes place over port 3260 (iSCSI).

|
To enable high write speed for new Google Cloud HA pair deployments, a maximum transmission unit (MTU) of at least 8,896 bytes is required for VPC-1, VPC-2, and VPC-3. If you choose to upgrade existing VPC-1, VPC-2, and VPC-3 to an MTU of 8,896 bytes, you must shutdown all existing HA systems using these VPCs during the configuration process. |
Requirements for the Connector
If you haven't created a Connector yet, you should review networking requirements for the Connector as well.


