Share an NFS volume across namespaces
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


Using Astra Trident, you can create a volume in a primary namespace and share it in one or more secondary namespaces.
Features
The Astra TridentVolumeReference CR allows you to securely share ReadWriteMany (RWX) NFS volumes across one or more Kubernetes namespaces. This Kubernetes-native solution has the following benefits:
-
Multiple levels of access control to ensure security
-
Works with all Trident NFS volume drivers
-
No reliance on tridentctl or any other non-native Kubernetes feature
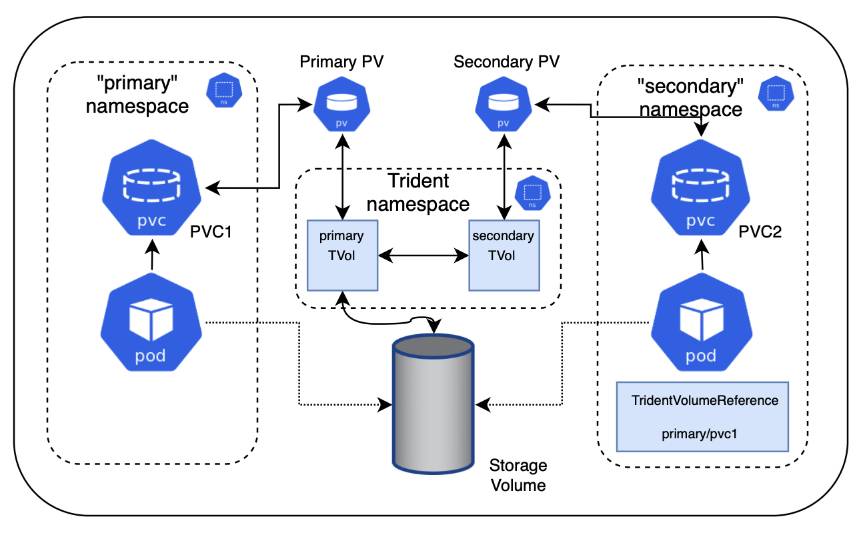
This diagram illustrates NFS volume sharing across two Kubernetes namespaces.
Quick start
You can set up NFS volume sharing in just a few steps.
 Configure source PVC to share the volume
Configure source PVC to share the volumeThe source namespace owner grants permission to access the data in the source PVC.
 Grant permission to create a CR in the destination namespace
Grant permission to create a CR in the destination namespaceThe cluster administrator grants permission to the owner of the destination namespace to create the TridentVolumeReference CR.
 Create TridentVolumeReference in the destination namespace
Create TridentVolumeReference in the destination namespaceThe owner of the destination namespace creates the TridentVolumeReference CR to refer to the source PVC.
 Create the subordinate PVC in the destination namespace
Create the subordinate PVC in the destination namespaceThe owner of the destination namespace creates the subordinate PVC to use the data source from the source PVC.
Configure the source and destination namespaces
To ensure security, cross namespace sharing requires collaboration and action by the source namespace owner, cluster administrator, and destination namespace owner. The user role is designated in each step.
-
Source namespace owner: Create the PVC (
pvc1) in the source namespace that grants permission to share with the destination namespace (namespace2) using theshareToNamespaceannotation.kind: PersistentVolumeClaim apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: pvc1 namespace: namespace1 annotations: trident.netapp.io/shareToNamespace: namespace2 spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany storageClassName: trident-csi resources: requests: storage: 100GiAstra Trident creates the PV and its backend NFS storage volume.
-
You can share the PVC to multiple namespaces using a comma-delimited list. For example,
trident.netapp.io/shareToNamespace: namespace2,namespace3,namespace4. -
You can share to all namespaces using
*. For example,trident.netapp.io/shareToNamespace: * -
You can update the PVC to include the
shareToNamespaceannotation at any time.
-
-
Cluster admin: Create the custom role and kubeconfig to grant permission to the destination namespace owner to create the TridentVolumeReference CR in the destination namespace.
-
Destination namespace owner: Create a TridentVolumeReference CR in the destination namespace that refers to the source namespace
pvc1.apiVersion: trident.netapp.io/v1 kind: TridentVolumeReference metadata: name: my-first-tvr namespace: namespace2 spec: pvcName: pvc1 pvcNamespace: namespace1
-
Destination namespace owner: Create a PVC (
pvc2) in destination namespace (namespace2) using theshareFromPVCannotation to designate the source PVC.kind: PersistentVolumeClaim apiVersion: v1 metadata: annotations: trident.netapp.io/shareFromPVC: namespace1/pvc1 name: pvc2 namespace: namespace2 spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany storageClassName: trident-csi resources: requests: storage: 100GiThe size of the destination PVC must be less than or equal than the source PVC.
Astra Trident reads the shareFromPVC annotation on the destination PVC and creates the destination PV as a subordinate volume with no storage resource of its own that points to the source PV and shares the source PV storage resource. The destination PVC and PV appear bound as normal.
Delete a shared volume
You can delete a volume that is shared across multiple namespaces. Astra Trident will remove access to the volume on the source namespace and maintain access for other namespaces that share the volume. When all namespaces that reference the volume are removed, Astra Trident deletes the volume.
Use tridentctl get to query subordinate volumes
Using the tridentctl utility, you can run the get command to get subordinate volumes. For more information, refer to tridentctl commands and options.
Usage: tridentctl get [option]
Flags:
-
`-h, --help: Help for volumes. -
--parentOfSubordinate string: Limit query to subordinate source volume. -
--subordinateOf string: Limit query to subordinates of volume.
Limitations
-
Astra Trident cannot prevent destination namespaces from writing to the shared volume. You should use file locking or other processes to prevent overwriting shared volume data.
-
You cannot revoke access to the source PVC by removing the
shareToNamespaceorshareFromNamespaceannotations or deleting theTridentVolumeReferenceCR. To revoke access, you must delete the subordinate PVC. -
Snapshots, clones, and mirroring are not possible on subordinate volumes.
For more information
To learn more about cross-namespace volume access:
-
Visit Sharing volumes between namespaces: Say hello to cross-namespace volume access.
-
Watch the demo on NetAppTV.



