Forensics - All Activity
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


The All Activity page helps you understand the actions performed on entities in the Workload Security environment.
Examining All Activity Data
Click Forensics > Activity Forensics and click the All Activity tab to access the All Activity page.
This page provides an overview of activities on your tenant, highlighting the following information:
-
A graph showing Activity History (based on selected global time range)
You can zoom the graph by dragging out a rectangle in the graph. The entire page will be loaded to display the zoomed time range. When zoomed in, a button is displayed that lets the user zoom out.
-
A list of the All Activity data.
-
A group by dropdown will provide the option to group the activity by users, folders, entity type, etc.
-
A common path button will be available above the table on click of which we can get slide out panel with entity path details.
The All Activity table shows the following information. Note that not all of these columns are displayed by default. You can select columns to display by clicking on the "gear" icon.
-
The time an entity was accessed including the year, month, day, and time of the last access.
-
The user that accessed the entity with a link to the User information as a slide-out panel.
-
The activity the user performed. Supported types are:
-
Change Group Ownership - Group Ownership is of file or folder is changed. For more details about group ownership please see this link.
-
Change Owner - Ownership of file or folder is changed to another user.
-
Change Permission - File or folder permission is changed.
-
Create - Create file or folder.
-
Delete - Delete file or folder. If a folder is deleted, delete events are obtained for all the files in that folder and subfolders.
-
Read - File is read.
-
Read Metadata - Only on enabling folder monitoring option. Will be generated on opening a folder on Windows or Running "ls" inside a folder in Linux.
-
Rename - Rename file or folder.
-
Write - Data is written to a file.
-
Write Metadata - File metadata is written, for example, permission changed.
-
Other Change - Any other event which are not described above. All unmapped events are mapped to "Other Change" activity type. Applicable to files and folders.
-
-
The Path is entity path. This should be either exact entity path (e.g., "/home/userX/nested1/nested2/abc.txt") OR directory portion of path for recursive search (e.g., "/home/userX/nested1/nested2/"). NOTE: regex path patterns (e.g., *nested*) are NOT allowed here. Alternatively, individual path folder level filters as mentioned below can also be specified for path filtering.
-
The 1st Level Folder (Root) is the root directory of entity path in lower case.
-
The 2nd Level Folder is the second level directory of entity path in lower case.
-
The 3rd Level Folder is the third level directory of entity path in lower case.
-
The 4th Level Folder is the forth level directory of entity path in lower case.
-
The Entity Type, including entity (i.e. file) extension (.doc, .docx, .tmp, etc.).
-
The Device where the entities reside.
-
The Protocol used to fetch events.
-
The Original Path used for rename events when the original file was renamed. This column is not visible in the table by default. Use the column selector to add this column to the table.
-
The Volume where the entities reside. This column is not visible in the table by default. Use the column selector to add this column to the table.
-
The Entity Name is the last component of the entity path; For the Entity Type as file, it is the file name.
Selecting a table row opens a slide-out panel with the user profile in one tab, and the activity and entity overview in another tab.
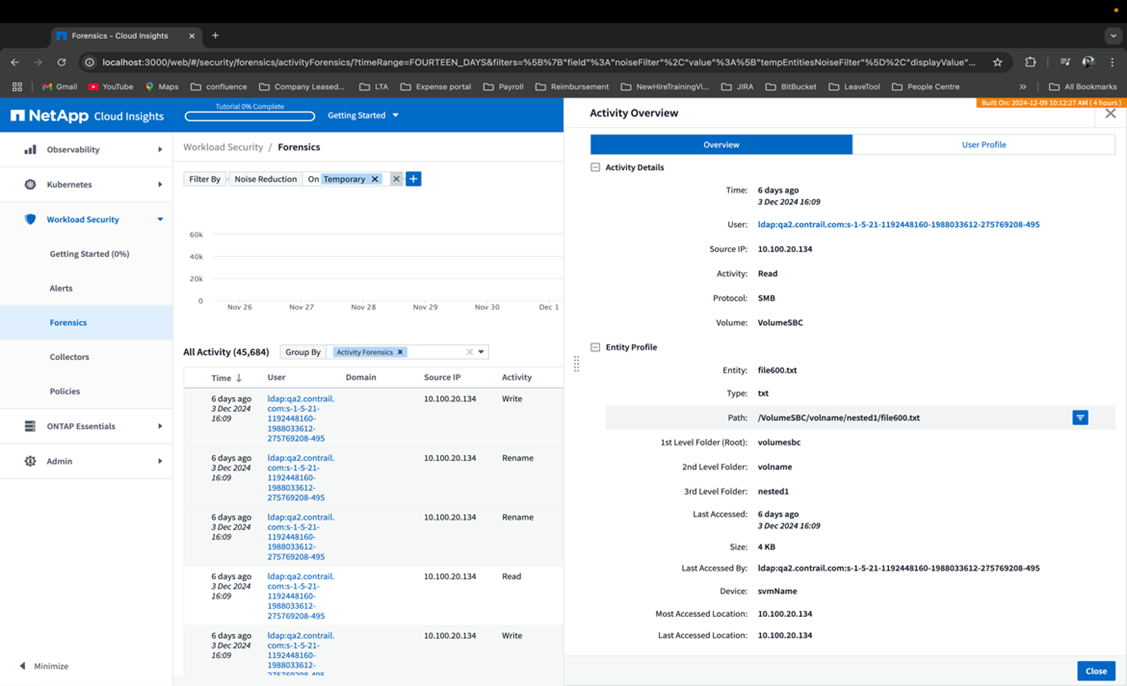
The default Group by method is Activity forensics. If you select a different Group By method—for example, Entity Type—the entity Group By table will be displayed. If no selection is made then Group By all is displayed.
-
Activity count is displayed as a hyperlink; selecting this will add the selected grouping as a filter. The table of activity will update based on that filter.
-
Note that if you change the filter, alter the time range, or refresh the screen, you will not be able to return to the filtered results without setting the filter again.
-
Please note that when Entity Name is selected as filter, the Group by dropdown will be disabled; Also, when the user is already on the Group By screen, the Entity Name as filter will be disabled.
Filtering Forensic Activity History Data
There are two methods you can use to filter data.
-
The Filter can be added from the slide-out panel. The value is added to the appropriate filters in the top Filter By list.
-
Filter data by typing in the Filter By field:
Select the appropriate filter from the top 'Filter By' widget by clicking the [+] button:
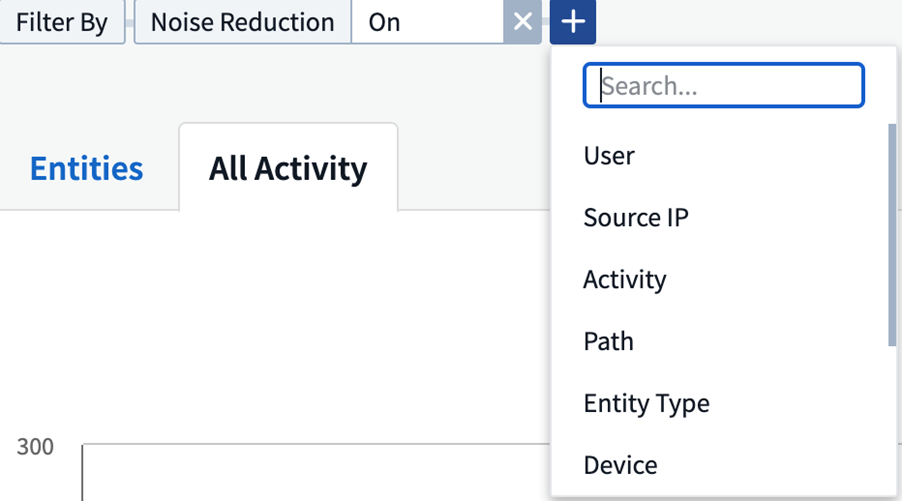
Enter the search text
Press Enter or click outside of the filter box to apply the filter.
You can filter Forensic Activity data by the following fields:
-
The Activity type.
-
Protocol to fetch protocol-specific activities.
-
Username of the user performing the activity. You need to provide the exact Username to filter. Search with partial username, or partial username prefixed or suffixed with '*' will not work.
-
Noise Reduction to filter files which are created in the last 2 hours by the user. It is also used to filter temporary files (for example, .tmp files) accessed by the user.
-
Domain of the user performing the activity. You need to provide the exact domain to filter. Searching for partial domain, or partial domain prefixed or suffixed with wildcard ('*'), will not work. None can be specified to search for missing domain.
The following fields are subject to special filtering rules:
-
Entity Type, using entity (file) extension - it is preferable to specify exact entity type within quotes. For example "txt".
-
Path of the entity - This should be either exact entity path(e.g., "/home/userX/nested1/nested2/abc.txt") OR directory portion of path for recursive search(e.g., "/home/userX/nested1/nested2/"). NOTE: regex path patterns (e.g., *nested*) are NOT allowed here. Directory Path filters (path string ending with /) up to 4 directories deep are recommended for faster results. For example, "/home/userX/nested1/nested2/". See the table below for more details.
-
1st Level Folder (Root) - root directory of entity Path as filters.
For example, if entity path is /home/userX/nested1/nested2/, then home OR "home" can be used. -
2nd Level Folder - 2nd level directory of entity Path filters.
For example, if entity path is /home/userX/nested1/nested2/, then userX OR "userX" can be used. -
3rd Level Folder – 3rd level directory of entity Path filters.
-
For example, if entity path is /home/userX/nested1/nested2/, then nested1 OR "nested1" can be used.
-
4th Level Folder - Directory 4th level directory of entity Path filters.
For example, if entity path is /home/userX/nested1/nested2/, then nested2 OR "nested2" can be used. -
User performing the activity - it is preferable to specify the exact user within quotes. For example, "Administrator".
-
Device (SVM) where entities reside
-
Volume where entities reside
-
The Original Path used for rename events when the original file was renamed.
-
Source IP from which the entity was accessed.
-
You can use wild-cards * and ?. For example:10.0.0., 10.0?.0.10, 10.10
-
If exact match is required then, you must provide a valid source IP address in double quotes, for example "10.1.1.1.". Incomplete IPs with double quotes such as "10.1.1.", "10.1..*", etc. will not work.
-
-
The Entity Name - the file name of the Entity Path as filters.
For example, if the entity path is /home/userX/nested1/testfile.txt then, entity name is testfile.txt.
Please note that it is recommended to specify the exact file name within quotes; Try to avoid the wildcard searches. For example, "testfile.txt".
Also, note that this entity name filter is recommended for shorter time ranges (up to 3 days).
The preceding fields are subject to the following when filtering:
-
Exact value should be within quotes: Example: "searchtext"
-
Wildcard strings must contain no quotes: Example: searchtext, *searchtext*, will filter for any strings containing 'searchtext'.
-
String with a prefix, Example: searchtext* , will search any strings which start with 'searchtext'.
Please note that all filter fields are case in-sensitive search. For example: if the applied filter is Entity Type with value as 'searchtext', it will return results with Entity Type as 'searchtext', 'SearchText', 'SEARCHTEXT'
Activity Forensics Filter Examples:
| User applied Filter expression | Expected Outcome | Performance assessment | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
Path = "/home/userX/nested1/nested2/" |
Recursive lookup of all files and folders under given directory |
Fast |
Directory searches up to 4 directories will be fast. |
Path = "/home/userX/nested1/" |
Recursive lookup of all files and folders under given directory |
Fast |
Directory searches up to 4 directories will be fast. |
Path = "/home/userX/nested1/test" |
Exact match where path value matches with /home/userX/nested1/test |
Slower |
Exact search will be slower to search on compared to Directory searches. |
Path = "/home/userX/nested1/nested2/nested3/" |
Recursive lookup of all files and folders under given directory |
Slower |
More than 4 directories searches are slower to search on. |
Any other Non path based filters. User and Entity Type filters recommended to be in quotes |
Fast |
||
Entity Name = "test.log" |
Exact match where file name is test.log |
Fast |
As it is exact match |
Entity Name = *test.log |
File names ending with test.log |
Slow |
Due to wild card, it can be slow. |
Entity Name = test*.log |
File names starting with test and ends with .log |
Slow |
Due to wild card, it can be slow. |
Entity Name = test.lo |
File names starting with test.lo |
Slower |
Due to wild card at the end, it can be slow. |
Entity Name = test |
File names starting with test |
Slowest |
Due to wild card at the end and more generic value used, it can be slowest. |
NOTE:
-
The Activity count displayed alongside the All Activity icon is rounded off to 30 mins when the selected time range spans more than 3 days. e.g., a time range of Sept 1st 10:15 am to Sept 7th 10:15 am will show Activity counts from Sept 1st 10:00 am to Sept 7th 10:30 am.
-
Likewise the count metrics shown in Activity History graph are rounded off to 30 mins when the selected time range spans more than 3 days.
Sorting Forensic Activity History Data
You can sort activity history data by Time, User, Source IP, Activity,, Entity Type, 1st Level Folder (Root), 2nd Level Folder, 3rd Level Folder and 4th Level Folder. By default, the table is sorted by descending Time order, meaning the latest data will be displayed first. Sorting is disabled for Device and Protocol fields.
User Guide for Asynchronous Exports
Overview
The Asynchronous Exports feature in Storage Workload Security is designed to handle large data exports.
Step-by-Step Guide: Exporting Data with Asynchronous Exports
-
Initiate Export: Select the desired time duration and filters for the export and click on the export button.
-
Wait for Export to Complete: The processing time can range from a few minutes to a few hours. You may need to refresh the forensics page a few times. Once the export job is complete, the "Download last export CSV file" button will be enabled.
-
Download: Click on the "Download last created export file" button to get the exported data in a .zip format. This data will be available for download until the user initiates another Asynchronous Export or 3 days have elapsed, whichever occurs first. The button will remain enabled until another Asynchronous Export is initiated.
-
Limitations:
-
The number of asynchronous downloads is currently limited to 1 per user for each Activities and Activities Analytics Table and 3 per tenant.
-
The exported data is limited to a maximum of 1 million records for Activities Table; while for Group By, the limit is half million records.
-
A sample script to extract forensic data via API is present at /opt/netapp/cloudsecure/agent/export-script/ on the agent. See the readme at this location for more details about the script.
Column Selection for All Activity
The All activity table shows select columns by default. To add, remove, or change the columns, click the gear icon on the right of the table and select from the list of available columns.
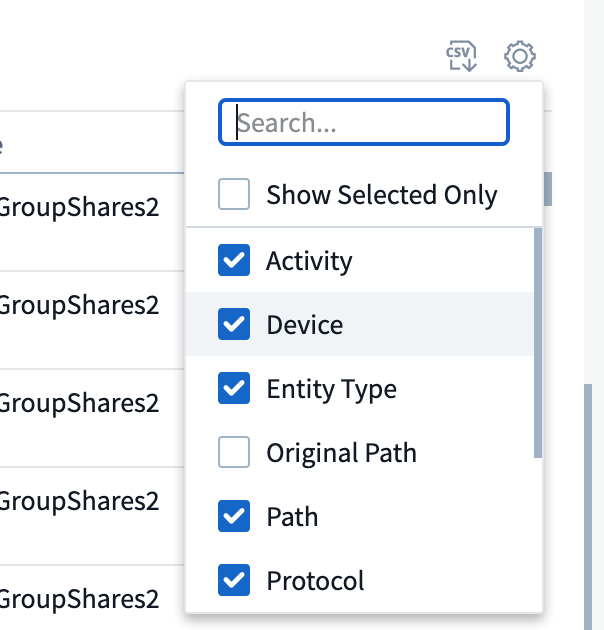
Activity History Retention
Activity history is retained for 13 months for active Workload Security environments.
Applicability of Filters in Forensics Page
| Filter | What it does | Example | Applicable for these Filters | Not applicable for these filters | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* (Asterisk) |
enables you to search for everything |
Auto*03172022 |
User, Entity Type, Device, Volume, Original Path, 1stLevel Folder, 2ndLevel Folder, 3rdLevel Folder, 4thLevel Folder, Entity Name, Source IP |
Returns all resources that start with "Auto" and end with "03172022" |
|
? (question mark) |
enables you to search for a specific number of characters |
AutoSabotageUser1_03172022? |
User, Entity Type, Device, Volume, 1stLevel Folder, 2ndLevel Folder, 3rdLevel Folder, 4thLevel Folder, Entity Name, Source IP |
returns AutoSabotageUser1_03172022A, AutoSabotageUser1_03172022B, AutoSabotageUser1_031720225, and so on |
|
OR |
enables you to specify multiple entities |
AutoSabotageUser1_03172022 OR AutoRansomUser4_03162022 |
User, Domain, Entity Type, Original Path, Entity Name, Source IP |
returns any of AutoSabotageUser1_03172022 OR AutoRansomUser4_03162022 |
|
NOT |
allows you to exclude text from the search results |
NOT AutoRansomUser4_03162022 |
User,Domain, Entity Type, Original Path, 1stLevel Folder, 2ndLevel Folder, 3rdLevel Folder, 4thLevel Folder, Entity Name, Source IP |
Device |
returns everything that does not start with"AutoRansomUser4_03162022" |
None |
searches for NULL values in all fields |
None |
Domain |
returns results where the target field is empty |
Path Search
Search results with and without / will be different
"/AutoDir1/AutoFile03242022" |
Only Exact search works; returns all activities with exact path as /AutoDir1/AutoFile03242022 (case insensitively) |
"/AutoDir1/ " |
Works; returns all activities with 1st level directory matching with AutoDir1 (case insensitively) |
"/AutoDir1/AutoFile03242022/" |
Works; returns all activities with 1st level directory matching with AutoDir1 and 2nd level directory matching with AutoFile03242022 (case insensitively) |
/AutoDir1/AutoFile03242022 OR /AutoDir1/AutoFile03242022 |
Doesn't work |
NOT /AutoDir1/AutoFile03242022 |
Doesn't work |
NOT /AutoDir1 |
Doesn't work |
NOT /AutoFile03242022 |
Doesn't work |
* |
Doesn't work |
Local root SVM user activity changes
If a local root SVM user is performing any activity, the IP of the client on which the NFS share is mounted is now considered in the username, which will be shown as root@<ip-address-of-the-client> in both forensic activity and user activity pages.
For example:
-
If SVM-1 is monitored by Workload Security, and the root user of that SVM mounts the share on a client with IP address 10.197.12.40, the username shown in forensic activity page will be root@10.197.12.40.
-
If the same SVM-1 is mounted into another client with IP address 10.197.12.41, the username shown in forensic activity page will be root@10.197.12.41.
*• This is done to segregate NFS root user activity by IP address. Previously, all the activity was considered to be done by root user only, with no IP distinction.
Troubleshooting
Problem |
Try This |
In the "All Activities" table, under the 'User' column, the user name is shown as: |
Possible reasons could be: |
Some NFS events are not seen in UI. |
Check the following: |
After typing some letters containing a wildcard character like asterisk (*) in the filters on the Forensics All Activity or Entities pages, the pages load very slowly. |
An asterisk (*) in the search string searches for everything. However, leading wildcard strings like *<searchTerm> or *<searchTerm>* will result in a slow query. |
I am encountering a "Request failed with status code 500/503" error when using a Path filter. |
Try using a smaller date range for filtering records. |
Forensic UI is loading data slowly when using the path filter. |
Directory Path filters (path string ending with /) up to 4 directories deep are recommended for faster results. e.g., If the directory path is /Aaa/Bbb/Ccc/Ddd, try searching for "/Aaa/Bbb/Ccc/Ddd/" to load data faster. |
Forensics UI is loading data slowly and facing failures when using the entity name filter. |
Please try with smaller time-ranges and with exact value search with double quotes. e.g., If the entityPath is "/home/userX/nested1/nested2/nested3/testfile.txt" then, try with "testfile.txt" as entity name filter. |


