Learn about NetApp Disaster Recovery for VMware
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


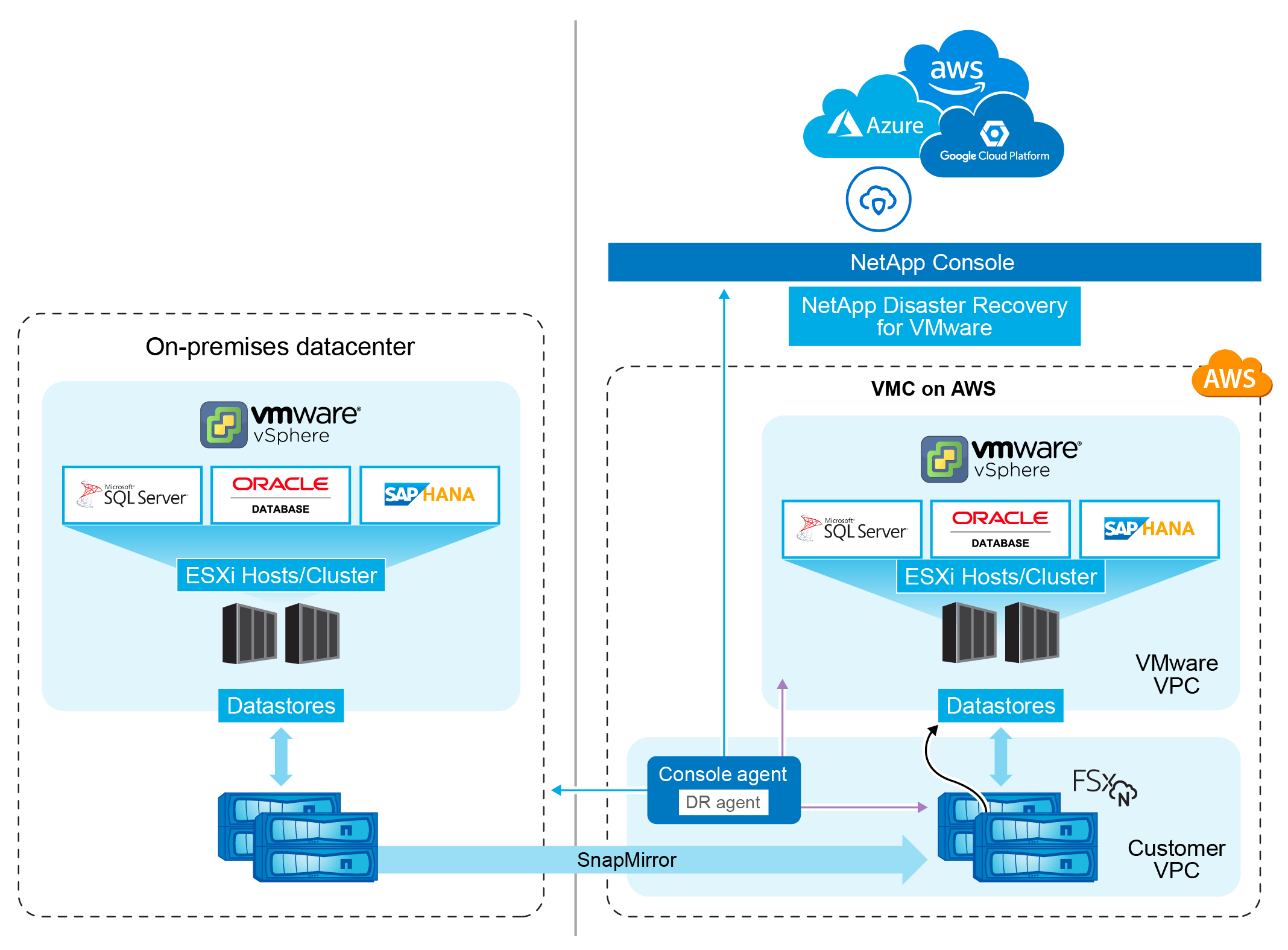
Disaster recovery to the cloud is a resilient and cost-effective way of protecting workloads against site outages and data corruption events. With NetApp Disaster Recovery for VMware, you can replicate your on-premises VMware VM or datastore workloads running ONTAP storage to a VMware software-defined data center in a public cloud using NetApp cloud storage or to another on-premises VMware environment with ONTAP storage as a disaster recovery site. You can use Disaster Recovery also to migrate VM workloads from one site to another.
NetApp Disaster Recovery is a cloud-based disaster recovery service that automates disaster recovery workflows. With NetApp Disaster Recovery, you can protect your on-premises, NFS-based workloads and VMware vSphere virtual machine file system (VMFS) datastores for iSCSI and FC running NetApp storage to one of the following:
-
Amazon Elastic VMware Service (EVS) with Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP For details, refer to Introduction of NetApp Disaster Recovery using Amazon Elastic VMware Service and Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP.
-
VMware Cloud (VMC) on AWS with Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP
-
Azure VMware Solution (AVS) with NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP (iSCSI) (Private preview)
-
Google Cloud VMware Engine (GCVE) with Google Cloud NetApp Volumes
-
Another on-premises NFS and or VMFS-based (iSCSI/FC) VMware environment with ONTAP storage
NetApp Disaster Recovery uses ONTAP SnapMirror technology with integrated native VMware orchestration to protect VMware VMs and their associated on-disk OS images, while retaining all storage efficiency benefits of ONTAP. Disaster Recovery uses these technologies as the replication transport to the disaster recovery site. This enables industry-best storage efficiency (compression and deduplication) on primary and secondary sites.
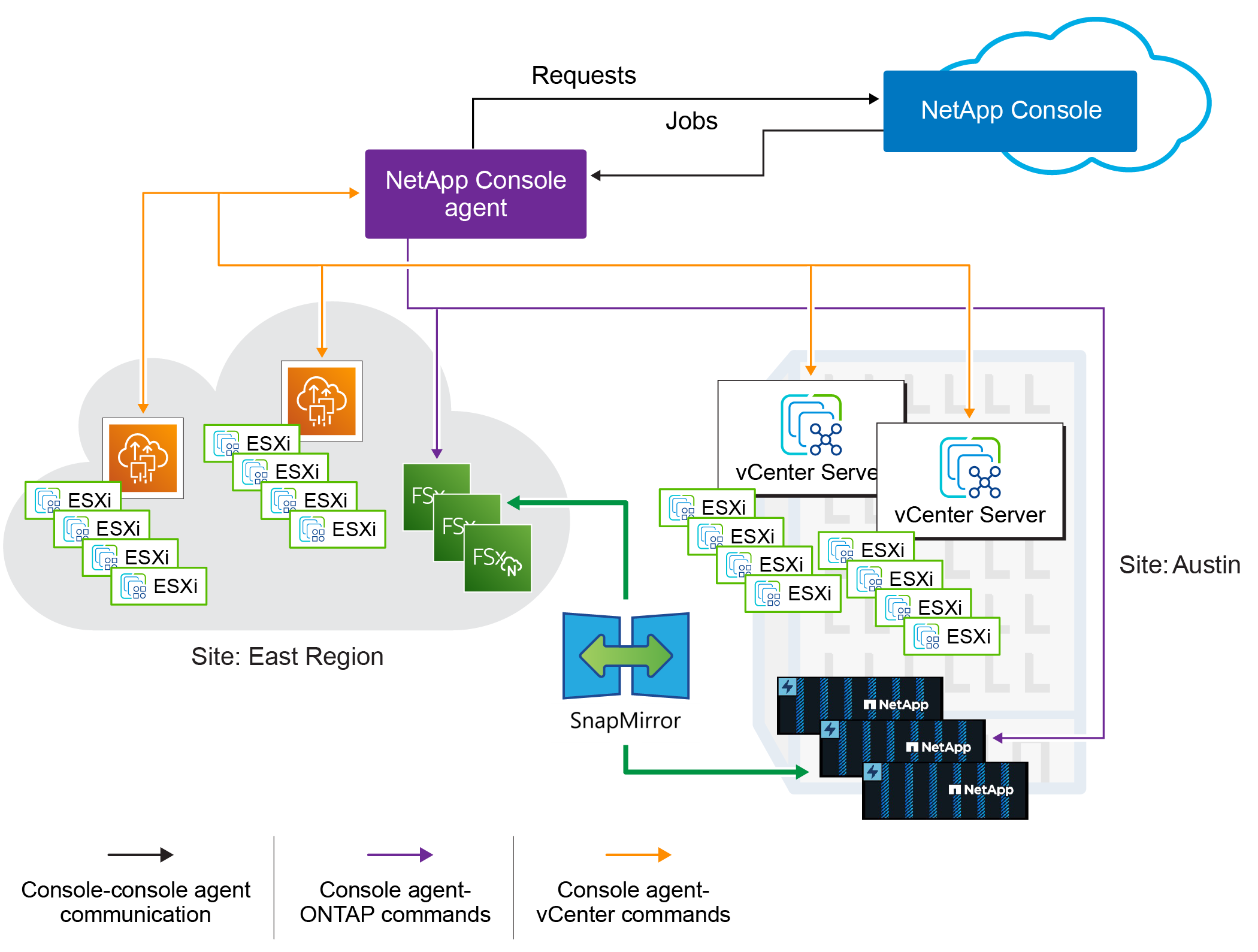
NetApp Console
NetApp Disaster Recovery is accessible through the NetApp Console.
The NetApp Console provides centralized management of NetApp storage and data services across on-premises and cloud environments at enterprise grade. The Console is required to access and use NetApp data services. As a management interface, it enables you to manage many storage resources from one interface. Console administrators can control access to storage and services for all systems within the enterprise.
You don’t need a license or subscription to start using NetApp Console and you only incur charges when you need to deploy Console agents in your cloud to ensure connectivity to your storage systems or NetApp data services. However, some NetApp data services accessible from the Console are licensed or subscription-based.
Learn more about the NetApp Console.
Benefits of using NetApp Disaster Recovery for VMware
NetApp Disaster Recovery offers the following benefits:
-
Simplified user experience for vCenter discovery and recovery of applications with multiple point-in-time recovery operations.
-
Lower total cost of ownership with reduced cost of operations and ability to create and adjust disaster recovery plans with minimal resources.
-
Continuous disaster recovery readiness with virtual failover testing that does not disrupt operations. You can regularly test your DR failover plans without impacting production workloads.
-
Faster time to value with dynamic changes in your IT environment and ability to address it in your disaster recovery plans.
-
Ability to manage both the storage and virtual layers through backend orchestration of both ONTAP and VMware at the same time without the need for virtual server appliances (VSAs) that need to be deployed and maintained.
-
DR solutions for VMware can be resource intensive. Many DR solutions replicate VMs at the VMware virtual layer using VSAs, which can consume more compute resources and lose the valuable storage efficiencies of ONTAP. Because Disaster Recovery uses ONTAP SnapMirror technology, it can replicate data from production datastores to the DR site using our incremental-forever replication model with all the native data compression and deduplication efficiencies of ONTAP.
What you can do with NetApp Disaster Recovery for VMware
NetApp Disaster Recovery provides you with full use of several NetApp technologies to accomplish the following goals:
-
Replicate VMware apps on your on-premises production site to a disaster recovery remote site in the cloud or on-premises using SnapMirror replication.
-
Migrate VMware workloads from your original site to another site.
-
Conduct a failover test. When you do this, the service creates temporary virtual machines. Disaster Recovery makes a new FlexClone volume from the selected snapshot, and a temporary datastore, which is backed by the FlexClone volume, is mapped to the ESXi hosts. This process doesn’t consume additional physical capacity on on-premises ONTAP storage or FSx for NetApp ONTAP storage in AWS. The original source volume is not modified and replica jobs can continue even during disaster recovery.
-
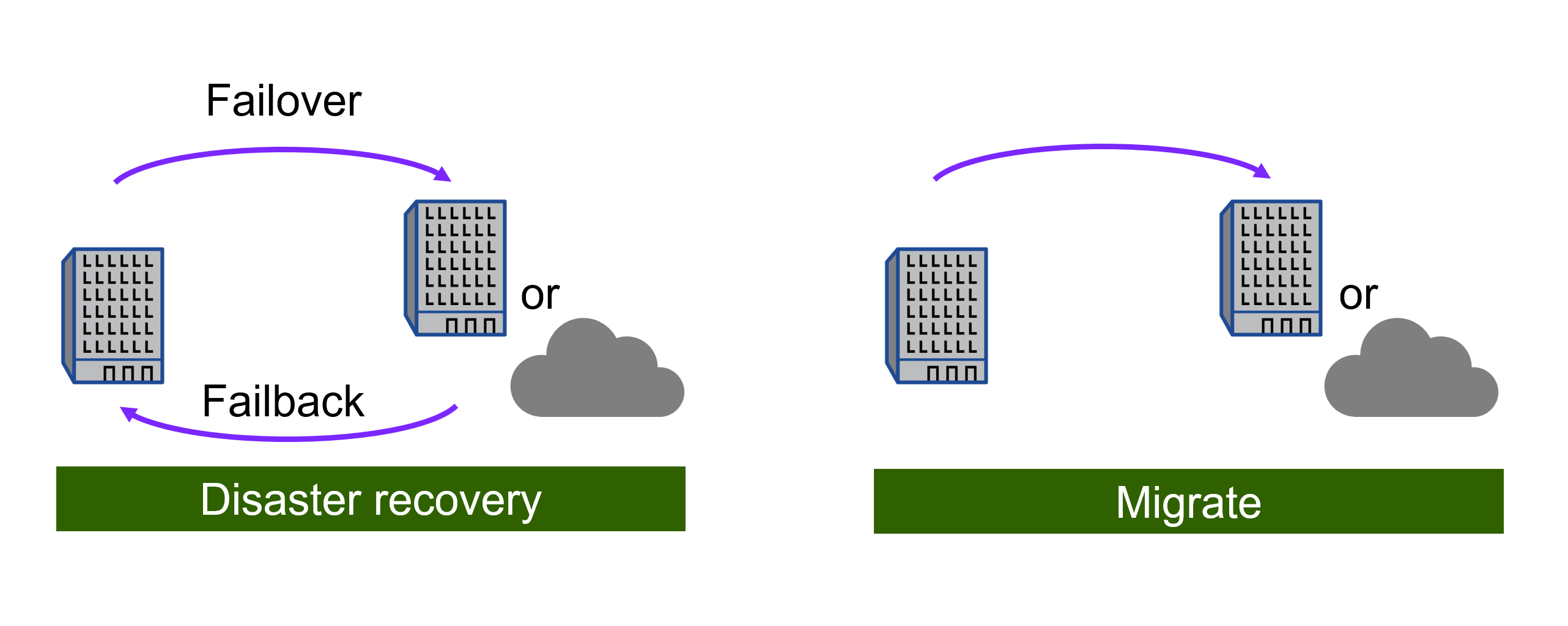
In case of disaster, fail over your primary site on demand to the disaster recovery site, which can be VMware Cloud on AWS with Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP or an on-premises VMware environment with ONTAP.
-
After the disaster has been resolved, fail back on demand from the disaster recovery site to the primary site.
-
Group VMs or datastores into logical resource groups for efficient management.

|
Configuration of the vSphere server is done outside of NetApp Disaster Recovery in vSphere Server. |
Cost
NetApp doesn't charge you for using the trial version of NetApp Disaster Recovery.
NetApp Disaster Recovery can be used either with a NetApp license or an annual subscription-based plan through Amazon Web Services.

|
Some releases include a technology preview. NetApp doesn't charge you for any previewed workload capacity. See What's new in NetApp Disaster Recovery for information about the latest technology previews. |
Licensing
You can use the following license types:
-
Sign up for a 30-day free trial.
-
Purchase a pay-as-you-go (PAYGO) subscription with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Marketplace or Microsoft Azure Marketplace. This license enables you to purchase a fixed protected capacity license without any long-term commitment.
-
Bring your own license (BYOL), which is a NetApp License File (NLF) that you obtain from your NetApp Sales Rep. You can use the license serial number to get the BYOL activated in the NetApp Console.
Licenses for all NetApp data services are managed through subscriptions in the NetApp Console. After you set up your BYOL, you can see an active license for the service in the Console.
The service is licensed based on the amount of data hosted on protected ONTAP volumes. The service determines which volumes should be considered for licensing purposes by mapping protected VMs to their vCenter datastores. Each datastore is hosted on an ONTAP volume or LUN. The used capacity reported by ONTAP for that volume or LUN is used for licensing determinations.
Protected volumes can host many VMs. Some might not be part of a NetApp Disaster Recovery resource group. Regardless, the storage consumed by all VMs on that volume or LUN is used against the license maximum capacity.

|
NetApp Disaster Recovery charges are based on used capacity of datastores on the source site when there is at least one VM that has a replication plan. Capacity for a failed over datastore is not included in the capacity allowance. For a BYOL, if the data exceeds the allowed capacity, operations in the service are limited until you obtain an additional capacity license or upgrade the license in the NetApp Console. |
For details about setting up licensing for NetApp Disaster Recovery, refer to Set up NetApp Disaster Recovery licensing.
30-day free trial
You can try out NetApp Disaster Recovery by using a 30-day free trial.
To continue after the 30-day trial, you'll need to obtain a Pay-as-you-go (PAYGO) subscription from your cloud provider or purchase a BYOL license from NetApp.
You can purchase a license at any time and you will not be charged until the 30-day trial ends.
How NetApp Disaster Recovery works
NetApp Disaster Recovery is a service hosted within the NetApp Console software as a service (SaaS) environment. Disaster Recovery can recover workloads replicated from an on-premises site to Amazon FSx for ONTAP or to another on-premises site. This service automates the recovery from the SnapMirror level, through virtual machine registration to VMware Cloud on AWS, and to network mappings directly on the VMware network virtualization and security platform, NSX-T. This feature is included with all Virtual Machine Cloud environments.
NetApp Disaster Recovery uses ONTAP SnapMirror technology, which provides highly efficient replication and preserves the ONTAP incremental-forever snapshot efficiencies. SnapMirror replication ensures that application-consistent snapshot copies are always in sync and the data is usable immediately after a failover.
When there is a disaster, this service helps you recover virtual machines in the other on-premises VMware environment or VMC by breaking the SnapMirror relationships and making the destination site active.
-
The service also lets you fail back virtual machines to the original source location.
-
You can test the disaster recovery failover process without disrupting the original virtual machines. The test recovers virtual machines to an isolated network by creating a FlexClone of the volume.
-
For the failover or test failover process, you can choose the latest (default) or selected snapshot from which to recover your virtual machine.
Components of Disaster Recovery
Disaster Recovery uses the following components to provide disaster recovery for VMware workloads:
-
NetApp Console: The user interface for managing your disaster recovery plans. You can use the NetApp Console to create and manage replication plans, resource groups, and failover operations across your on-premises and cloud environments.
-
Console agent: A lightweight software component that runs in your cloud-hosted network or your on-premises VMware environment. It communicates with the NetApp Console and manages the replication of data between your on-premises environment and the disaster recovery site. The Console agent is installed on a virtual machine in your VMware environment.
-
ONTAP storage clusters: The ONTAP storage clusters are the primary storage systems that host your VMware workloads. The ONTAP storage clusters provide the underlying storage infrastructure for your disaster recovery plans. Disaster Recovery uses ONTAP storage APIs to manage ONTAP storage clusters such as on-premises arrays, and cloud-based solutions, such as Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP.
-
vCenter servers: The VMware vCenter is the management server for your VMware environment. It manages the ESXi hosts and their associated datastores. The Console agent communicates with the VMware vCenter to manage the replication of data between your on-premises environment and the disaster recovery site. This includes registering ONTAP LUNs and volumes as datastores, reconfiguring VMs, and starting and stopping VMs.
The Disaster Recovery protection workflow
When a replication plan is assigned to a resource group, Disaster Recovery performs a discovery check of all the components in the resource group and plan to ensure that the plan can be activated.
If this check is successful, Disaster Recovery performs the following initialization steps:
-
For each VM in the target resource group, identify the hosting VMware datastore.
-
For each VMware datastore found, identify the hosting ONTAP FlexVol volume or LUN.
-
For each ONTAP volume and LUN found, determine if there is an existing SnapMirror relationship between the source volumes and a destination volume in the destination site.
-
If there is no pre-existing SnapMirror relationship, create any new destination volumes and create a new SnapMirror relationship between each unprotected source volume.
-
If there is a pre-existing SnapMirror relationship, use that relationship to perform all replication operations.
-
After Disaster Recovery creates and initializes all relationships, at each scheduled backup, the service perform the following data protection steps:
-
For each VM flagged as “application consistent,” use VMtools to place the supported application into a backup state.
-
Create a new snapshot of all ONTAP volumes hosting protected VMware datastores.
-
Perform a SnapMirror update operation to replicate those snapshots to the destination ONTAP cluster.
-
Determine if the number of retained snapshots has exceeded the maximum snapshot retention defined in the replication plan and delete any extraneous snapshots from both the source and destination volumes.
Supported protection targets and datastore types
Datastore types supported
NetApp Disaster Recovery supports the following datastore types:
-
NFS datastores hosted on ONTAP FlexVol volumes residing on ONTAP clusters.
-
VMware vSphere virtual machine file system (VMFS) datastores using the iSCSI or FC protocol
Protection targets supported
-
VMware Cloud (VMC) on AWS with Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP
-
Another on-premises, NFS-based VMware environment with ONTAP storage or an on-premises FC/iSCSI VMSF
-
Amazon Elastic VMware Service
-
Azure VMware Solution (AVS) with NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP (iSCSI) (Private preview)
-
Google Cloud VMware Engine (GCVE) with Google Cloud NetApp Volumes
Terms that might help you with NetApp Disaster Recovery
You might benefit by understanding some terminology related to disaster recovery.
-
Datastore: A VMware vCenter data container, which uses a file system to hold VMDK files. Typical datastore types are NFS, VMFS, vSAN or vVol. Disaster Recovery supports NFS and VMFS datastores. Each VMware datastore is hosted on a single ONTAP volume or LUN. Disaster Recovery supports NFS and VMFS datastores hosted on FlexVol volumes residing on ONTAP clusters.
-
Replication plan: A set of rules about how often backups occur and how to handle failover events. Plans are assigned to one or more resource groups.
-
Recovery point objective (RPO): The maximum amount of data loss that is acceptable in the event of a disaster. RPO is defined in the replication plan's frequency of data replication or replication schedule.
-
Recovery time objective (RTO): The maximum amount of time that is acceptable to recover from a disaster. RTO is defined in the replication plan and is the time it takes to fail over to the DR site and restart all VMs.
-
Resource group: A logical container that enables you to manage multiple VMs as a single unit. A VM can be in only one resource group at a time. You can create a resource group for each application or workload that you want to protect.
-
Site: A logical container typically associated with a physical datacenter or cloud location hosting one or more vCenter clusters and ONTAP storage.


