Overview of snapshot storage
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


A snapshot image is a logical, read-only copy of volume content, captured at a particular point in time. You can use snapshots to protect against data loss.
Snapshot images also are useful for test environments. By creating a virtual copy of data, you can test data using the snapshot without altering the actual volume itself. In addition, hosts do not have write access to snapshot images, so your snapshots are always a secure backup resource.
The Snapshots feature uses copy-on-write technology to store snapshot images and use allocated reserved capacity. As snapshots are created, the Snapshots feature stores image data as follows:
-
When a snapshot image is created, it exactly matches the base volume. The Snapshots feature uses copy-on-write technology. After the snapshot is taken, the first write to any block or set of blocks on the base volume causes the original data to be copied to the reserved capacity before writing the new data to the base volume.
-
Subsequent snapshots include only changed data blocks. Before data is overwritten on the base volume, the Snapshots feature uses its copy-on-write technology to save the required images of the affected sectors to the snapshot reserved capacity.
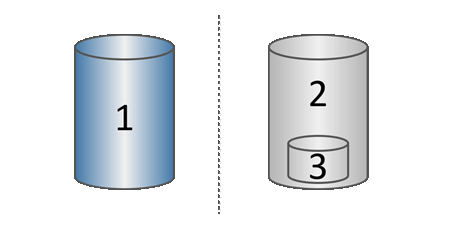
1 Base volume (physical disk capacity); 2 Snapshots (logical disk capacity); 3 Reserved capacity (physical disk capacity)
-
The reserved capacity stores original data blocks for portions of the base volume that have changed after the snapshot was taken and includes an index for tracking changes. Generally, the size of the reserved capacity defaults to 40 percent of the base volume. (If you need more reserved capacity, you can increase reserved capacity.)
-
Snapshot images are stored in a specific order, based on their timestamp. Only the oldest snapshot image of a base volume is available for manual deletion.
To restore data to a base volume, you can use either a snapshot volume or snapshot image:
-
Snapshot volume — If you need to retrieve deleted files, create a snapshot volume from a known good snapshot image, and then assign it to the host.
-
Snapshot image — If you need to restore a base volume to a specific point-in-time, use a previous snapshot image to roll back data to the base volume.

