Solution validation - Virtualization
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


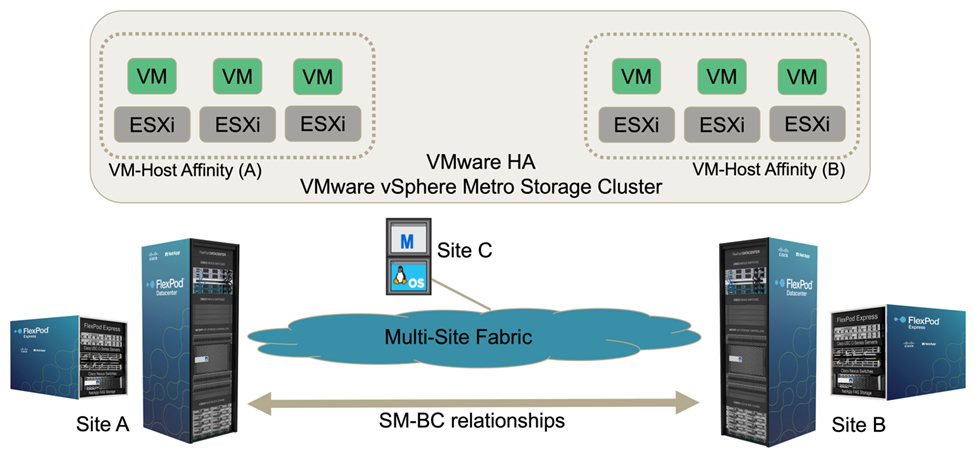
In the multi-site FlexPod SM-BC solution, a single VMware vCenter manages the virtual infrastructure resources for the entire solution. The hosts in both data centers participate in the single VMware HA cluster which spans both data centers. The hosts have access to the NetApp SM-BC solution where storage with defined SM-BC relationships can be accessed from both sites.
Th SM-BC solution storage conforms to the uniform access model in the VMware vSphere Metro Storage Cluster (vMSC) feature to avoid disaster and downtime. For optimal virtual-machine performance, the virtual-machine disks should be hosted on the local NetApp AFF A250 systems to minimize latency and traffic across the WAN links under normal operation.
As part of the design implementation, the distribution of the virtual machines across the two sites must be determined. You can determine this virtual machine site affinity and application distribution across the two sites according to your site preferences and application requirements. The VMware cluster VM/Host Groups and VM/Host Rules are used to configure VM/Host affinity to make sure that VMs are running on hosts at the desired site.
However, configurations allowing the VMs to run at both sites will make sure that VMs can be restarted by VMware HA at remote-site hosts to provide solution resiliency. To accommodate virtual machines to run at both sites, all the iSCSI shared datastores must be mounted on all the ESXi hosts to ensure a smooth vMotion operation of virtual machines between sites.
The following figure shows a high-level FlexPod SM-BC solution virtualization view which includes both VMware HA and vMSC features to provide high availability for compute and storage services. The active-active datacenter solution architecture enables workload mobility between sites and provides DR/BC protection.
End-to-end network connectivity
The FlexPod SM-BC solution includes FlexPod infrastructures at each site, network connectivity between sites, and the ONTAP mediator deployed at a third site to meet the required RPO and RTO objectives. The following figure shows the end-to-end network connectivity between the Cisco UCS B200M5 servers at each site and the NetApp storage featuring SM-BC capabilities within a site and across sites.
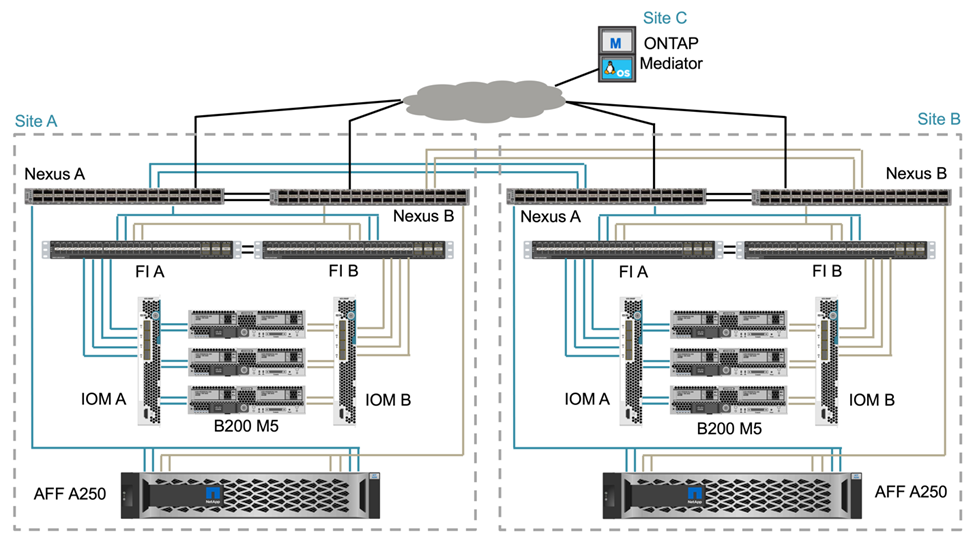
The FlexPod deployment architecture is identical at each site for this solution validation. However, the solution supports asymmetric deployments and can also be added onto an existing FlexPod solutions if they meet the requirements.
Extended layer-2 architecture is used for a seamless multi-site data fabric that provides connectivity between port-channeled Cisco UCS compute and NetApp storage in each data center, as well as connectivity between data centers. Port channel configuration, and virtual port channel configuration where appropriate, is used for bandwidth aggregation and fault tolerance between the compute, network, and storage layers as well as for the cross-site links. As a result, The UCS blade servers have connectivity and multipath access to both local and remote NetApp storage.
Virtual networking
Each host in the cluster is deployed using identical virtual networking regardless of its location. The design separates the different traffic types using VMware virtual switches (vSwitch) and VMware Virtual Distributed Switches (vDS). The VMware vSwitch is used primarily for the FlexPod infrastructure networks and vDS for application networks, but it is not required.
The virtual switches (vSwitch, vDS) are deployed with two uplinks per virtual switch; the uplinks at the ESXi hypervisor level are referred to as vmnics and virtual NICs (vNICs) on Cisco UCS Software. The vNICs are created on the Cisco UCS VIC adapter in each server using Cisco UCS service profiles. Six vNICs are defined, two for vSwitch0, two for vDS0, two for vSwitch1, and two for the iSCSI uplinks as shown in the following figure.
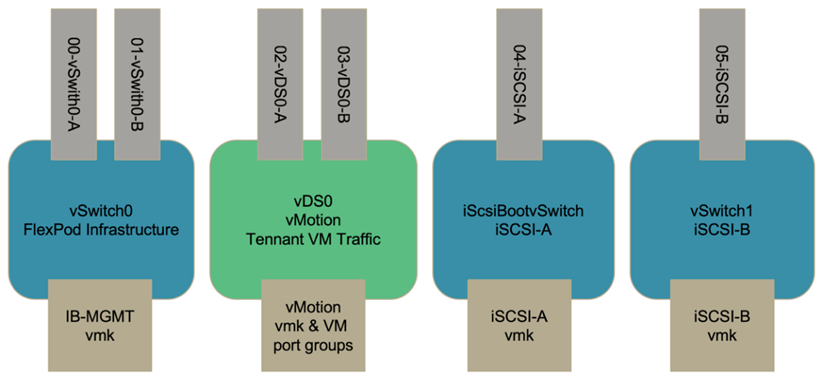
vSwitch0 is defined during VMware ESXi host configuration, and it contains the FlexPod infrastructure management VLAN and the ESXi host VMkernel (VMK) ports for management. An infrastructure management virtual machine port group is also placed on vSwitch0 for any critical infrastructure management virtual machines that are needed.
It is important to place such management infrastructure virtual machines on vSwitch0 instead of the vDS because if the FlexPod infrastructure is shut down or power cycled and you attempt to activate that management virtual machine on a host other than the host on which it was originally running, it boots up fine on the network on vSwitch0. This process is particularly important if VMware vCenter is the management virtual machine. If vCenter were on the vDS and moved to another host and then booted, it would not be connected to the network after booting up.
Two iSCSI boot vSwitches are used in this design. Cisco UCS iSCSI boot requires separate vNICs for iSCSI boot. These vNICs use iSCSI VLAN of the appropriate fabric as the native VLAN and are attached to the appropriate iSCSI boot vSwitch. Optionally, you could also deploy iSCSI networks on vDS by deploying a new vDS or using an existing one.
VM-Host affinity groups and rules
To enable virtual machines to run on any ESXi host at both SM-BC sites, all ESXi hosts must mount the iSCSI datastores from both sites. If the datastores from both sites are properly mounted by all ESXi hosts, you can migrate a virtual machine between any hosts with vMotion and the VM still maintains access to all its virtual disks created from those datastores.
For a virtual machine that uses local datastores, its access to virtual disks becomes remote if it is migrated to a host at the remote site and thus increasing read operation latency due to the physical distance between the sites. Therefore, it is a best practice to keep virtual machines on the local hosts and utilize local storage at the site.
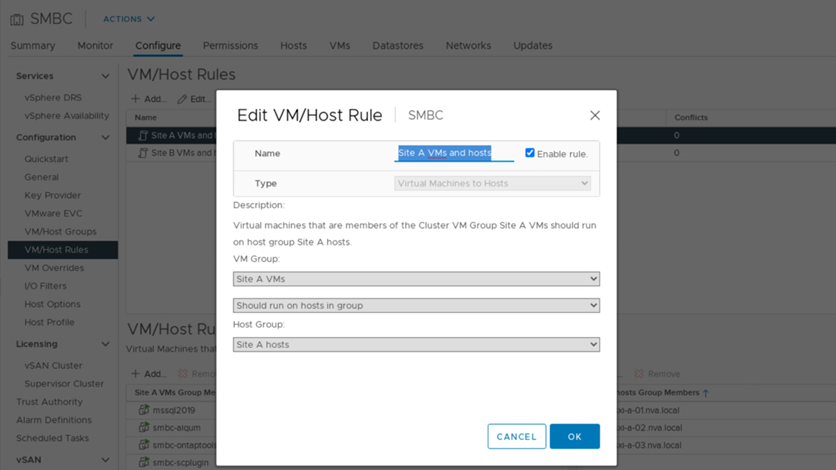
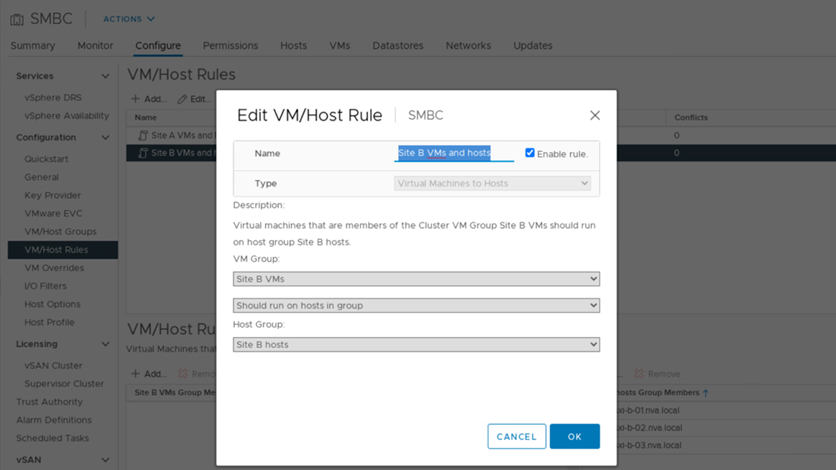
By using a VM/host affinity mechanism, you can use VM/Host Groups to create a VM group and a host group for virtual machines and hosts located at a particular site. Using VM/Host Rules, you can specify the policy for the VMs and hosts to follow. To allow virtual-machine migration across sites during a site maintenance or disaster scenario, use the “Should run on hosts in group” policy specification for that flexibility.
The following screenshot shows that two host groups and two VM groups are created for site A and site B hosts and VMs
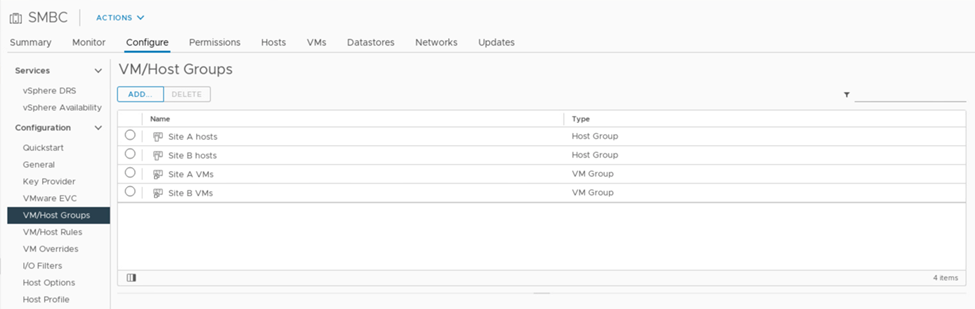
In addition, the following two figures show the VM/Host rules that are created for site A and site B VMs to run on the hosts in their respective sites using the “Should run on hosts in group” policy.
vSphere HA heartbeat
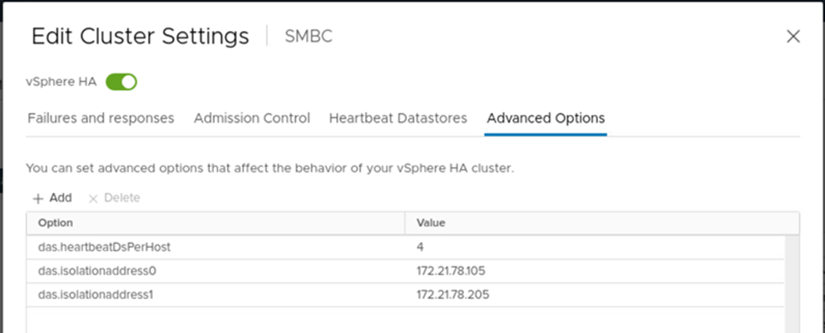
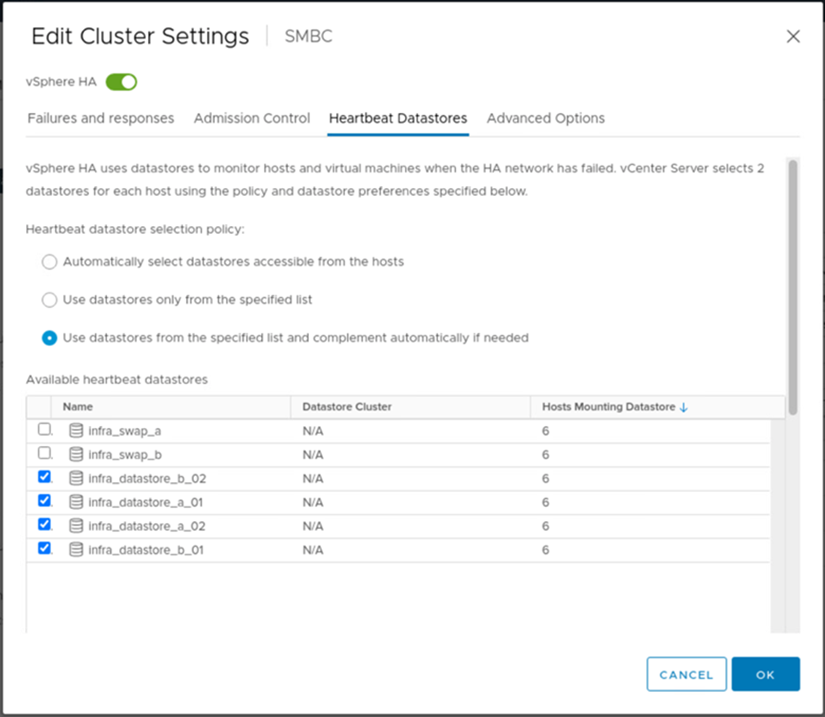
VMware vSphere HA has a heartbeat mechanism for host state validation. The primary heartbeat mechanism is through networking, and the secondary heartbeat mechanism is through the datastore. If heartbeats are not received, it then decides if it is isolated from the network by pinging the default gateway or the manually configured isolation addresses. For the datastore heartbeat, VMware recommends increasing the heartbeat datastores from the minimum of two to four for a stretched cluster.
For the solution validation, the two ONTAP cluster management IP addresses are used as the isolation address. In addition, the recommended vSphere HA advanced option ds.heartbeatDsPerHost with a value of 4 was added as shown in the following figure.
For the heartbeat datastore, specify the four shared datastores from the cluster and complement automatically, as shown in the following figure.
For additional best practices and configurations for VMware HA Cluster and VMware vSphere Metro storage cluster, see Creating and Using vSphere HA Clusters, VMware vSphere Metro Storage Cluster (vMSC) and the VMWare KB for NetApp ONTAP with NetApp SnapMirror Business Continuity (SM-BC) and VMware vSphere Metro Storage Cluster (vMSC).


