Design Considerations
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


Network Design
The switches used to handle the NetApp HCI traffic require a specific configuration for successful deployment.
Consult the NetApp HCI Network Setup Guide for the physical cabling and switch details. This solution uses a two-cable design for compute nodes. Optionally, compute nodes can be configured in a six-node cable design affording options for deployment of compute nodes.
The diagram under Architecture depicts the network topology of this NetApp HCI solution with a two-cable design for the compute nodes.
Compute Design
The NetApp HCI compute nodes are available in two form factors, half-width and full-width, and in two rack unit sizes, 1 RU and 2 RU. The 410c nodes used in this solution are half-width and 1 RU and are housed in a chassis that can hold a maximum of four such nodes. The other compute node that is used in this solution is the H615c, which is a full-width node, 1 RU in size. The H410c nodes are based on Intel Skylake processors, and the H615c nodes are based on the second-generation Intel Cascade Lake processors. NVIDIA GPUs can be added to the H615c nodes, and each node can host a maximum of three NVIDIA Tesla T4 16GB GPUs.
The H615c nodes are the latest series of compute nodes for NetApp HCI and the second series that can support GPUs. The first model to support GPUs is the H610c node (full width, 2RU), which can support two NVIDIA Tesla M10 GPUs.
In this solution, H615c nodes are preferred over H610c nodes because of the following advantages:
-
Reduced data center footprint, critical for edge deployments
-
Support for a newer generation of GPUs designed for faster inferencing
-
Reduced power consumption
-
Reduced heat dissipation
NVIDIA T4 GPUs
The resource requirements of inferencing are nowhere close to those of training workloads. In fact, most modern hand-held devices are capable of handling small amounts of inferencing without powerful resources like GPUs. However, for mission-critical applications and data centers that are dealing with a wide variety of applications that demand very low inferencing latencies while subject to extreme parallelization and massive input batch sizes, the GPUs play a key role in reducing inference time and help to boost application performance.
The NVIDIA Tesla T4 is an x16 PCIe Gen3 single-slot low-profile GPU based on the Turing architecture. The T4 GPUs deliver universal inference acceleration that spans applications such as image classification and tagging, video analytics, natural language processing, automatic speech recognition, and intelligent search. The breadth of the Tesla T4’s inferencing capabilities enables it to be used in enterprise solutions and edge devices.
These GPUs are ideal for deployment in edge infrastructures due to their low power consumption and small PCIe form factor. The size of the T4 GPUs enables the installation of two T4 GPUs in the same space as a double-slot full-sized GPU. Although they are small, with 16GB memory, the T4s can support large ML models or run inference on multiple smaller models simultaneously.
The Turing- based T4 GPUs include an enhanced version of Tensor Cores and support a full range of precisions for inferencing FP32, FP16, INT8, and INT4. The GPU includes 2,560 CUDA cores and 320 Tensor Cores, delivering up to 130 tera operations per second (TOPS) of INT8 and up to 260 TOPS of INT4 inferencing performance. When compared to CPU-based inferencing, the Tesla T4, powered by the new Turing Tensor Cores, delivers up to 40 times higher inference performance.
The Turing Tensor Cores accelerate the matrix-matrix multiplication at the heart of neural network training and inferencing functions. They particularly excel at inference computations in which useful and relevant information can be inferred and delivered by a trained deep neural network based on a given input.
The Turing GPU architecture inherits the enhanced Multi-Process Service (MPS) feature that was introduced in the Volta architecture. Compared to Pascal-based Tesla GPUs, MPS on Tesla T4 improves inference performance for small batch sizes, reduces launch latency, improves QoS, and enables the servicing of higher numbers of concurrent client requests.
The NVIDIA T4 GPU is a part of the NVIDIA AI Inference Platform that supports all AI frameworks and provides comprehensive tooling and integrations to drastically simplify the development and deployment of advanced AI.
Storage Design: Element Software
NetApp Element software powers the storage of the NetApp HCI systems. It delivers agile automation through scale-out flexibility and guaranteed application performance to accelerate new services.
Storage nodes can be added to the system non-disruptively in increments of one, and the storage resources are made available to the applications instantly. Every new node added to the system delivers a precise amount of additional performance and capacity to a usable pool. The data is automatically load balanced in the background across all nodes in the cluster, maintaining even utilization as the system grows.
Element software supports the NetApp HCI system to comfortably host multiple workloads by guaranteeing QoS to each workload. By providing fine-grained performance control with minimum, maximum, and burst settings for each workload, the software allows well-planned consolidations while protecting application performance. It decouples performance from capacity and allows each volume to be allocated with a specific amount of capacity and performance. These specifications can be modified dynamically without any interruption to data access.
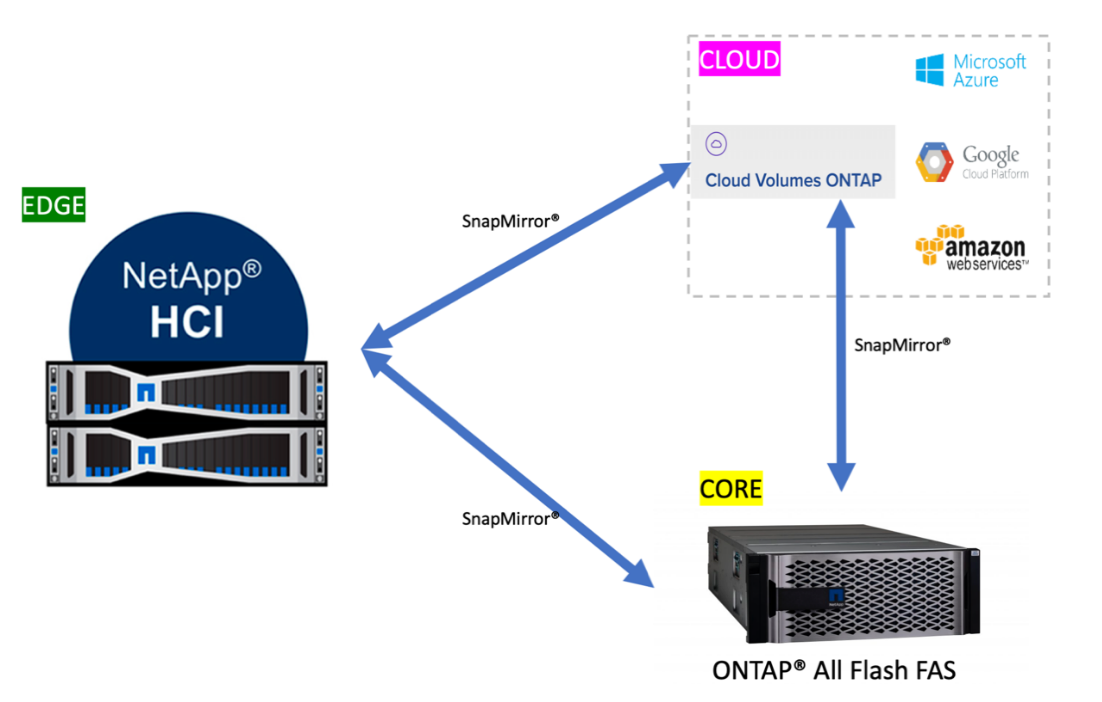
As illustrated in the following figure, Element software integrates with NetApp ONTAP to enable data mobility between NetApp storage systems that are running different storage operating systems. Data can be moved from the Element software to ONTAP or vice versa by using NetApp SnapMirror technology. Element uses the same technology to provide cloud connectivity by integrating with NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP, which enables data mobility from the edge to the core and to multiple public cloud service providers.
In this solution, the Element-backed storage provides the storage services that are required to run the workloads and applications on the NetApp HCI system.
Storage Design: ONTAP Select
NetApp ONTAP Select introduces a software-defined data storage service model on top of NetApp HCI. It builds on NetApp HCI capabilities, adding a rich set of file and data services to the HCI platform while extending the data fabric.
Although ONTAP Select is an optional component for implementing this solution, it does provide a host of benefits, including data gathering, protection, mobility, and so on, that are extremely useful in the context of the overall AI data lifecycle. It helps to simplify several day-to-day challenges for data handling, including ingestion, collection, training, deployment, and tiering.
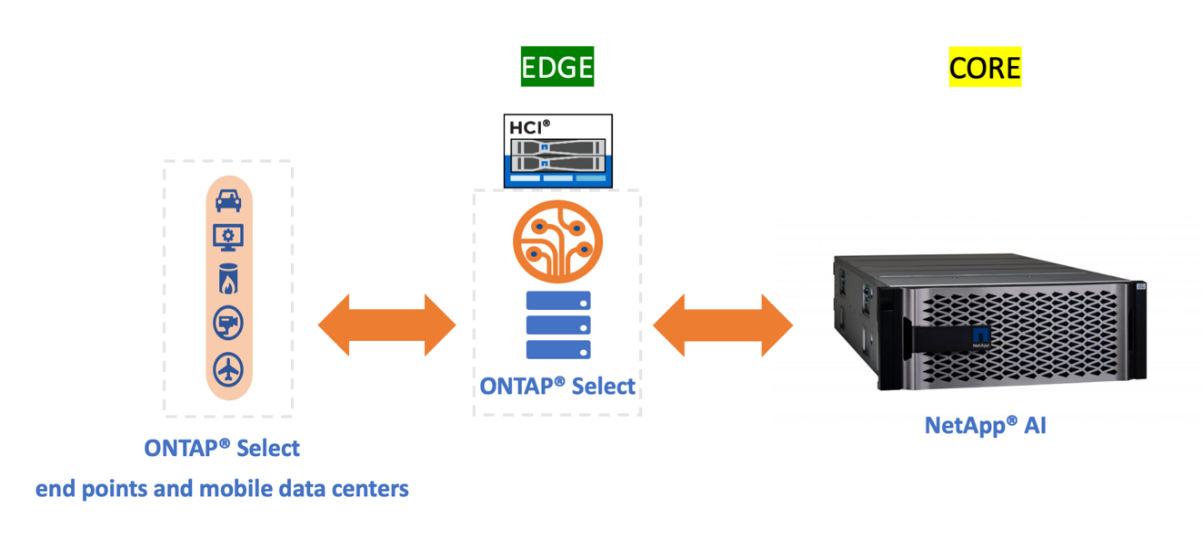
ONTAP Select can run as a VM on VMware and still bring in most of the ONTAP capabilities that are available when it is running on a dedicated FAS platform, such as the following:
-
Support for NFS and CIFS
-
NetApp FlexClone technology
-
NetApp FlexCache technology
-
NetApp ONTAP FlexGroup volumes
-
NetApp SnapMirror software
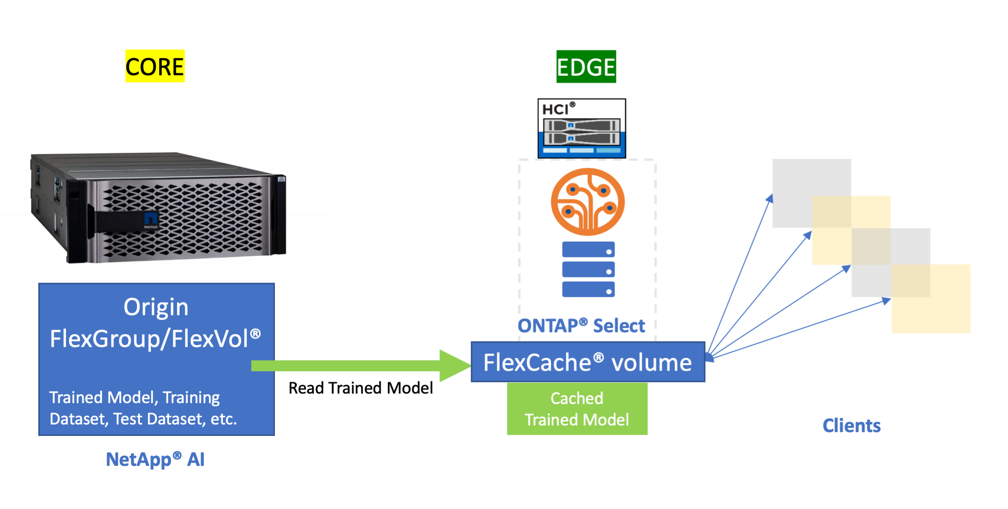
ONTAP Select can be used to leverage the FlexCache feature, which helps to reduce data-read latencies by caching frequently read data from a back-end origin volume, as is shown in the following figure. In the case of high-end inferencing applications with a lot of parallelization, multiple instances of the same model are deployed across the inferencing platform, leading to multiple reads of the same model. Newer versions of the trained model can be seamlessly introduced to the inferencing platform by verifying that the desired model is available in the origin or source volume.
NetApp Trident
NetApp Trident is an open-source dynamic storage orchestrator that allows you to manage storage resources across all major NetApp storage platforms. It integrates with Kubernetes natively so that persistent volumes (PVs) can be provisioned on demand with native Kubernetes interfaces and constructs. Trident enables microservices and containerized applications to use enterprise-class storage services such as QoS, storage efficiencies, and cloning to meet the persistent storage demands of applications.
Containers are among the most popular methods of packaging and deploying applications, and Kubernetes is one of the most popular platforms for hosting containerized applications. In this solution, the inferencing platform is built on top of a Kubernetes infrastructure.
Trident currently supports storage orchestration across the following platforms:
-
ONTAP: NetApp AFF, FAS, and Select
-
Element software: NetApp HCI and NetApp SolidFire all-flash storage
-
NetApp SANtricity software: E-Series and EF-series
-
Cloud Volumes ONTAP
-
Azure NetApp Files
-
Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP
-
Google Cloud NetApp Volumes
Trident is a simple but powerful tool to enable storage orchestration not just across multiple storage platforms, but also across the entire spectrum of the AI data lifecycle, ranging from the edge to the core to the cloud.
Trident can be used to provision a PV from a NetApp Snapshot copy that makes up the trained model. The following figure illustrates the Trident workflow in which a persistent volume claim (PVC) is created by referring to an existing Snapshot copy. Following this, Trident creates a volume by using the Snapshot copy.
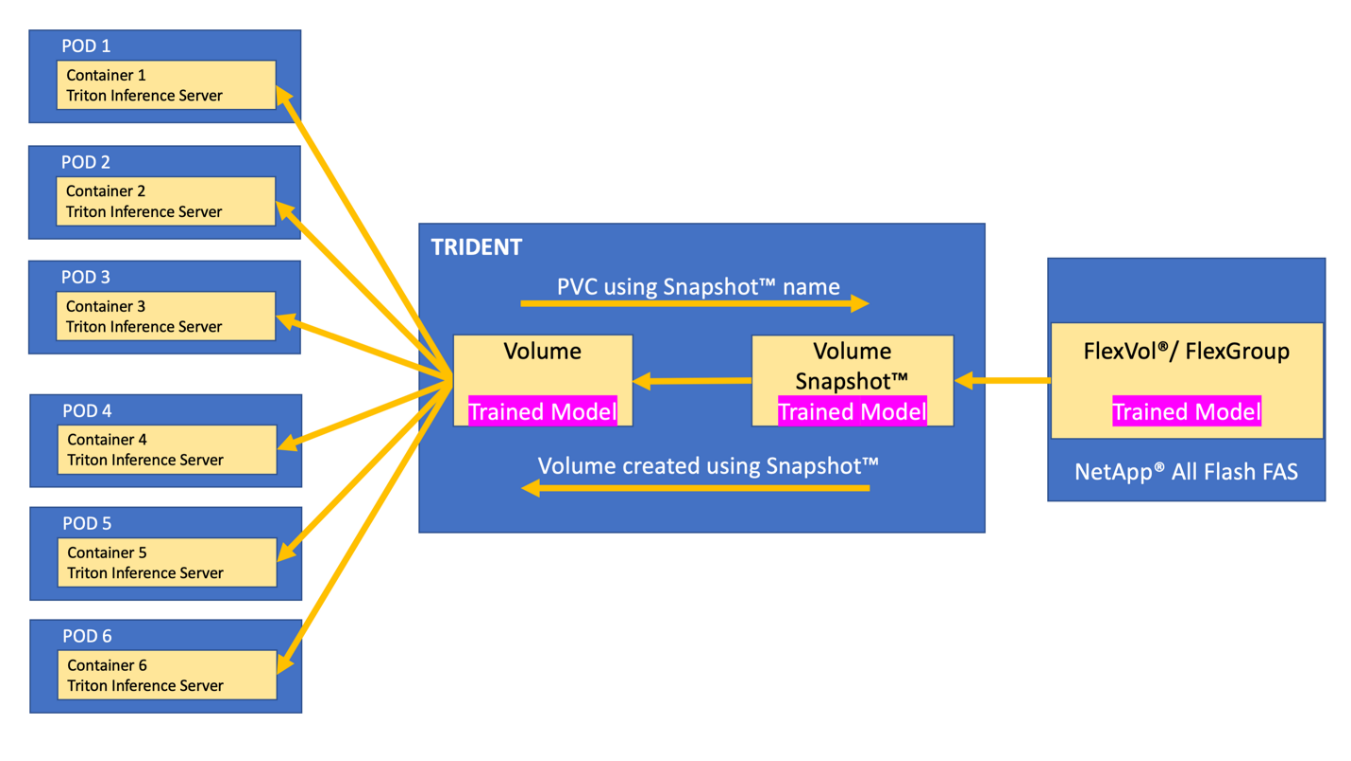
This method of introducing trained models from a Snapshot copy supports robust model versioning. It simplifies the process of introducing newer versions of models to applications and switching inferencing between different versions of the model.
NVIDIA DeepOps
NVIDIA DeepOps is a modular collection of Ansible scripts that can be used to automate the deployment of a Kubernetes infrastructure. There are multiple deployment tools available that can automate the deployment of a Kubernetes cluster. In this solution, DeepOps is the preferred choice because it does not just deploy a Kubernetes infrastructure, it also installs the necessary GPU drivers, NVIDIA Container Runtime for Docker (nvidia-docker2), and various other dependencies for GPU-accelerated work. It encapsulates the best practices for NVIDIA GPUs and can be customized or run as individual components as needed.
DeepOps internally uses Kubespray to deploy Kubernetes, and it is included as a submodule in DeepOps. Therefore, common Kubernetes cluster management operations such as adding nodes, removing nodes, and cluster upgrades should be performed using Kubespray.
A software based L2 LoadBalancer using MetalLb and an Ingress Controller based on NGINX are also deployed as part of this solution by using the scripts that are available with DeepOps.
In this solution, three Kubernetes master nodes are deployed as VMs, and the two H615c compute nodes with NVIDIA Tesla T4 GPUs are set up as Kubernetes worker nodes.
NVIDIA GPU Operator
The GPU operator deploys the NVIDIA k8s-device-plugin for GPU support and runs the NVIDIA drivers as containers. It is based on the Kubernetes operator framework, which helps to automate the management of all NVIDIA software components that are needed to provision GPUs. The components include NVIDIA drivers, Kubernetes device plug-in for GPUs, the NVIDIA container runtime, and automatic node labeling, which is used in tandem with Kubernetes Node Feature Discovery.
The GPU operator is an important component of the NVIDIA EGX software-defined platform that is designed to make large-scale hybrid-cloud and edge operations possible and efficient. It is specifically useful when the Kubernetes cluster needs to scale quickly—for example, when provisioning additional GPU-based worker nodes and managing the lifecycle of the underlying software components. Because the GPU operator runs everything as containers, including NVIDIA drivers, administrators can easily swap various components by simply starting or stopping containers.
NVIDIA Triton Inference Server
NVIDIA Triton Inference Server (Triton Server) simplifies the deployment of AI inferencing solutions in production data centers. This microservice is specifically designed for inferencing in production data centers. It maximizes GPU utilization and integrates seamlessly into DevOps deployments with Docker and Kubernetes.
Triton Server provides a common solution for AI inferencing. Therefore, researchers can focus on creating high-quality trained models, DevOps engineers can focus on deployment, and developers can focus on applications without the need to redesign the platform for each AI-powered application.
Here are some of the key features of Triton Server:
-
Support for multiple frameworks. Triton Server can handle a mix of models, and the number of models is limited only by system disk and memory resources. It can support the TensorRT, TensorFlow GraphDef, TensorFlow SavedModel, ONNX, PyTorch, and Caffe2 NetDef model formats.
-
*Concurrent model execution. *Multiple models or multiple instances of the same model can be run simultaneously on a GPU.
-
Multi-GPU support. Triton Server can maximize GPU utilization by enabling inference for multiple models on one or more GPUs.
-
Support for batching. Triton Server can accept requests for a batch of inputs and respond with the corresponding batch of outputs. The inference server supports multiple scheduling and batching algorithms that combine individual inference requests together to improve inference throughput. Batching algorithms are available for both stateless and stateful applications and need to be used appropriately. These scheduling and batching decisions are transparent to the client that is requesting inference.
-
Ensemble support. An ensemble is a pipeline with multiple models with connections of input and output tensors between those models. An inference request can be made to an ensemble, which results in the execution of the complete pipeline.
-
Metrics. Metrics are details about GPU utilization, server throughput, server latency, and health for auto scaling and load balancing.
NetApp HCI is a hybrid multi-cloud infrastructure that can host multiple workloads and applications, and the Triton Inference Server is well equipped to support the inferencing requirements of multiple applications.
In this solution, Triton Server is deployed on the Kubernetes cluster using a deployment file. With this method, the default configuration of Triton Server can be overridden and customized as required. Triton Server also provides an inference service using an HTTP or GRPC endpoint, allowing remote clients to request inferencing for any model that is being managed by the server.
A Persistent Volume is presented via NetApp Trident to the container that runs the Triton Inference Server and this persistent volume is configured as the model repository for the Inference server.
The Triton Inference Server is deployed with varying sets of resources using Kubernetes deployment files, and each server instance is presented with a LoadBalancer front end for seamless scalability. This approach also illustrates the flexibility and simplicity with which resources can be allocated to the inferencing workloads.


