Deploy and configure OpenShift Dedicated on Google Cloud with Google Cloud NetApp Volumes
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


This section describes a high-level workflow of setting up OpenShift Dedicated (OSD) clusters on the Google Cloud platform. It shows NetApp Trident using Google Cloud NetApp Volumes as the storage backend to provide persistent volumes for stateful applications running with Kubernetes.
Here is a diagram that depicts an OSD cluster deployed on Google Cloud and using NetApp Volumes as the backend storage.
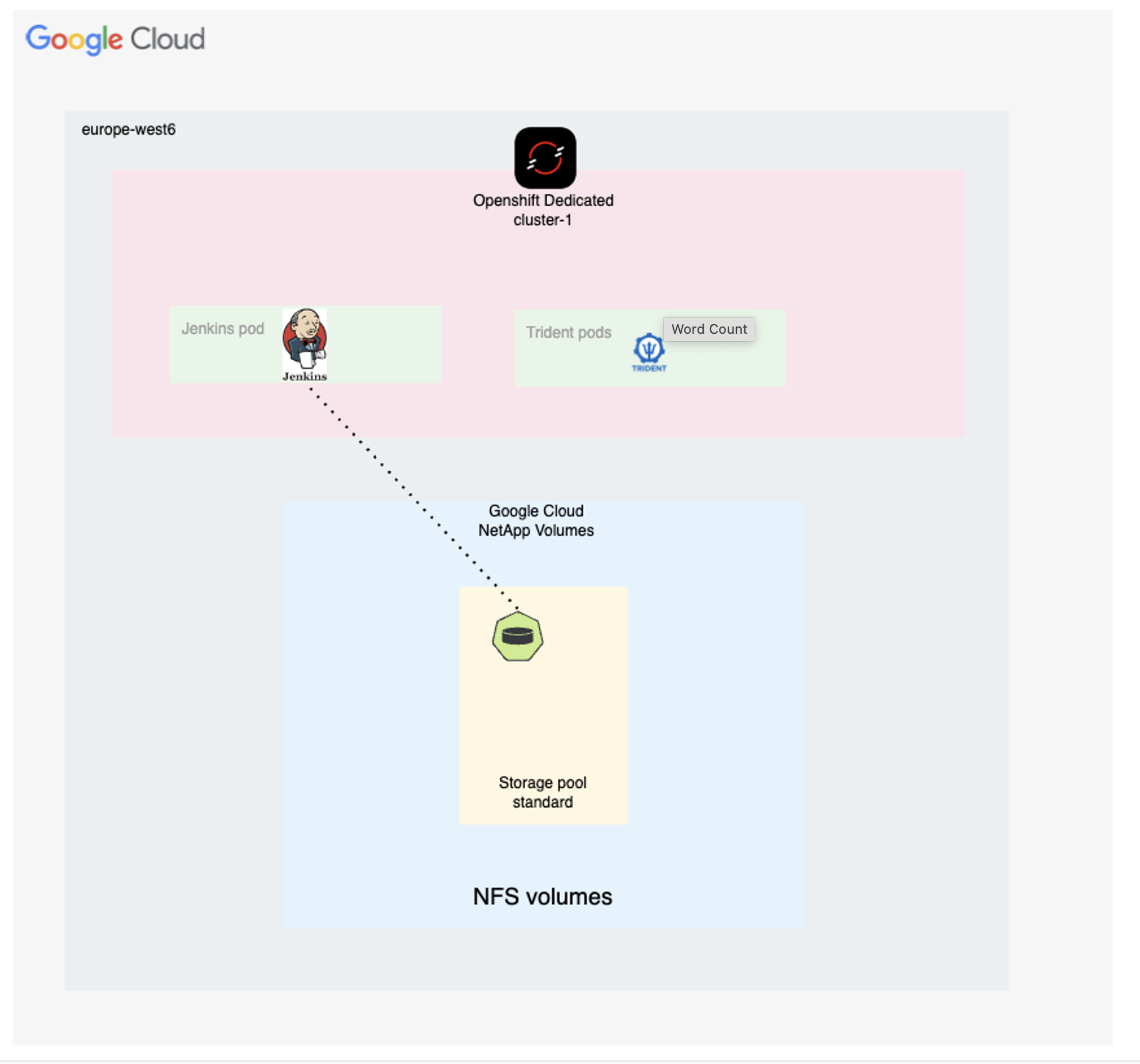
The setup process can be broken down into the following steps:
-
If you wish to use an existing VPC for the cluster, you must create the VPC, two subnets, a cloud router, and two GCP cloud NATs for the OSD cluster. Refer here for instructions.
-
Refer here for instructions to install OSD clusters on GCP using the Customer Cloud Subscription (CCS) billing model. OSD is also included on Google Cloud Marketplace. A video showing how to install OSD using the Google Cloud Marketplace solution is located here.
-
Refer here for information on setting up access to Google Cloud NetApp Volumes. Follow all the steps up to and including
-
Create a storage pool. Refer here for information on how to set up a storage pool on Google Cloud NetApp Volumes. Volumes for the stateful Kubernetes applications running on OSD will be created within the storage pool.
Create backend and storage classes using Trident (for Google Cloud NetApp Volumes)
-
Refer here for details about creating backend.
-
If any of the current storage classes in kubernetes are marked as default, remove that annotation by editing the storage class.
-
Create at least one storage class for NetApp volumes with the Trident CSI provisioner. Make exactly one of the storage classes the default using an annotation. This will allow a PVC to use this storage class when it is not explicitly called out in the PVC manifest. An example with the annotation is shown below.
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: gcnv-standard-k8s
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
provisioner: csi.trident.netapp.io
parameters:
backendType: "google-cloud-netapp-volumes"
trident.netapp.io/nasType: "nfs"
allowVolumeExpansion: trueOpen the console of Argo CD and deploy an app.
As an example, you can deploy a Jenkins App using Argo CD with a Helm Chart.
When creating the application, the following details were provided:
Project: default
cluster: 'https://kubernetes.default.svc' (without the quotes)
Namespace: Jenkins
The url for the Helm Chart: 'https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami' (without the quotes)


