Deploy and configure the Red Hat OpenShift Container platform on Azure
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


This section describes a high-level workflow of how to set up and manage OpenShift Clusters in Azure and deploy stateful applications on them. It shows the use of NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP storage with the help of Trident to provide persistent volumes. Details are provided about the use of Trident Protect to perform data protection and migration activities for the stateful applications.
Here is a diagram that shows the clusters deployed on Azure and connected to the data center using a VPN.
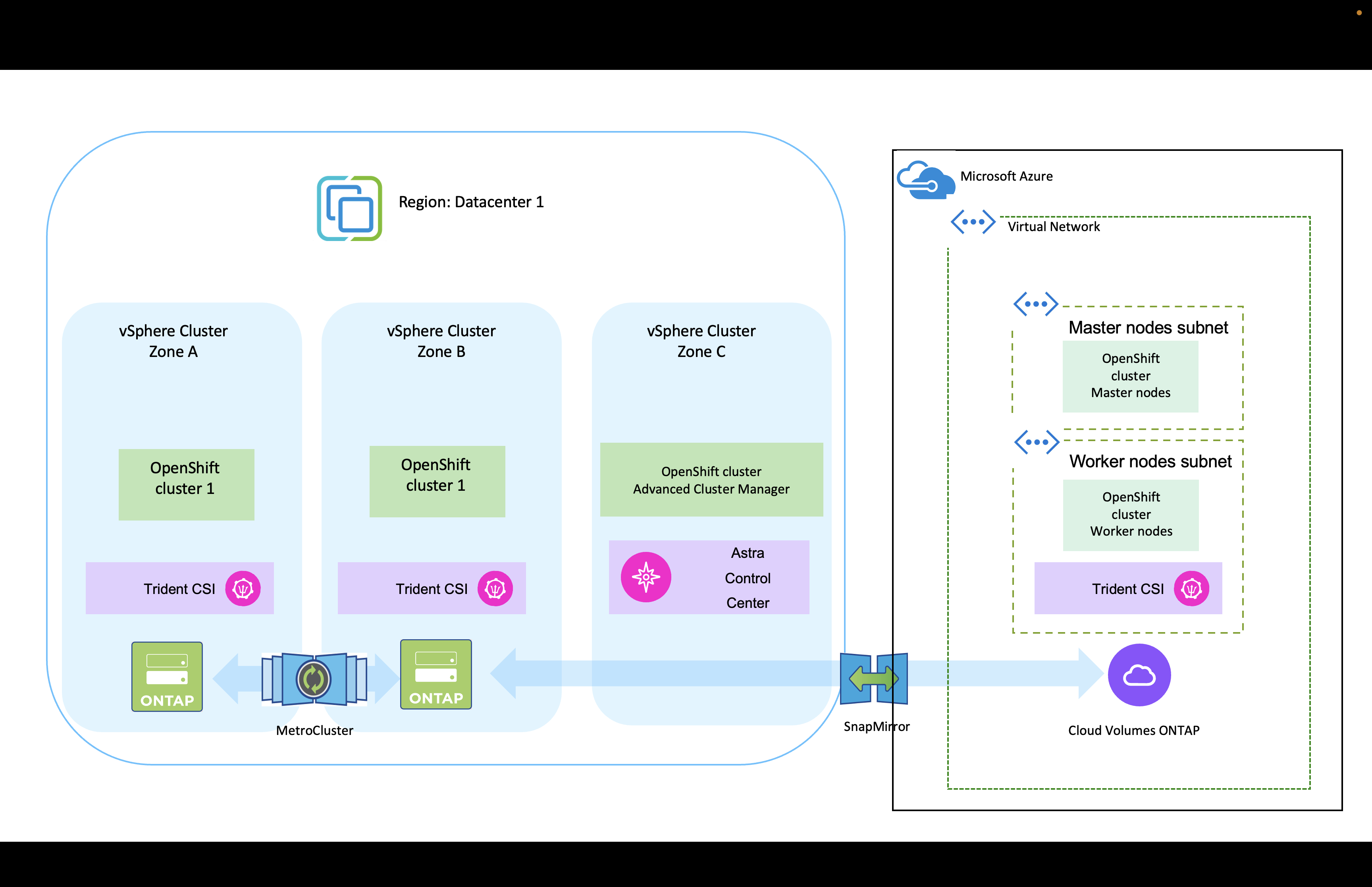

|
There are several ways of deploying Red Hat OpenShift Container platform clusters in Azure. This high-level description of the setup provides documentation links for the specific method that was used. You can refer to the other methods in the relevant links provided in the resources section. |
The setup process can be broken down into the following steps:
Install an OCP cluster on Azure from the CLI.
-
Ensure that you have met all the prerequisites stated here.
-
Create a VPN, subnets and network security groups and a private DNS zone. Create VPN gateway and site-to-site VPN Connection.
-
For the VPN connectivity between on-premises and Azure, a pfsense VM was created and configured. For instructions, see here.
-
Obtain the installation program and the pull secret and deploy the cluster following the steps provided in the documentation here.
-
The installation of the cluster completes and will provide a kubeconfig file and username and password to login to the console of the cluster.
A sample install-config.yaml file is given below.
apiVersion: v1
baseDomain: sddc.netapp.com
compute:
- architecture: amd64
hyperthreading: Enabled
name: worker
platform:
azure:
encryptionAtHost: false
osDisk:
diskSizeGB: 512
diskType: "StandardSSD_LRS"
type: Standard_D2s_v3
ultraSSDCapability: Disabled
#zones:
#- "1"
#- "2"
#- "3"
replicas: 3
controlPlane:
architecture: amd64
hyperthreading: Enabled
name: master
platform:
azure:
encryptionAtHost: false
osDisk:
diskSizeGB: 1024
diskType: Premium_LRS
type: Standard_D8s_v3
ultraSSDCapability: Disabled
replicas: 3
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: azure-cluster
networking:
clusterNetwork:
- cidr: 10.128.0.0/14
hostPrefix: 23
machineNetwork:
- cidr: 10.0.0.0/16
networkType: OVNKubernetes
serviceNetwork:
- 172.30.0.0/16
platform:
azure:
baseDomainResourceGroupName: ocp-base-domain-rg
cloudName: AzurePublicCloud
computeSubnet: ocp-subnet2
controlPlaneSubnet: ocp-subnet1
defaultMachinePlatform:
osDisk:
diskSizeGB: 1024
diskType: "StandardSSD_LRS"
ultraSSDCapability: Disabled
networkResourceGroupName: ocp-nc-us-rg
#outboundType: UserDefinedRouting
region: northcentralus
resourceGroupName: ocp-cluster-ncusrg
virtualNetwork: ocp_vnet_ncus
publish: Internal
pullSecret:
Deploy Cloud Volumes ONTAP in Azure using BlueXP.
-
Install a connector in in Azure. Refer to instructions here.
-
Deploy a CVO instance in Azure using the connector. Refer to instructions link:https://docs.netapp.com/us-en/bluexp-cloud-volumes-ontap/task-getting-started-azure.html [here.]
Cloud providers, today, enable Kubernetes/OpenShift cluster administrators to spawn nodes of the clusters that are zone based. Nodes can be located in different availability zones within a region, or across various regions. To facilitate the provisioning of volumes for workloads in a multi-zone architecture, Trident uses CSI Topology. Using the CSI Topology feature, access to volumes can be limited to a subset of nodes, based on regions and availability zones. Refer here for additional details.

|
Kubernetes supports two volume binding modes: - When VolumeBindingMode is set to Immediate (default), Trident creates the volume without any topology awareness. Persistent Volumes are created without having any dependency on the requesting pod's scheduling requirements. - When VolumeBindingMode set to WaitForFirstConsumer, the creation and binding of a Persistent Volume for a PVC is delayed until a pod that uses the PVC is scheduled and created. This way, volumes are created to meet the scheduling constraints that are enforced by topology requirements. Trident storage backends can be designed to selectively provision volumes based on availability zones (Topology-aware backend). For StorageClasses that make use of such a backend, a volume would only be created if requested by an application that is scheduled in a supported region/zone. (Topology-aware StorageClass) Refer here for additional details. |


