Replace a PCIe or mezzanine card - AFF A400
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


To replace a PCIe or mezzanine card, you must disconnect the cables and any SFP and QSFP modules from the cards, replace the failed PCIe or mezzanine card, and then recable the cards.
-
You can use this procedure with all versions of ONTAP supported by your system
-
All other components in the system must be functioning properly; if not, you must contact technical support.
Step 1: Shut down the impaired controller
You can shut down or take over the impaired controller using different procedures, depending on the storage system hardware configuration.
To shut down the impaired controller, you must determine the status of the controller and, if necessary, take over the controller so that the healthy controller continues to serve data from the impaired controller storage.
-
If you have a SAN system, you must have checked event messages (
cluster kernel-service show) for the impaired controller SCSI blade. Thecluster kernel-service showcommand (from priv advanced mode) displays the node name, quorum status of that node, availability status of that node, and operational status of that node.Each SCSI-blade process should be in quorum with the other nodes in the cluster. Any issues must be resolved before you proceed with the replacement.
-
If you have a cluster with more than two nodes, it must be in quorum. If the cluster is not in quorum or a healthy controller shows false for eligibility and health, you must correct the issue before shutting down the impaired controller; see Synchronize a node with the cluster.
-
If AutoSupport is enabled, suppress automatic case creation by invoking an AutoSupport message:
system node autosupport invoke -node * -type all -message MAINT=<# of hours>hThe following AutoSupport message suppresses automatic case creation for two hours:
cluster1:> system node autosupport invoke -node * -type all -message MAINT=2h -
Disable automatic giveback:
-
Enter the following command from the console of the healthy controller:
storage failover modify -node impaired_node_name -auto-giveback false -
Enter
ywhen you see the prompt Do you want to disable auto-giveback?
-
-
Take the impaired controller to the LOADER prompt:
If the impaired controller is displaying… Then… The LOADER prompt
Go to the next step.
Waiting for giveback…
Press Ctrl-C, and then respond
ywhen prompted.System prompt or password prompt
Take over or halt the impaired controller from the healthy controller:
storage failover takeover -ofnode impaired_node_name -halt trueThe -halt true parameter brings you to the LOADER prompt.
To shut down the impaired controller, you must determine the status of the controller and, if necessary, switch over the controller so that the healthy controller continues to serve data from the impaired controller storage.
-
You must leave the power supplies turned on at the end of this procedure to provide power to the healthy controller.
-
Check the MetroCluster status to determine whether the impaired controller has automatically switched over to the healthy controller:
metrocluster show -
Depending on whether an automatic switchover has occurred, proceed according to the following table:
If the impaired controller… Then… Has automatically switched over
Proceed to the next step.
Has not automatically switched over
Perform a planned switchover operation from the healthy controller:
metrocluster switchoverHas not automatically switched over, you attempted switchover with the
metrocluster switchovercommand, and the switchover was vetoedReview the veto messages and, if possible, resolve the issue and try again. If you are unable to resolve the issue, contact technical support.
-
Resynchronize the data aggregates by running the
metrocluster heal -phase aggregatescommand from the surviving cluster.controller_A_1::> metrocluster heal -phase aggregates [Job 130] Job succeeded: Heal Aggregates is successful.
If the healing is vetoed, you have the option of reissuing the
metrocluster healcommand with the-override-vetoesparameter. If you use this optional parameter, the system overrides any soft vetoes that prevent the healing operation. -
Verify that the operation has been completed by using the metrocluster operation show command.
controller_A_1::> metrocluster operation show Operation: heal-aggregates State: successful Start Time: 7/25/2016 18:45:55 End Time: 7/25/2016 18:45:56 Errors: - -
Check the state of the aggregates by using the
storage aggregate showcommand.controller_A_1::> storage aggregate show Aggregate Size Available Used% State #Vols Nodes RAID Status --------- -------- --------- ----- ------- ------ ---------------- ------------ ... aggr_b2 227.1GB 227.1GB 0% online 0 mcc1-a2 raid_dp, mirrored, normal...
-
Heal the root aggregates by using the
metrocluster heal -phase root-aggregatescommand.mcc1A::> metrocluster heal -phase root-aggregates [Job 137] Job succeeded: Heal Root Aggregates is successful
If the healing is vetoed, you have the option of reissuing the
metrocluster healcommand with the -override-vetoes parameter. If you use this optional parameter, the system overrides any soft vetoes that prevent the healing operation. -
Verify that the heal operation is complete by using the
metrocluster operation showcommand on the destination cluster:mcc1A::> metrocluster operation show Operation: heal-root-aggregates State: successful Start Time: 7/29/2016 20:54:41 End Time: 7/29/2016 20:54:42 Errors: - -
On the impaired controller module, disconnect the power supplies.
Step 2: Remove the controller module
To access components inside the controller module, you must remove the controller module from the chassis.
-
If you are not already grounded, properly ground yourself.
-
Release the power cable retainers, and then unplug the cables from the power supplies.
-
Loosen the hook and loop strap binding the cables to the cable management device, and then unplug the system cables and SFPs (if needed) from the controller module, keeping track of where the cables were connected.
Leave the cables in the cable management device so that when you reinstall the cable management device, the cables are organized.
-
Remove the cable management device from the controller module and set it aside.
-
Press down on both of the locking latches, and then rotate both latches downward at the same time.
The controller module moves slightly out of the chassis.


Locking latches

Controller moves slightly out of chassis
-
Slide the controller module out of the chassis.
Make sure that you support the bottom of the controller module as you slide it out of the chassis.
-
Place the controller module on a stable, flat surface.
Step 3: Replace a PCIe card
To replace a PCIe card, you must locate the failed PCIe card, remove the riser that contains the card from the controller module, replace the card, and then reinstall the PCIe riser in the controller module.
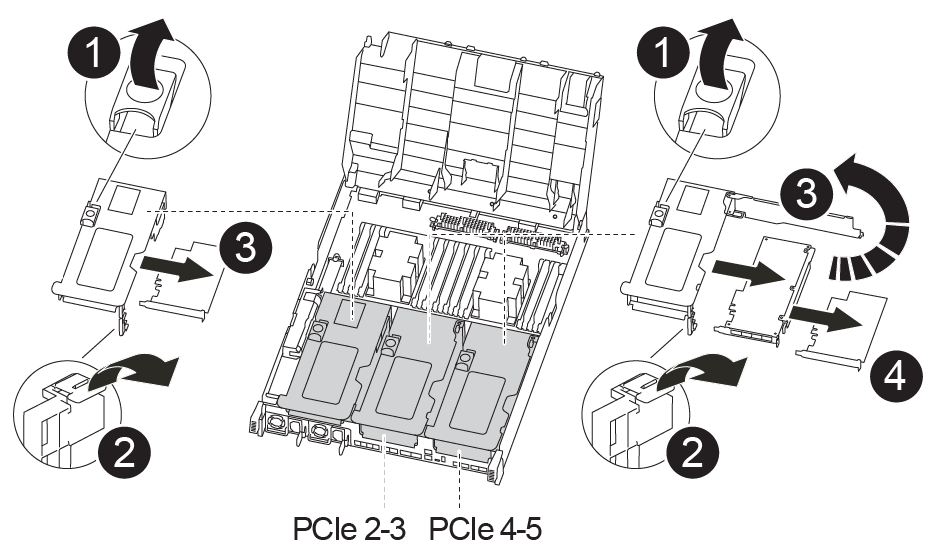
|
Riser locking latch |
|
PCI card locking latch |
|
PCI locking plate |
|
PCI card |
-
Remove the riser containing the card to be replaced:
-
Open the air duct by pressing the locking tabs on the sides of the air duct, slide it toward the back of the controller module, and then rotate it to its completely open position.
-
Remove any SFP or QSFP modules that might be in the PCIe cards.
-
Rotate the riser locking latch on the left side of the riser up and toward air duct.
The riser raises up slightly from the controller module.
-
Lift the riser up straight up and set it aside on a stable flat surface,
-
-
Remove the PCIe card from the riser:
-
Turn the riser so that you can access the PCIe card.
-
Press the locking bracket on the side of the PCIe riser, and then rotate it to the open position.
-
For risers 2 and 3 only, swing the side panel up.
-
Remove the PCIe card from the riser by gently pushing up on the bracket and lift the card straight out of the socket.
-
-
Install the replacement PCIe card in the riser by aligning the card with the socket, press the card into the socket and then close the side panel on the riser, if present.
Be sure that you properly align the card in the slot and exert even pressure on the card when seating it in the socket. The PCIe card must be fully and evenly seated in the slot.
If you are installing a card in the bottom slot and cannot see the card socket well, remove the top card so that you can see the card socket, install the card, and then reinstall the card you removed from the top slot. -
Reinstall the riser:
-
Align the riser with the pins to the side of the riser socket, lower the riser down on the pins.
-
Push the riser squarely into the socket on the motherboard.
-
Rotate the latch down flush with the sheet metal on the riser.
-
Step 4: Replace the mezzanine card
The mezzanine card is located under riser number 3 (slots 4 and 5). You must remove that riser to access the mezzanine card, replace the mezzanine card, and then reinstall riser number 3. See the FRU map on the controller module for more information.
You can use the following animation, illustration, or the written steps to replace the mezzanine card.
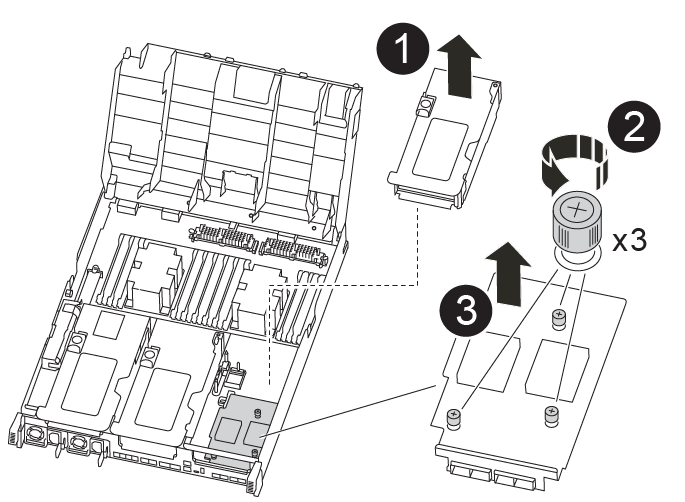
|
PCI riser |
|
Riser thumbscrew |
|
Riser card |
-
Remove riser number 3 (slots 4 and 5):
-
Open the air duct by pressing the locking tabs on the sides of the air duct, slide it toward the back of the controller module, and then rotate it to its completely open position.
-
Remove any SFP or QSFP modules that might be in the PCIe cards.
-
Rotate the riser locking latch on the left side of the riser up and toward air duct.
The riser raises up slightly from the controller module.
-
Lift the riser up, and then set it aside on a stable, flat surface.
-
-
Replace the mezzanine card:
-
Remove any QSFP or SFP modules from the card.
-
Loosen the thumbscrews on the mezzanine card, and gently lift the card directly out of the socket and set it aside.
-
Align the replacement mezzanine card over the socket and the guide pins and gently push the card into the socket.
-
Tighten the thumbscrews on the mezzanine card.
-
-
Reinstall the riser:
-
Align the riser with the pins to the side of the riser socket, lower the riser down on the pins.
-
Push the riser squarely into the socket on the motherboard.
-
Rotate the latch down flush with the sheet metal on the riser.
-
Step 5: Install the controller module
After you have replaced the component in the controller module, you must reinstall the controller module into the chassis, and then boot it to Maintenance mode.
-
If you have not already done so, close the air duct.
-
Align the end of the controller module with the opening in the chassis, and then gently push the controller module halfway into the system.
Do not completely insert the controller module in the chassis until instructed to do so. -
Recable the system, as needed.
If you removed the media converters (QSFPs or SFPs), remember to reinstall them if you are using fiber optic cables.
-
Complete the installation of the controller module:
-
Using the locking latches, firmly push the controller module into the chassis until it meets the midplane and is fully seated.
The locking latches rise when the controller module is fully seated.
Do not use excessive force when sliding the controller module into the chassis to avoid damaging the connectors. -
Fully seat the controller module in the chassis by rotating the locking latches upward, tilting them so that they clear the locking pins, gently push the controller all the way in, and then lower the locking latches into the locked position.
-
Plug the power cords into the power supplies, reinstall the power cable locking collar, and then connect the power supplies to the power source.
The controller module begins to boot as soon as power is restored. Be prepared to interrupt the boot process.
-
If you have not already done so, reinstall the cable management device.
-
Interrupt the normal boot process and boot to LOADER by pressing
Ctrl-C.If your system stops at the boot menu, select the option to boot to LOADER. -
At the LOADER prompt, enter
byeto reinitialize the PCIe cards and other components and let the controller reboot.
-
-
Return the controller to normal operation by giving back its storage:
storage failover giveback -ofnode impaired_node_name -
If automatic giveback was disabled, reenable it:
storage failover modify -node local -auto-giveback true
Step 6: Restore the controller module to operation
To restore the controller, you must recable the system, give back the controller module, and then reenable automatic giveback.
-
Recable the system, as needed.
If you removed the media converters (QSFPs or SFPs), remember to reinstall them if you are using fiber optic cables.
-
Return the controller to normal operation by giving back its storage:
storage failover giveback -ofnode impaired_node_name -
If automatic giveback was disabled, reenable it:
storage failover modify -node local -auto-giveback true
Step 7: Switch back aggregates in a two-node MetroCluster configuration
This task only applies to two-node MetroCluster configurations.
-
Verify that all nodes are in the
enabledstate:metrocluster node showcluster_B::> metrocluster node show DR Configuration DR Group Cluster Node State Mirroring Mode ----- ------- -------------- -------------- --------- -------------------- 1 cluster_A controller_A_1 configured enabled heal roots completed cluster_B controller_B_1 configured enabled waiting for switchback recovery 2 entries were displayed. -
Verify that resynchronization is complete on all SVMs:
metrocluster vserver show -
Verify that any automatic LIF migrations being performed by the healing operations were completed successfully:
metrocluster check lif show -
Perform the switchback by using the
metrocluster switchbackcommand from any node in the surviving cluster. -
Verify that the switchback operation has completed:
metrocluster showThe switchback operation is still running when a cluster is in the
waiting-for-switchbackstate:cluster_B::> metrocluster show Cluster Configuration State Mode -------------------- ------------------- --------- Local: cluster_B configured switchover Remote: cluster_A configured waiting-for-switchback
The switchback operation is complete when the clusters are in the
normalstate.:cluster_B::> metrocluster show Cluster Configuration State Mode -------------------- ------------------- --------- Local: cluster_B configured normal Remote: cluster_A configured normal
If a switchback is taking a long time to finish, you can check on the status of in-progress baselines by using the
metrocluster config-replication resync-status showcommand. -
Reestablish any SnapMirror or SnapVault configurations.
Step 8: Return the failed part to NetApp
Return the failed part to NetApp, as described in the RMA instructions shipped with the kit. See the Part Return and Replacements page for further information.



