Restore and recover an auto discovered cluster backup
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


You can use SnapCenter to restore and recover data from one or more backups.
-
You must have backed up the resource or resource groups.
-
You must have canceled any backup operation that is currently in progress for the resource or resource group that you want to restore.
-
For pre restore, post restore, mount, and unmount commands, you should check if the commands exist in the command list available on the plug-in host from the following paths:
-
Default location on the Windows host: C:\Program Files\NetApp\SnapCenter\Snapcenter Plug-in Creator\etc\allowed_commands.config
-
Default location on the Linux host: /opt/NetApp/snapcenter/scc/etc/allowed_commands.config
-

|
If the commands do not exist in the command list, then the operation will fail. |
-
File-based backup copies cannot be restored from SnapCenter.
-
For Auto-discovered resources, restore is supported with SFSR.
-
Auto-recovery is not supported.
-
For ONTAP 9.12.1 and below version, the clones created from the SnapLock Vault snapshots as part of restore will inherit the SnapLock Vault expiry time. Storage admin should manually cleanup the clones post the SnapLock expiry time.
-
In the left navigation pane, click Resources, and then select the appropriate plug-in from the list.
-
In the Resources page, filter resources from the View drop-down list based on resource type.
The resources are displayed along with type, host, associated resource groups and policies, and status.
Although a backup might be for a resource group, when you restore, you must select the individual resources you want to restore. If the resource is not protected, “Not protected” is displayed in the Overall Status column. This can mean either that the resource is not protected, or that the resource was backed up by a different user.
-
Select the resource, or select a resource group and then select a resource in that group.
The resource topology page is displayed.
-
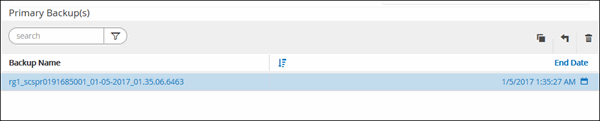
From the Manage Copies view, select Backups either from the primary or secondary (mirrored or vaulted) storage systems.
-
In the Primary backup(s) table, select the backup that you want to restore from, and then click
 .
.
-
In the Restore Scope page, select Complete Resource to restore the configured data volumes of the PostgreSQL cluster.
-
In the Recovery scope page, select one of the following options:
If you…
Do this…
Want to recover as close as possible to the current time
Select Recover to most recent state. For single container resources specify one or more log and catalog backup locations.
Want to recover to the specified point in time
Select Recover to point in time.
-
Enter date and time. Enter date and time. For example, the PostgreSQL Linux host is located in Sunnyvale, CA and the user in Raleigh, NC is recovering the logs in to SnapCenter.
If the user wants to perform a recovery to 5 a.m .Sunnyvale, CA, then the user has to set the browser time zone to the PostgreSQL Linux host time zone, which is GMT-07:00 and specify the date and time as 5:00 a.m.
Do not want to recover
Select No recovery.
-

|
You cannot recover manually added PostgreSQL resources. |

|
SnapCenter Plug-in for PostgreSQL creates a backup_label and tablespace_map in /<OS_temp_folder>/postgresql_sc_recovery<Restore_JobId>/_ folder to help recover manually. |
-
In the Pre ops page, enter pre restore and unmount commands to run before performing a restore job.
Unmount commands are not available for auto discovered resources.
-
In the Post ops page, enter mount and post restore commands to run after performing a restore job.
Mount commands are not available for auto discovered resources.
-
In the Notification page, from the Email preference drop-down list, select the scenarios in which you want to send the emails.
You must also specify the sender and receiver email addresses and the subject of the email. SMTP must also be configured on the Settings > Global Settings page.
-
Review the summary, and then click Finish.
-
Monitor the operation progress by clicking Monitor > Jobs.


