Storage and performance requirements
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


You must understand the storage requirements for StorageGRID nodes, so you can provide enough space to support the initial configuration and future storage expansion.
StorageGRID nodes require three logical categories of storage:
-
Container pool — Performance-tier (10K SAS or SSD) storage for the node containers, which will be assigned to the Docker storage driver when you install and configure Docker on the hosts that will support your StorageGRID nodes.
-
System data — Performance-tier (10K SAS or SSD) storage for per-node persistent storage of system data and transaction logs, which the StorageGRID host services will consume and map into individual nodes.
-
Object data — Performance-tier (10K SAS or SSD) storage and capacity-tier (NL-SAS/SATA) bulk storage for the persistent storage of object data and object metadata.
You must use RAID-backed block devices for all storage categories. Non-redundant disks, SSDs, or JBODs aren't supported. You can use shared or local RAID storage for any of the storage categories; however, if you want to use the node migration capability in StorageGRID, you must store both system data and object data on shared storage. For more information, see Node container migration requirements.
Performance requirements
The performance of the volumes used for the container pool, system data, and object metadata significantly impacts the overall performance of the system. You should use performance-tier (10K SAS or SSD) storage for these volumes to ensure adequate disk performance in terms of latency, input/output operations per second (IOPS), and throughput. You can use capacity-tier (NL-SAS/SATA) storage for the persistent storage of object data.
The volumes used for the container pool, system data, and object data must have write-back caching enabled. The cache must be on a protected or persistent media.
Requirements for hosts that use NetApp ONTAP storage
If the StorageGRID node uses storage assigned from a NetApp ONTAP system, confirm that the volume does not have a FabricPool tiering policy enabled. Disabling FabricPool tiering for volumes used with StorageGRID nodes simplifies troubleshooting and storage operations.

|
Never use FabricPool to tier any data related to StorageGRID back to StorageGRID itself. Tiering StorageGRID data back to StorageGRID increases troubleshooting and operational complexity. |
Number of hosts required
Each StorageGRID site requires a minimum of three Storage Nodes.

|
In a production deployment, don't run more than one Storage Node on a single physical or virtual host. Using a dedicated host for each Storage Node provides an isolated failure domain. |
Other types of nodes, such as Admin Nodes or Gateway Nodes, can be deployed on the same hosts, or they can be deployed on their own dedicated hosts as required.
Number of storage volumes for each host
The following table shows the number of storage volumes (LUNs) required for each host and the minimum size required for each LUN, based on which nodes will be deployed on that host.
The maximum tested LUN size is 39 TB.

|
These numbers are for each host, not for the entire grid. |
| LUN purpose | Storage category | Number of LUNs | Minimum size/LUN |
|---|---|---|---|
Container engine storage pool |
Container pool |
1 |
Total number of nodes × 100 GB |
|
System data |
1 for each node on this host |
90 GB |
Storage Node |
Object data |
3 for each Storage Node on this host Note: A software-based Storage Node can have 1 to 16 storage volumes; at least 3 storage volumes are recommended. |
12 TB (4 TB/LUN) See Storage requirements for Storage Nodes for more information. |
Storage Node (metadata-only) |
Object metadata |
1 |
4 TB See Storage requirements for Storage Nodes for more information. Note: Only one rangedb is required for metadata-only Storage Nodes. |
Admin Node audit logs |
System data |
1 for each Admin Node on this host |
200 GB |
Admin Node tables |
System data |
1 for each Admin Node on this host |
200 GB |

|
Depending on the audit level configured, the size of user inputs such as S3 object key name, and how much audit log data you need to preserve, you might need to increase the size of the audit log LUN on each Admin Node.Generally, a grid generates approximately 1 KB of audit data per S3 operation, which would mean that a 200 GB LUN would support 70 million operations per day or 800 operations per second for two to three days. |
Minimum storage space for a host
The following table shows the minimum storage space required for each type of node. You can use this table to determine the minimum amount of storage you must provide to the host in each storage category, based on which nodes will be deployed on that host.

|
Disk snapshots can't be used to restore grid nodes. Instead, refer to the grid node recovery procedures for each type of node. |
| Type of node | Container pool | System data | Object data |
|---|---|---|---|
Storage Node |
100 GB |
90 GB |
4,000 GB |
Admin Node |
100 GB |
490 GB (3 LUNs) |
not applicable |
Gateway Node |
100 GB |
90 GB |
not applicable |
Archive Node |
100 GB |
90 GB |
not applicable |
Example: Calculating the storage requirements for a host
Suppose you plan to deploy three nodes on the same host: one Storage Node, one Admin Node, and one Gateway Node. You should provide a minimum of nine storage volumes to the host. You will need a minimum of 300 GB of performance-tier storage for the node containers, 670 GB of performance-tier storage for system data and transaction logs, and 12 TB of capacity-tier storage for object data.
| Type of node | LUN purpose | Number of LUNs | LUN size |
|---|---|---|---|
Storage Node |
Docker storage pool |
1 |
300 GB (100 GB/node) |
Storage Node |
|
1 |
90 GB |
Storage Node |
Object data |
3 |
12 TB (4 TB/LUN) |
Admin Node |
|
1 |
90 GB |
Admin Node |
Admin Node audit logs |
1 |
200 GB |
Admin Node |
Admin Node tables |
1 |
200 GB |
Gateway Node |
|
1 |
90 GB |
Total |
9 |
Container pool: 300 GB System data: 670 GB Object data: 12,000 GB |
Storage requirements for Storage Nodes
A software-based Storage Node can have 1 to 16 storage volumes—3 or more storage volumes are recommended. Each storage volume should be 4 TB or larger.

|
An appliance Storage Node can have up to 48 storage volumes. |
As shown in the figure, StorageGRID reserves space for object metadata on storage volume 0 of each Storage Node. Any remaining space on storage volume 0 and any other storage volumes in the Storage Node are used exclusively for object data.
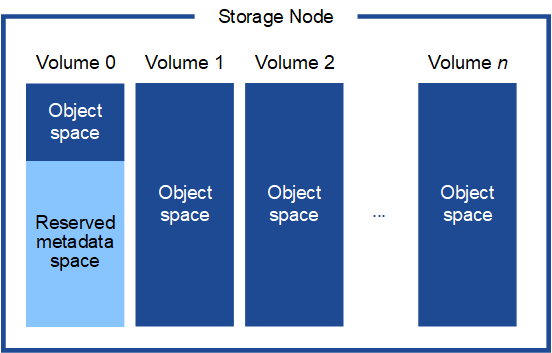
To provide redundancy and to protect object metadata from loss, StorageGRID stores three copies of the metadata for all objects in the system at each site. The three copies of object metadata are evenly distributed across all Storage Nodes at each site.
When installing a grid with metadata-only Storage Nodes, the grid must also contain a minimum number of nodes for object storage. See Types of Storage Nodes for more information about metadata-only Storage Nodes.
-
For a single-site grid, at least two Storage Nodes are configured for objects and metadata.
-
For a multi-site grid, at least one Storage Node per site are configured for objects and metadata.
When you assign space to volume 0 of a new Storage Node, you must ensure there is adequate space for that node's portion of all object metadata.
-
At a minimum, you must assign at least 4 TB to volume 0.
If you use only one storage volume for a Storage Node and you assign 4 TB or less to the volume, the Storage Node might enter the Storage Read-Only state on startup and store object metadata only. If you assign less than 500 GB to volume 0 (non-production use only), 10% of the storage volume's capacity is reserved for metadata. -
Software-based metadata-only node resources must match the existing Storage Nodes resources. For example:
-
If the existing StorageGRID site is using SG6000 or SG6100 appliances, the software-based metadata-only nodes must meet the following minimum requirements:
-
128 GB RAM
-
8 core CPU
-
8 TB SSD or equivalent storage for the Cassandra database (rangedb/0)
-
-
If the existing StorageGRID site is using virtual Storage Nodes with 24 GB RAM, 8 core CPU, and 3 TB or 4TB of metadata storage, the software-based metadata-only nodes should use similar resources (24 GB RAM, 8 core CPU, and 4TB of metadata storage (rangedb/0).
When adding a new StorageGRID site, the new site total metadata capacity should, at minimum, match existing StorageGRID sites and new site resources should match the Storage Nodes at existing StorageGRID sites.
-
-
If you are installing a new system (StorageGRID 11.6 or higher) and each Storage Node has 128 GB or more of RAM, assign 8 TB or more to volume 0. Using a larger value for volume 0 can increase the space allowed for metadata on each Storage Node.
-
When configuring different Storage Nodes for a site, use the same setting for volume 0 if possible. If a site contains Storage Nodes of different sizes, the Storage Node with the smallest volume 0 will determine the metadata capacity of that site.
For details, go to Manage object metadata storage.


