Manage object metadata storage
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


The object metadata capacity of a StorageGRID system controls the maximum number of objects that can be stored on that system. To ensure that your StorageGRID system has adequate space to store new objects, you must understand where and how StorageGRID stores object metadata.
What is object metadata?
Object metadata is any information that describes an object. StorageGRID uses object metadata to track the locations of all objects across the grid and to manage each object's lifecycle over time.
For an object in StorageGRID, object metadata includes the following types of information:
-
System metadata, including a unique ID for each object (UUID), the object name, the name of the S3 bucket or Swift container, the tenant account name or ID, the logical size of the object, the date and time the object was first created, and the date and time the object was last modified.
-
Any custom user metadata key-value pairs associated with the object.
-
For S3 objects, any object tag key-value pairs associated with the object.
-
For replicated object copies, the current storage location of each copy.
-
For erasure-coded object copies, the current storage location of each fragment.
-
For object copies in a Cloud Storage Pool, the location of the object, including the name of the external bucket and the object's unique identifier.
-
For segmented objects and multipart objects, segment identifiers and data sizes.
How is object metadata stored?
StorageGRID maintains object metadata in a Cassandra database, which is stored independently of object data. To provide redundancy and to protect object metadata from loss, StorageGRID stores three copies of the metadata for all objects in the system at each site.
This figure represents the Storage Nodes at two sites. Each site has the same amount of object metadata, and each site's metadata is subdivided among all Storage Nodes at that site.
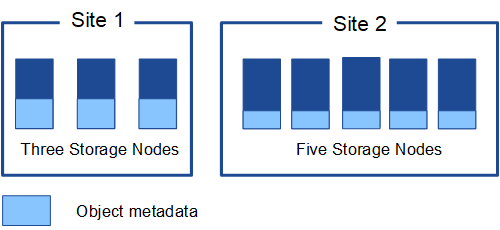
Where is object metadata stored?
This figure represents the storage volumes for a single Storage Node.
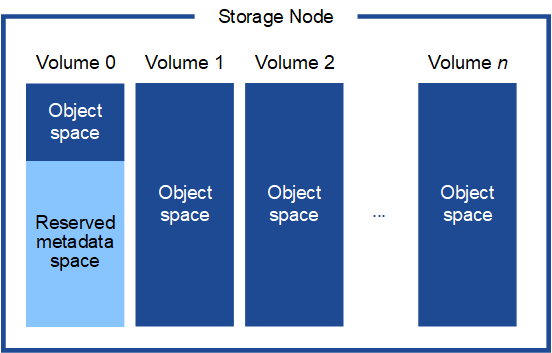
As shown in the figure, StorageGRID reserves space for object metadata on storage volume 0 of each Storage Node. It uses the reserved space to store object metadata and to perform essential database operations. Any remaining space on storage volume 0 and all other storage volumes in the Storage Node are used exclusively for object data (replicated copies and erasure-coded fragments).
The amount of space that is reserved for object metadata on a particular Storage Node depends on several factors, which are described below.
Metadata reserved space setting
The Metadata reserved space is a system-wide setting that represents the amount of space that will be reserved for metadata on volume 0 of every Storage Node. As shown in the table, the default value of this setting is based on:
-
The software version you were using when you initially installed StorageGRID.
-
The amount of RAM on each Storage Node.
| Version used for initial StorageGRID installation | Amount of RAM on Storage Nodes | Default Metadata reserved space setting |
|---|---|---|
11.5 to 11.8 |
128 GB or more on each Storage Node in the grid |
8 TB (8,000 GB) |
Less than 128 GB on any Storage Node in the grid |
3 TB (3,000 GB) |
|
11.1 to 11.4 |
128 GB or more on each Storage Node at any one site |
4 TB (4,000 GB) |
Less than 128 GB on any Storage Node at each site |
3 TB (3,000 GB) |
|
11.0 or earlier |
Any amount |
2 TB (2,000 GB) |
View Metadata reserved space setting
Follow these steps to view the Metadata reserved space setting for your StorageGRID system.
-
Select CONFIGURATION > System > Storage settings.
-
On the Storage settings page, expand the Metadata reserved space section.
For StorageGRID 11.8 or higher, the Metadata reserved space value must be at least 100 GB and no more than 1 PB.
The default setting for a new StorageGRID 11.6 or higher installation in which each Storage Node has 128 GB or more of RAM is 8,000 GB (8 TB).
Actual reserved space for metadata
In contrast to the system-wide Metadata reserved space setting, the actual reserved space for object metadata is determined for each Storage Node. For any given Storage Node, the actual reserved space for metadata depends on the size of volume 0 for the node and the system-wide Metadata reserved space setting.
| Size of volume 0 for the node | Actual reserved space for metadata |
|---|---|
Less than 500 GB (non-production use) |
10% of volume 0 |
500 GB or more |
The smaller of these values:
Note: Only one rangedb is required for metadata-only Storage Nodes. |
View actual reserved space for metadata
Follow these steps to view the actual reserved space for metadata on a particular Storage Node.
-
From the Grid Manager, select NODES > Storage Node.
-
Select the Storage tab.
-
Position your cursor over the Storage Used - Object Metadata chart and locate the Actual reserved value.
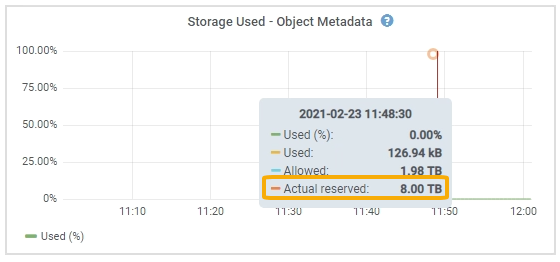
In the screenshot, the Actual reserved value is 8 TB. This screenshot is for a large Storage Node in a new StorageGRID 11.6 installation. Because the system-wide Metadata reserved space setting is smaller than volume 0 for this Storage Node, the actual reserved space for this node equals the Metadata reserved space setting.
Example for actual reserved metadata space
Suppose you install a new StorageGRID system using version 11.7 or later. For this example, assume that each Storage Node has more than 128 GB of RAM and that volume 0 of Storage Node 1 (SN1) is 6 TB. Based on these values:
-
The system-wide Metadata reserved space is set to 8 TB. (This is the default value for a new StorageGRID 11.6 or higher installation if each Storage Node has more than 128 GB RAM.)
-
The actual reserved space for metadata for SN1 is 6 TB. (The entire volume is reserved because volume 0 is smaller than the Metadata reserved space setting.)
Allowed metadata space
Each Storage Node's actual reserved space for metadata is subdivided into the space available for object metadata (the allowed metadata space) and the space required for essential database operations (such as compaction and repair) and future hardware and software upgrades. The allowed metadata space governs overall object capacity.
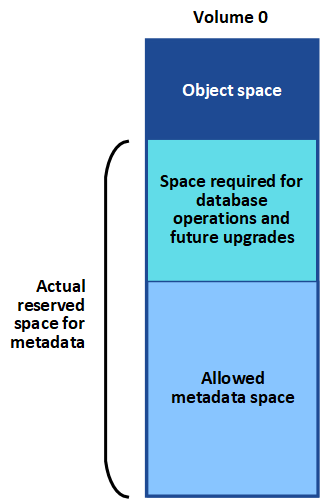
The following table shows how StorageGRID calculates the allowed metadata space for different Storage Nodes, based on the amount of memory for the node and the actual reserved space for metadata.
Amount of memory on Storage Node |
|||
< 128 GB |
>= 128 GB |
||
Actual reserved space for metadata |
<= 4 TB |
60% of actual reserved space for metadata, up to a maximum of 1.32 TB |
60% of actual reserved space for metadata, up to a maximum of 1.98 TB |
> 4 TB |
(Actual reserved space for metadata − 1 TB) × 60%, up to a maximum of 1.32 TB |
(Actual reserved space for metadata − 1 TB) × 60%, up to a maximum of 3.96 TB |
|
View allowed metadata space
Follow these steps to view the allowed metadata space for a Storage Node.
-
From the Grid Manager, select NODES.
-
Select the Storage Node.
-
Select the Storage tab.
-
Position your cursor over the Storage used - object metadata chart and locate the Allowed value.
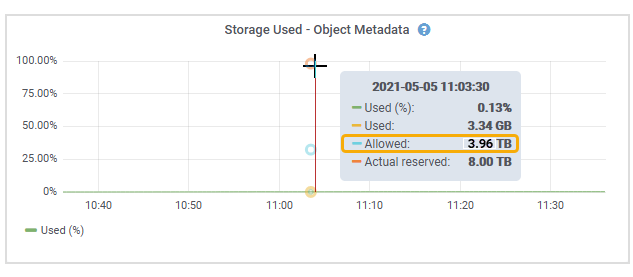
In the screenshot, the Allowed value is 3.96 TB, which is the maximum value for a Storage Node whose actual reserved space for metadata is more than 4 TB.
The Allowed value corresponds to this Prometheus metric:
storagegrid_storage_utilization_metadata_allowed_bytes
Example for allowed metadata space
Suppose you install a StorageGRID system using version 11.6. For this example, assume that each Storage Node has more than 128 GB of RAM and that volume 0 of Storage Node 1 (SN1) is 6 TB. Based on these values:
-
The system-wide Metadata reserved space is set to 8 TB. (This is the default value for StorageGRID 11.6 or higher when each Storage Node has more than 128 GB RAM.)
-
The actual reserved space for metadata for SN1 is 6 TB. (The entire volume is reserved because volume 0 is smaller than the Metadata reserved space setting.)
-
The allowed space for metadata on SN1 is 3 TB, based on the calculation shown in the table for allowed space for metadata: (Actual reserved space for metadata − 1 TB) × 60%, up to a maximum of 3.96 TB.
How Storage Nodes of different sizes affect object capacity
As described above, StorageGRID evenly distributes object metadata across the Storage Nodes at each site. For this reason, if a site contains Storage Nodes of different sizes, the smallest node at the site determines the site's metadata capacity.
Consider the following example:
-
You have a single-site grid containing three Storage Nodes of different sizes.
-
The Metadata reserved space setting is 4 TB.
-
The Storage Nodes have the following values for the actual reserved metadata space and the allowed metadata space.
Storage Node Size of volume 0 Actual reserved metadata space Allowed metadata space SN1
2.2 TB
2.2 TB
1.32 TB
SN2
5 TB
4 TB
1.98 TB
SN3
6 TB
4 TB
1.98 TB
Because object metadata is evenly distributed across the Storage Nodes at a site, each node in this example can only hold 1.32 TB of metadata. The additional 0.66 TB of allowed metadata space for SN2 and SN3 can't be used.
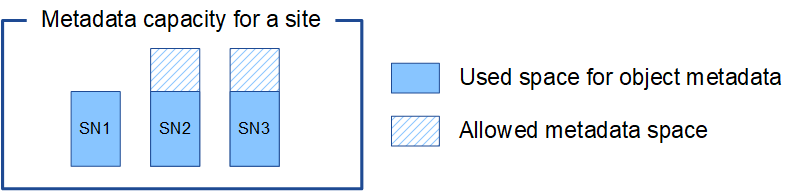
Similarly, because StorageGRID maintains all object metadata for a StorageGRID system at each site, the overall metadata capacity of a StorageGRID system is determined by the object metadata capacity of the smallest site.
And because object metadata capacity controls the maximum object count, when one node runs out of metadata capacity, the grid is effectively full.
-
To learn how to monitor the object metadata capacity for each Storage Node, see the instructions for Monitoring StorageGRID.
-
To increase the object metadata capacity for your system, expand a grid by adding new Storage Nodes.


