Workload Security notifications using webhooks
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


Webhooks allow users to send critical or warning alert notifications to various applications using a customized webhook channel.
Many commercial applications support webhooks as a standard input interface, for example: Slack, PagerDuty, Teams, and Discord. By supporting a generic, customizable webhook channel, Workload Security can support many of these delivery channels. Information about configuring the webhooks can be found on the respective application's websites. For example, Slack provides this useful guide.
You can create multiple webhook channels, each channel targeted for a different purpose, separate applications, different recipients, etc.
The webhook channel instance is comprised of the following elements
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
URL |
Webhook target URL, including the http:// or https:// prefix along with the url params |
Method |
GET/POST - Default is POST |
Custom Header |
Specify any custom headers here |
Message Body |
Put the body of your message here |
Default Alert Parameters |
Lists the default parameters for the webhook |
Custom Parameters and Secrets |
Custom parameters and secrets allows you to add unique parameters and secure elements such as passwords |
Creating a webhook
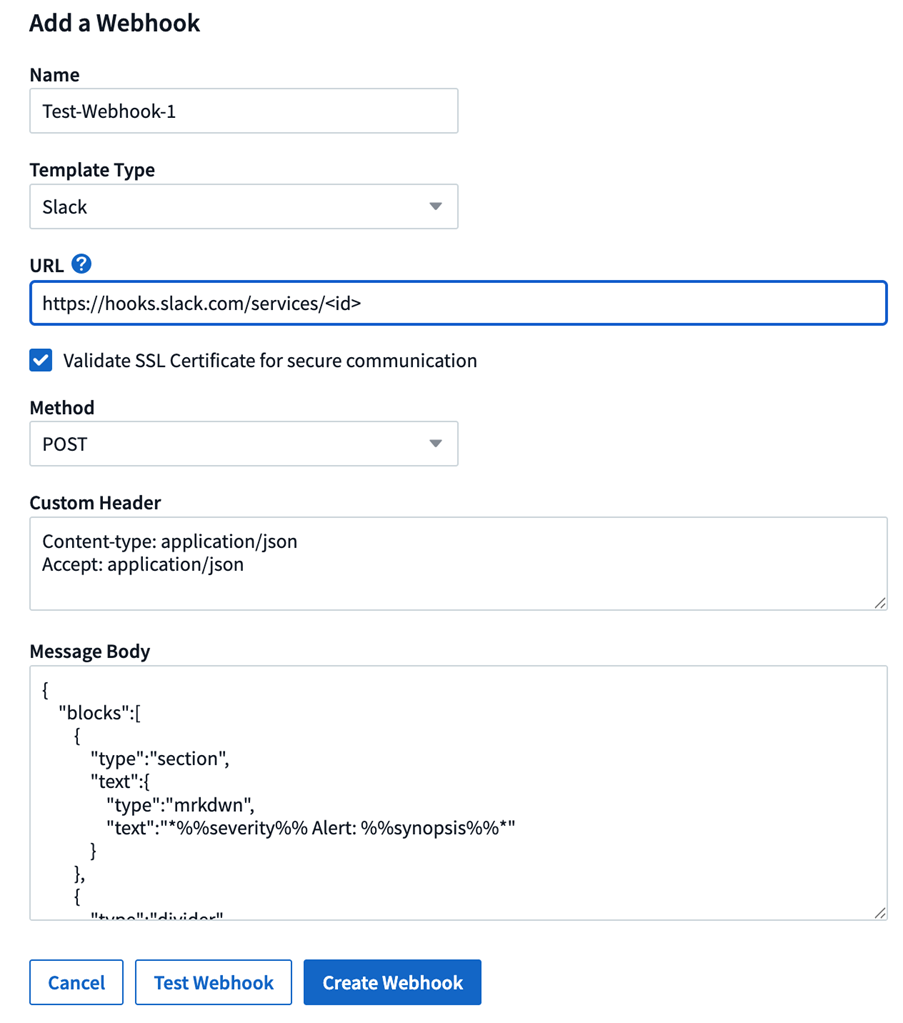
To create a Workload Security Webhook, go to Admin > Notifications and select “Workload Security Webhooks” tab. The following image shows a sample slack webhook creation screen.
Note: User must be a Workload Security Admin in order to create and manage Workload Security Webhooks.
-
Enter appropriate information for each of the fields, and click "Save".
-
You can also click the "Test Webhook" button to test the connection. Note that this will send the "Message Body" (without substitutions) to the defined URL according to the selected Method.
-
SWS webhooks comprise a number of default parameters. Additionally, you can create your own custom parameters or secrets.
Parameters: What are they and how to use them?
Alert Parameters are dynamic values populated per alert. For example, the %%severity%% parameter will be replaced with the severity type of the alert.
Note that substitutions are not performed when clicking the "Test Webhook" button; the test sends a payload that shows the parameter's placeholders (%%<param-name>%%) but does not replace them with data.
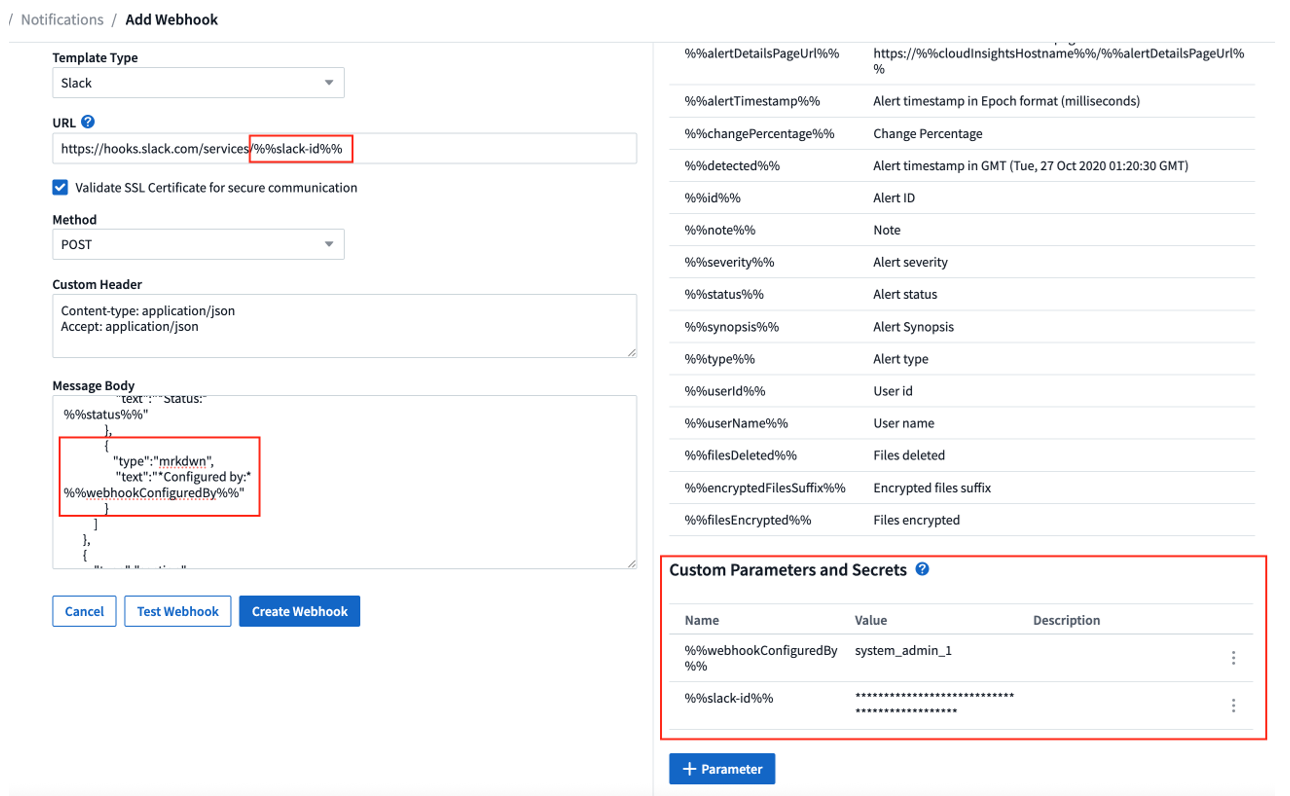
Custom Parameters and Secrets
In this section you can add any custom parameters and/or secrets you wish. A custom parameter or secret can be in the URL or message body. Secrets allow user to configure a secure custom parameter like password, apiKey etc.
The following sample image shows how custom parameters are used in webhook creation.
Workload Security Webhooks List Page
On the Webhooks list page, displayed are the Name, Created By, Created On, Status, Secure, and Last Reported fields.
Note: The value of 'status' column will keep changing based on the result of last webhook trigger result. The following are examples of status results.
Status |
Description |
OK |
Successfully sent notification. |
403 |
Forbidden. |
404 |
URL not found. |
400 |
Bad Request. You might see this status if there is any error in the message body, for example:
|
410 |
Resource is no longer available |
“Last Reported” column indicates the time when the webhook was last triggered.
From the webhooks listing page users can also Edit/Duplicate/Delete webhooks.
Configure Webhook notification in alert policy
To add a webhook notification to an alert policy, go to -Workload Security > Policies- and select an existing policy or add a new policy. In the Actions section > Webhook Notifications dropdown, select the required webhooks.
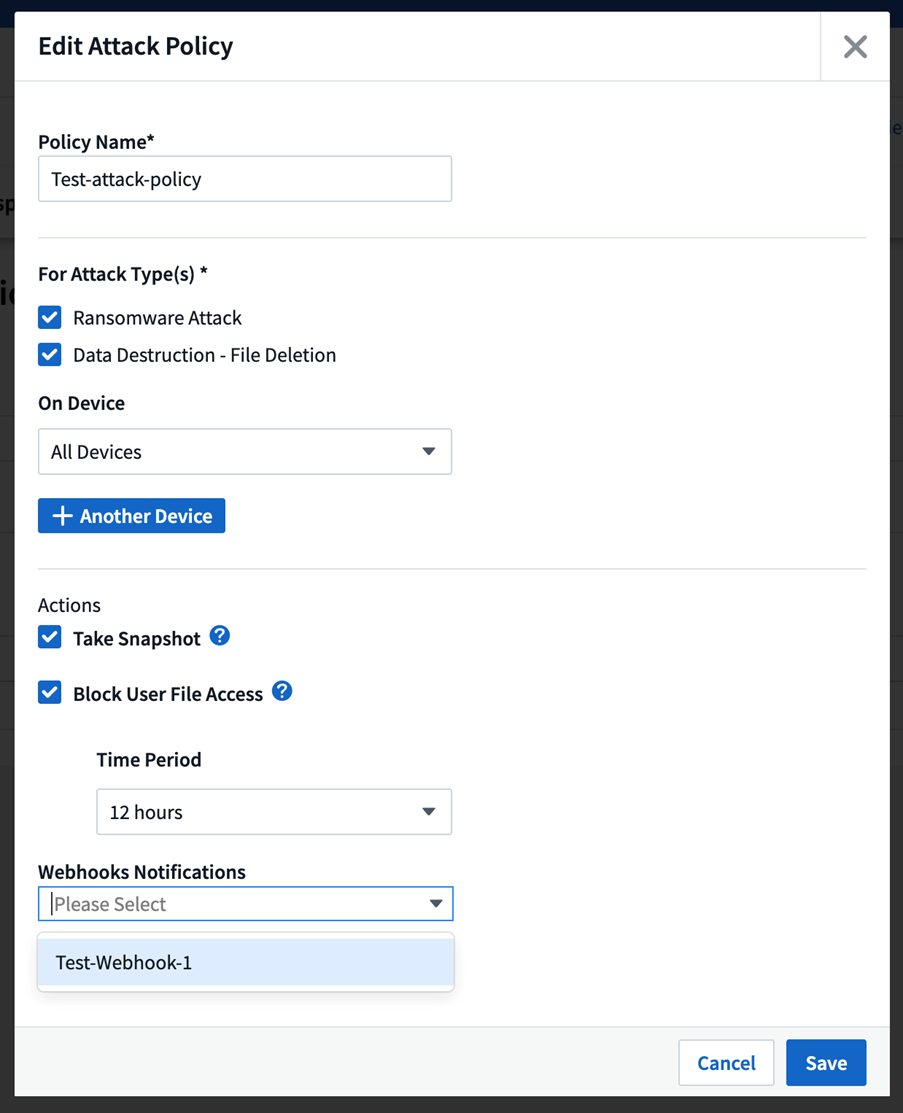
Webhook notifications are tied to policies. When the attack (RW/DD/WARN) happens, the action configured (Take snapshot / user blocking) will be taken and then the associated webhook notification will be triggered.
Note: Email notifications are independent of policies, they will be triggered as usual.
-
If a policy is paused, webhook notifications will not be triggered.
-
Multiple webhooks can be attached to a single policy but it is recommended to attach no more than 5 webhooks to a policy.


