Launch Cloud Volumes ONTAP in AWS
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


You can launch Cloud Volumes ONTAP in a single-system configuration or as an HA pair in AWS. This method provides an advanced deployment experience that offers more configuration options and flexibility than the quick deployment method.
Before you begin
You need the following before you begin.
-
A Console agent that's up and running.
-
An understanding of the configuration that you want to use.
You should have prepared by choosing a configuration and by obtaining AWS networking information from your administrator. For details, refer to Planning your Cloud Volumes ONTAP configuration.
-
An understanding of what's required to set up licensing for Cloud Volumes ONTAP.
-
DNS and Active Directory for CIFS configurations.
For details, refer to Networking requirements for Cloud Volumes ONTAP in AWS.
Launch a single-node Cloud Volumes ONTAP system in AWS
If you want to launch Cloud Volumes ONTAP in AWS, you need to create a new system in the NetApp Console.
Immediately after you create the system, the Console launches a test instance in the specified VPC to verify connectivity. If successful, the Console immediately terminates the instance and then starts deploying the Cloud Volumes ONTAP system. If the connectivity can't be verified, system creation fails. The test instance is either a t2.nano (for default VPC tenancy) or m3.medium (for dedicated VPC tenancy).
-
From the left navigation menu, select Storage > Management.
-
On the Systems page, click Add System and follow the prompts.
-
Select Amazon Web Services and Cloud Volumes ONTAP Single Node.
-
Select Advanced create. Because the Quick create mode is selected by default, you might see a message for default values. Click Continue.
-
If you're prompted, create a Console agent.
-
Details and Credentials: Optionally change the AWS credentials and subscription, enter a system name, add tags if needed, and then enter a password.
Some of the fields in this page are self-explanatory. The following table describes fields for which you might need guidance:
Field Description System Name
The Console uses the system name to name both the Cloud Volumes ONTAP system and the Amazon EC2 instance. It also uses the name as the prefix for the predefined security group, if you select that option.
Add tags
AWS tags are metadata for your AWS resources. The Console adds the tags to the Cloud Volumes ONTAP instance and each AWS resource associated with the instance.
You can add up to four tags from the user interface when creating a system, and then you can add more after it's created. Note that the API does not limit you to four tags when creating a system.
For information about tags, refer to AWS Documentation: Tagging your Amazon EC2 Resources.User name and password
These are the credentials for the Cloud Volumes ONTAP cluster administrator account. You can use these credentials to connect to Cloud Volumes ONTAP through ONTAP System Manager or the ONTAP CLI. Keep the default admin user name or change it to a custom user name.
Edit Credentials
Choose the AWS credentials associated with the account where you want to deploy this system. You can also associate the AWS marketplace subscription to use with this Cloud Volumes ONTAP system.
Click Add Subscription to associate the selected credentials with a new AWS marketplace subscription. The subscription can be for an annual contract or to pay for Cloud Volumes ONTAP at an hourly rate.
Learn how to add additional AWS credentials to NetApp Console.If multiple IAM users work in the same AWS account, then each user needs to subscribe. After the first user subscribes, the AWS marketplace informs subsequent users that they're already subscribed, as shown in the image below. While a subscription is in place for the AWS account, each IAM user needs to associate themselves with that subscription. If you see the message shown below, click the click here link to go to the Console website and complete the process.
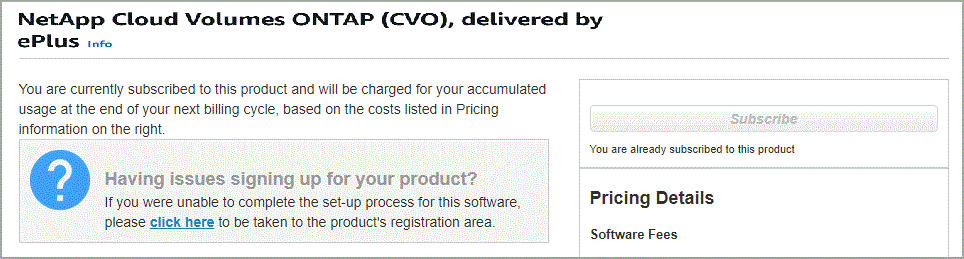
-
Services: Keep the services enabled or disable the individual services that you don't want to use with Cloud Volumes ONTAP.
-
Learn more about NetApp Backup and Recovery
If you would like to utilize WORM and data tiering, you must disable Backup and Recovery and deploy a Cloud Volumes ONTAP system with version 9.8 or above.
-
Location & Connectivity: Enter the network information that you recorded in the AWS worksheet.
The following table describes fields for which you might need guidance:
Field Description VPC
If you have an AWS Outpost, you can deploy a single node Cloud Volumes ONTAP system in that Outpost by selecting the Outpost VPC. The experience is the same as any other VPC that resides in AWS.
Generated security group
If you let the Console generate the security group for you, you need to choose how you'll allow traffic:
-
If you choose Selected VPC only, the source for inbound traffic is the subnet range of the selected VPC and the subnet range of the VPC where the Console agent resides. This is the recommended option.
-
If you choose All VPCs, the source for inbound traffic is the 0.0.0.0/0 IP range.
Use existing security group
If you use an existing firewall policy, ensure that it includes the required rules. Learn about firewall rules for Cloud Volumes ONTAP.
-
-
Data Encryption: Choose no data encryption or AWS-managed encryption.
For AWS-managed encryption, you can choose a different Customer Master Key (CMK) from your account or another AWS account.
You can't change the AWS data encryption method after you create a Cloud Volumes ONTAP system. -
Charging Methods and NSS Account: Specify which charging option would you like to use with this system, and then specify a NetApp Support Site account.
-
Cloud Volumes ONTAP Configuration (annual AWS marketplace contract only): Review the default configuration and click Continue or click Change Configuration to select your own configuration.
If you keep the default configuration, then you only need to specify a volume and then review and approve the configuration.
-
Preconfigured Packages: Select one of the packages to quickly launch Cloud Volumes ONTAP, or click Change Configuration to select your own configuration.
If you choose one of the packages, then you only need to specify a volume and then review and approve the configuration.
-
IAM Role: It's best to keep the default option to let the Console create the role for you.
If you prefer to use your own policy, it must meet policy requirements for Cloud Volumes ONTAP nodes.
-
Licensing: Change the Cloud Volumes ONTAP version as needed and select an instance type and the instance tenancy.
If a newer Release Candidate, General Availability, or patch release is available for the selected version, then the Console updates the system to that version when creating the system. For example, the update occurs if you select Cloud Volumes ONTAP 9.13.1 and 9.13.1 P4 is available. The update does not occur from one release to another—for example, from 9.13 to 9.14. -
Underlying Storage Resources: Choose a disk type, configure the underlying storage, and choose whether to keep data tiering enabled.
Note the following:
-
The disk type is for the initial volume (and aggregate). You can choose a different disk type for subsequent volumes (and aggregates).
-
If you choose a gp3 or io1 disk, the Console uses the Elastic Volumes feature in AWS to automatically increase the underlying storage disk capacity as needed. You can choose the initial capacity based on your storage needs and revise it after Cloud Volumes ONTAP is deployed. Learn more about support for Elastic Volumes in AWS.
-
If you choose a gp2 or st1 disk, you can select a disk size for all disks in the initial aggregate and for any additional aggregates that the Console creates when you use the simple provisioning option. You can create aggregates that use a different disk size by using the advanced allocation option.
-
You can choose a specific volume tiering policy when you create or edit a volume.
-
If you disable data tiering, you can enable it on subsequent aggregates.
-
-
Write Speed & WORM:
-
Choose Normal or High write speed, if desired.
-
Activate write once, read many (WORM) storage, if desired.
WORM can't be enabled if data tiering was enabled for Cloud Volumes ONTAP versions 9.7 and below. Reverting or downgrading to Cloud Volumes ONTAP 9.8 is blocked after enabling WORM and tiering.
-
If you activate WORM storage, select the retention period.
-
-
Create Volume: Enter details for the new volume or click Skip.
Some of the fields in this page are self-explanatory. The following table describes fields for which you might need guidance:
Field Description Size
The maximum size that you can enter largely depends on whether you enable thin provisioning, which enables you to create a volume that is bigger than the physical storage currently available to it.
Access control (for NFS only)
An export policy defines the clients in the subnet that can access the volume. By default, the Console enters a value that provides access to all instances in the subnet.
Permissions and Users / Groups (for CIFS only)
These fields enable you to control the level of access to a share for users and groups (also called access control lists or ACLs). You can specify local or domain Windows users or groups, or UNIX users or groups. If you specify a domain Windows user name, you must include the user's domain using the format domain\username.
Snapshot Policy
A Snapshot copy policy specifies the frequency and number of automatically created NetApp Snapshot copies. A NetApp Snapshot copy is a point-in-time file system image that has no performance impact and requires minimal storage. You can choose the default policy or none. You might choose none for transient data: for example, tempdb for Microsoft SQL Server.
Advanced options (for NFS only)
Select an NFS version for the volume: either NFSv3 or NFSv4.
Initiator group and IQN (for iSCSI only)
iSCSI storage targets are called LUNs (logical units) and are presented to hosts as standard block devices.
Initiator groups are tables of iSCSI host node names and control which initiators have access to which LUNs.
iSCSI targets connect to the network through standard Ethernet network adapters (NICs), TCP offload engine (TOE) cards with software initiators, converged network adapters (CNAs) or dedicated host bust adapters (HBAs) and are identified by iSCSI qualified names (IQNs).
When you create an iSCSI volume, the Console automatically creates a LUN for you. We’ve made it simple by creating just one LUN per volume, so there’s no management involved. After you create the volume, use the IQN to connect to the LUN from your hosts.The following image shows the first page of the volume creation wizard:
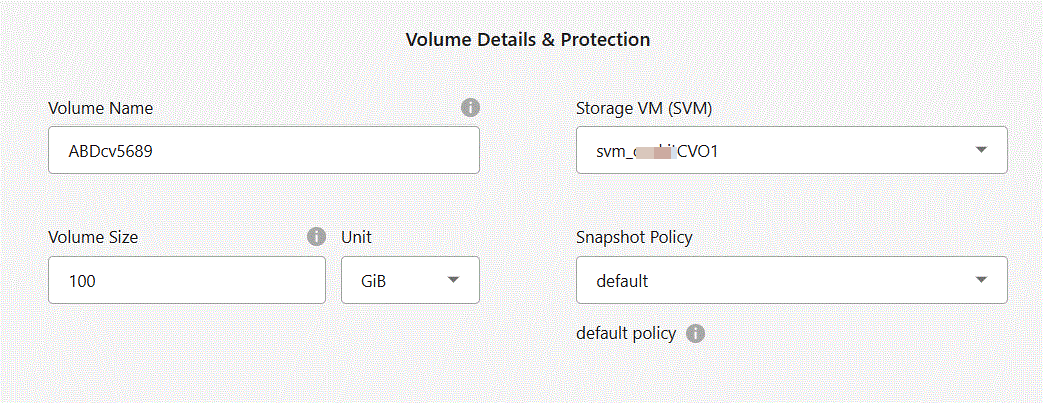
-
CIFS Setup: If you chose the CIFS protocol, set up a CIFS server.
Field Description DNS Primary and Secondary IP Address
The IP addresses of the DNS servers that provide name resolution for the CIFS server.
The listed DNS servers must contain the service location records (SRV) needed to locate the Active Directory LDAP servers and domain controllers for the domain that the CIFS server will join.Active Directory Domain to join
The FQDN of the Active Directory (AD) domain that you want the CIFS server to join.
Credentials authorized to join the domain
The name and password of a Windows account with sufficient privileges to add computers to the specified Organizational Unit (OU) within the AD domain.
CIFS server NetBIOS name
A CIFS server name that is unique in the AD domain.
Organizational Unit
The organizational unit within the AD domain to associate with the CIFS server. The default is CN=Computers.
If you configure AWS Managed Microsoft AD as the AD server for Cloud Volumes ONTAP, you should enter OU=Computers,OU=corp in this field.DNS Domain
The DNS domain for the Cloud Volumes ONTAP storage virtual machine (SVM). In most cases, the domain is the same as the AD domain.
NTP Server
Select Use Active Directory Domain to configure an NTP server using the Active Directory DNS. If you need to configure an NTP server using a different address, then you should use the API. Refer to the NetApp Console automation docs for details.
Note that you can configure an NTP server only when creating a CIFS server. It's not configurable after you create the CIFS server. -
Usage Profile, Disk Type, and Tiering Policy: Choose whether you want to enable storage efficiency features and edit the volume tiering policy, if needed.
For more information, refer to Understanding volume usage profiles, Data tiering overview, and KB: What Inline Storage Efficiency features are supported with CVO?
-
Review & Approve: Review and confirm your selections.
-
Review details about the configuration.
-
Click More information to review details about support and the AWS resources that the Console will purchase.
-
Select the I understand… check boxes.
-
Click Go.
-
The Console launches the Cloud Volumes ONTAP instance. You can track the progress on the Audit page.
If you have any issues launching the Cloud Volumes ONTAP instance, review the failure message. You can also select the system and click Re-create environment.
For additional help, go to NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP Support.

|
After the deployment process completes, do not modify the system-generated Cloud Volumes ONTAP configurations in the AWS cloud portal, especially the system tags. Any changes made to these configurations may lead to unexpected behavior or data loss. |
-
If you provisioned a CIFS share, give users or groups permissions to the files and folders and verify that those users can access the share and create a file.
-
If you want to apply quotas to volumes, use ONTAP System Manager or the ONTAP CLI.
Quotas enable you to restrict or track the disk space and number of files used by a user, group, or qtree.
Launch a Cloud Volumes ONTAP HA pair in AWS
If you want to launch a Cloud Volumes ONTAP HA pair in AWS, you need to create an HA system in the Console.
At this time, HA pairs are not supported with AWS Outposts.
Immediately after you create the Cloud Volumes ONTAP system, the Console launches a test instance in the specified VPC to verify connectivity. If successful, the Console immediately terminates the instance and then starts deploying the Cloud Volumes ONTAP system. If the connectivity can't be verified, system creation fails. The test instance is either a t2.nano (for default VPC tenancy) or m3.medium (for dedicated VPC tenancy).
-
From the left navigation menu, select Storage > Management.
-
On the Systems page, click Add System and follow the prompts.
-
Select Amazon Web Services and Cloud Volumes ONTAP HA.
Some AWS Local Zones are available.
Before you can use AWS Local Zones, you must enable Local Zones and create a subnet in the Local Zone in your AWS account. Follow the Opt in to an AWS Local Zone and Extend your Amazon VPC to the Local Zone steps in the AWS tutorial "Get Started Deploying Low Latency Applications with AWS Local Zones.
If you are running the Console agent 3.9.36 or below, you need to add the
DescribeAvailabilityZonespermission to the AWS role in the AWS EC2 console. -
Details and Credentials: Optionally change the AWS credentials and subscription, enter a system name, add tags if needed, and then enter a password.
Some of the fields in this page are self-explanatory. The following table describes fields for which you might need guidance:
Field Description System Name
The Console uses the system name to name both the Cloud Volumes ONTAP system and the Amazon EC2 instance. It also uses the name as the prefix for the predefined security group, if you select that option.
Add tags
AWS tags are metadata for your AWS resources. The Console adds the tags to the Cloud Volumes ONTAP instance and each AWS resource associated with the instance.
You can add up to four tags from the user interface when creating a system, and then you can add more after it's created. Note that the API does not limit you to four tags when creating a system.
For information about tags, refer to AWS Documentation: Tagging your Amazon EC2 Resources.User name and password
These are the credentials for the Cloud Volumes ONTAP cluster administrator account. You can use these credentials to connect to Cloud Volumes ONTAP through ONTAP System Manager or the ONTAP CLI. Keep the default admin user name or change it to a custom user name.
Edit Credentials
Choose the AWS credentials and marketplace subscription to use with this Cloud Volumes ONTAP system.
Click Add Subscription to associate the selected credentials with a new AWS marketplace subscription. The subscription can be for an annual contract or to pay for Cloud Volumes ONTAP at an hourly rate.
If you purchased a license directly from NetApp (bring your own license (BYOL)), then an AWS subscription isn't required. NetApp has restricted the purchase, extension, and renewal of BYOL licensing. For more information, refer to Restricted availability of BYOL licensing for Cloud Volumes ONTAP.
Learn how to add additional AWS credentials to the Console.If multiple IAM users work in the same AWS account, then each user needs to subscribe. After the first user subscribes, the AWS marketplace informs subsequent users that they're already subscribed, as shown in the image below. While a subscription is in place for the AWS account, each IAM user needs to associate themselves with that subscription. If you see the message shown below, click the click here link to go to the Console website and complete the process.

-
Services: Keep the services enabled or disable the individual services that you don't want to use with this Cloud Volumes ONTAP system.
-
Learn more about Backup and Recovery
If you would like to utilize WORM and data tiering, you must disable Backup and Recovery and deploy a Cloud Volumes ONTAP system with version 9.8 or above.
-
HA Deployment Models: Choose an HA configuration.
For an overview of the deployment models, refer to Cloud Volumes ONTAP HA for AWS.
-
Location and Connectivity (single availability zone (AZ)) or Region & VPC (multiple AZs): Enter the network information that you recorded in the AWS worksheet.
The following table describes fields for which you might need guidance:
Field Description Generated security group
If you let the Console generate the security group for you, you need to choose how you'll allow traffic:
-
If you choose Selected VPC only, the source for inbound traffic is the subnet range of the selected VPC and the subnet range of the VPC where the Console agent resides. This is the recommended option.
-
If you choose All VPCs, the source for inbound traffic is the 0.0.0.0/0 IP range.
Use existing security group
If you use an existing firewall policy, ensure that it includes the required rules. Learn about firewall rules for Cloud Volumes ONTAP.
-
-
Connectivity and SSH Authentication: Choose connection methods for the HA pair and the mediator.
-
Floating IPs: If you chose multiple AZs, specify the floating IP addresses.
The IP addresses must be outside of the CIDR block for all VPCs in the region. For additional details, refer to AWS networking requirements for Cloud Volumes ONTAP HA in multiple AZs.
-
Route Tables: If you chose multiple AZs, select the route tables that should include routes to the floating IP addresses.
If you have more than one route table, it is very important to select the correct route tables. Otherwise, some clients might not have access to the Cloud Volumes ONTAP HA pair. For more information about route tables, refer to the AWS Documentation: Route Tables.
-
Data Encryption: Choose no data encryption or AWS-managed encryption.
For AWS-managed encryption, you can choose a different Customer Master Key (CMK) from your account or another AWS account.
You can't change the AWS data encryption method after you create a Cloud Volumes ONTAP system. -
Charging Methods and NSS Account: Specify which charging option would you like to use with this system, and then specify a NetApp Support Site account.
-
Cloud Volumes ONTAP Configuration (annual AWS Marketplace contract only): Review the default configuration and click Continue or click Change Configuration to select your own configuration.
If you keep the default configuration, then you only need to specify a volume and then review and approve the configuration.
-
Preconfigured Packages (hourly or BYOL only): Select one of the packages to quickly launch Cloud Volumes ONTAP, or click Change Configuration to select your own configuration.
If you choose one of the packages, then you only need to specify a volume and then review and approve the configuration.
-
IAM Role: It's best to keep the default option to let the Console create the role for you.
If you prefer to use your own policy, it must meet policy requirements for Cloud Volumes ONTAP nodes and the HA mediator.
-
Licensing: Change the Cloud Volumes ONTAP version as needed and select an instance type and the instance tenancy.
If a newer Release Candidate, General Availability, or patch release is available for the selected version, then the Console updates the system to that version when creating the system. For example, the update occurs if you select Cloud Volumes ONTAP 9.13.1 and 9.13.1 P4 is available. The update does not occur from one release to another—for example, from 9.13 to 9.14. -
Underlying Storage Resources: Choose a disk type, configure the underlying storage, and choose whether to keep data tiering enabled.
Note the following:
-
The disk type is for the initial volume (and aggregate). You can choose a different disk type for subsequent volumes (and aggregates).
-
If you choose a gp3 or io1 disk, the Console uses the Elastic Volumes feature in AWS to automatically increase the underlying storage disk capacity as needed. You can choose the initial capacity based on your storage needs and revise it after Cloud Volumes ONTAP is deployed. Learn more about support for Elastic Volumes in AWS.
-
If you choose a gp2 or st1 disk, you can select a disk size for all disks in the initial aggregate and for any additional aggregates that the Console creates when you use the simple provisioning option. You can create aggregates that use a different disk size by using the advanced allocation option.
-
You can choose a specific volume tiering policy when you create or edit a volume.
-
If you disable data tiering, you can enable it on subsequent aggregates.
-
-
Write Speed & WORM:
-
Choose Normal or High write speed, if desired.
-
Activate write once, read many (WORM) storage, if desired.
WORM can't be enabled if data tiering was enabled for Cloud Volumes ONTAP versions 9.7 and below. Reverting or downgrading to Cloud Volumes ONTAP 9.8 is blocked after enabling WORM and tiering.
-
If you activate WORM storage, select the retention period.
-
-
Create Volume: Enter details for the new volume or click Skip.
Some of the fields in this page are self-explanatory. The following table describes fields for which you might need guidance:
Field Description Size
The maximum size that you can enter largely depends on whether you enable thin provisioning, which enables you to create a volume that is bigger than the physical storage currently available to it.
Access control (for NFS only)
An export policy defines the clients in the subnet that can access the volume. By default, the Console enters a value that provides access to all instances in the subnet.
Permissions and Users / Groups (for CIFS only)
These fields enable you to control the level of access to a share for users and groups (also called access control lists or ACLs). You can specify local or domain Windows users or groups, or UNIX users or groups. If you specify a domain Windows user name, you must include the user's domain using the format domain\username.
Snapshot Policy
A Snapshot copy policy specifies the frequency and number of automatically created NetApp Snapshot copies. A NetApp Snapshot copy is a point-in-time file system image that has no performance impact and requires minimal storage. You can choose the default policy or none. You might choose none for transient data: for example, tempdb for Microsoft SQL Server.
Advanced options (for NFS only)
Select an NFS version for the volume: either NFSv3 or NFSv4.
Initiator group and IQN (for iSCSI only)
iSCSI storage targets are called LUNs (logical units) and are presented to hosts as standard block devices.
Initiator groups are tables of iSCSI host node names and control which initiators have access to which LUNs.
iSCSI targets connect to the network through standard Ethernet network adapters (NICs), TCP offload engine (TOE) cards with software initiators, converged network adapters (CNAs) or dedicated host bust adapters (HBAs) and are identified by iSCSI qualified names (IQNs).
When you create an iSCSI volume, the Console automatically creates a LUN for you. We’ve made it simple by creating just one LUN per volume, so there’s no management involved. After you create the volume, use the IQN to connect to the LUN from your hosts.The following image shows the first page of the volume creation wizard:

-
CIFS Setup: If you selected the CIFS protocol, set up a CIFS server.
Field Description DNS Primary and Secondary IP Address
The IP addresses of the DNS servers that provide name resolution for the CIFS server.
The listed DNS servers must contain the service location records (SRV) needed to locate the Active Directory LDAP servers and domain controllers for the domain that the CIFS server will join.Active Directory Domain to join
The FQDN of the Active Directory (AD) domain that you want the CIFS server to join.
Credentials authorized to join the domain
The name and password of a Windows account with sufficient privileges to add computers to the specified Organizational Unit (OU) within the AD domain.
CIFS server NetBIOS name
A CIFS server name that is unique in the AD domain.
Organizational Unit
The organizational unit within the AD domain to associate with the CIFS server. The default is CN=Computers.
If you configure AWS Managed Microsoft AD as the AD server for Cloud Volumes ONTAP, you should enter OU=Computers,OU=corp in this field.DNS Domain
The DNS domain for the Cloud Volumes ONTAP storage virtual machine (SVM). In most cases, the domain is the same as the AD domain.
NTP Server
Select Use Active Directory Domain to configure an NTP server using the Active Directory DNS. If you need to configure an NTP server using a different address, then you should use the API. Refer to the NetApp Console automation docs for details.
Note that you can configure an NTP server only when creating a CIFS server. It's not configurable after you create the CIFS server. -
Usage Profile, Disk Type, and Tiering Policy: Choose whether you want to enable storage efficiency features and edit the volume tiering policy, if needed.
For more information, refer to Choose a volume usage profile and Data tiering overview.
-
Review & Approve: Review and confirm your selections.
-
Review details about the configuration.
-
Click More information to review details about support and the AWS resources that the Console will purchase.
-
Select the I understand… check boxes.
-
Click Go.
-
The Console launches the Cloud Volumes ONTAP HA pair. You can track the progress on the Audit page.
If you experience any issues launching the HA pair, review the failure message. You can also select the system and click Re-create environment.
For additional help, go to NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP Support.
-
If you provisioned a CIFS share, give users or groups permissions to the files and folders and verify that those users can access the share and create a file.
-
If you want to apply quotas to volumes, use ONTAP System Manager or the ONTAP CLI.
Quotas enable you to restrict or track the disk space and number of files used by a user, group, or qtree.
After the deployment process completes, do not modify the system-generated Cloud Volumes ONTAP configurations in the AWS cloud portal, especially the system tags. Any changes made to these configurations may lead to unexpected behavior or data loss.




