Manage data-serving storage VMs for Cloud Volumes ONTAP in AWS
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


A storage VM is a virtual machine running within ONTAP that provides storage and data services to your clients. You might know this as an SVM or a vserver. Cloud Volumes ONTAP is configured with one storage VM by default, but some configurations support additional storage VMs.
To create additional data-serving storage VMs, you need to allocate IP addresses in AWS and then run ONTAP commands based on your Cloud Volumes ONTAP configuration.
Supported number of storage VMs
Multiple storage VMs are supported with specific Cloud Volumes ONTAP configurations starting with the 9.7 release. Go to the Cloud Volumes ONTAP Release Notes to verify the supported number of storage VMs for your version of Cloud Volumes ONTAP.
All other Cloud Volumes ONTAP configurations support one data-serving storage VM and one destination storage VM used for disaster recovery. You can activate the destination storage VM for data access if there's an outage on the source storage VM.
Verify limits for your configuration
Each EC2 instance supports a maximum number of private IPv4 addresses per network interface. You need to verify the limit before you allocate IP addresses in AWS for the new storage VM.
-
Go the Storage limits section in the Cloud Volumes ONTAP Release Notes.
-
Identify the maximum number of IP addresses per interface for your instance type.
-
Make note of this number because you'll need it in the next section when you allocate IP addresses in AWS.
Allocate IP addresses in AWS
Private IPv4 addresses must be assigned to port e0a in AWS before you create LIFs for the new storage VM.
Note that an optional management LIF for a storage VM requires a private IP address on a single-node system and on an HA pair in a single AZ. This management LIF provides a connection to management tools like SnapCenter.
-
Log in to AWS and open the EC2 service.
-
Select the Cloud Volumes ONTAP instance and click Networking.
If you're creating a storage VM on an HA pair, select node 1.
-
Scroll down to Network interfaces and click the Interface ID for port e0a.
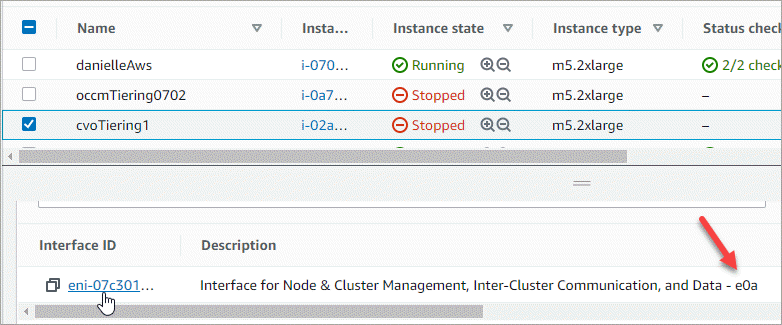
-
Select the network interface and click Actions > Manage IP addresses.
-
Expand the list of IP addresses for e0a.
-
Verify the IP addresses:
-
Count the number of allocated IP addresses to confirm that the port has room for additional IPs.
You should have identified the maximum number of supported IP addresses per interface in the previous section of this page.
-
Optional: Go to the ONTAP CLI for Cloud Volumes ONTAP and run network interface show to confirm that each of these IP addresses are in use.
If an IP address isn't in use, then you can use it with the new storage VM.
-
-
Back in the AWS Console, click Assign new IP address to assign additional IP addresses based on the amount that you need for the new storage VM.
-
single-node system: One unused secondary private IP is required.
An optional secondary private IP is required if you want to create a management LIF on the storage VM.
-
HA pair in a single AZ: One unused secondary private IP is required on node 1.
An optional secondary private IP is required if you want to create a management LIF on the storage VM.
-
HA pair in multiple AZs: One unused secondary private IP is required on each node.
-
-
If you're allocating the IP address on an HA pair in a single AZ, enable Allow secondary private IPv4 addresses to be reassigned.
-
Click Save.
-
If you have an HA pair in multiple AZs, then you'll need to repeat these steps for node 2.
Create a storage VM on a single-node system
These steps create a new storage VM on a single-node system. One private IP address is required to create a NAS LIF and another optional private IP address is needed if you want to create a management LIF.
-
Create the storage VM and a route to the storage VM.
vserver create -rootvolume-security-style unix -rootvolume root_svm_2 -snapshot-policy default -vserver svm_2 -aggregate aggr1network route create -destination 0.0.0.0/0 -vserver svm_2 -gateway subnet_gateway -
Create a NAS LIF.
network interface create -auto-revert true -vserver svm_2 -service-policy default-data-files -home-port e0a -address private_ip_x -netmask node1Mask -lif ip_nas_2 -home-node cvo-nodeWhere private_ip_x is an unused secondary private IP on e0a.
-
Optional: Create a storage VM management LIF.
network interface create -auto-revert true -vserver svm_2 -service-policy default-management -home-port e0a -address private_ip_y -netmask node1Mask -lif ip_svm_mgmt_2 -home-node cvo-nodeWhere private_ip_y is another unused secondary private IP on e0a.
-
Assign one or more aggregates to the storage VM.
vserver add-aggregates -vserver svm_2 -aggregates aggr1,aggr2This step is required because the new storage VM needs access to at least one aggregate before you can create volumes on the storage VM.
Create a storage VM on an HA pair in a single AZ
These steps create a new storage VM on an HA pair in a single AZ. One private IP address is required to create a NAS LIF and another optional private IP address is needed if you want to create a management LIF.
Both of these LIFs get allocated on node 1. The private IP addresses can move between nodes if failures occur.
-
Create the storage VM and a route to the storage VM.
vserver create -rootvolume-security-style unix -rootvolume root_svm_2 -snapshot-policy default -vserver svm_2 -aggregate aggr1network route create -destination 0.0.0.0/0 -vserver svm_2 -gateway subnet_gateway -
Create a NAS LIF on node 1.
network interface create -auto-revert true -vserver svm_2 -service-policy default-data-files -home-port e0a -address private_ip_x -netmask node1Mask -lif ip_nas_2 -home-node cvo-node1Where private_ip_x is an unused secondary private IP on e0a of cvo-node1. This IP address can be relocated to the e0a of cvo-node2 in case of takeover because the service policy default-data-files indicates that IPs can migrate to the partner node.
-
Optional: Create a storage VM management LIF on node 1.
network interface create -auto-revert true -vserver svm_2 -service-policy default-management -home-port e0a -address private_ip_y -netmask node1Mask -lif ip_svm_mgmt_2 -home-node cvo-node1Where private_ip_y is another unused secondary private IP on e0a.
-
Assign one or more aggregates to the storage VM.
vserver add-aggregates -vserver svm_2 -aggregates aggr1,aggr2This step is required because the new storage VM needs access to at least one aggregate before you can create volumes on the storage VM.
-
If you're running Cloud Volumes ONTAP 9.11.1 or later, modify the network service policies for the storage VM.
Modifying the services is required because it ensures that Cloud Volumes ONTAP can use the iSCSI LIF for outbound management connections.
network interface service-policy remove-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-files -service data-fpolicy-client network interface service-policy remove-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-files -service management-ad-client network interface service-policy remove-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-files -service management-dns-client network interface service-policy remove-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-files -service management-ldap-client network interface service-policy remove-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-files -service management-nis-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-blocks -service data-fpolicy-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-blocks -service management-ad-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-blocks -service management-dns-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-blocks -service management-ldap-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-blocks -service management-nis-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-iscsi -service data-fpolicy-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-iscsi -service management-ad-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-iscsi -service management-dns-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-iscsi -service management-ldap-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-iscsi -service management-nis-client
Create a storage VM on an HA pair in multiple AZs
These steps create a new storage VM on an HA pair in multiple AZs.
A floating IP address is required for a NAS LIF and is optional for a management LIF. These floating IP addresses don't require you to allocate private IPs in AWS. Instead, the floating IPs are automatically configured in the AWS route table to point to a specific node's ENI in the same VPC.
In order for floating IPs to work with ONTAP, a private IP address must be configured on every storage VM on each node. This is reflected in the steps below where an iSCSI LIF is created on node 1 and on node 2.
-
Create the storage VM and a route to the storage VM.
vserver create -rootvolume-security-style unix -rootvolume root_svm_2 -snapshot-policy default -vserver svm_2 -aggregate aggr1network route create -destination 0.0.0.0/0 -vserver svm_2 -gateway subnet_gateway -
Create a NAS LIF on node 1.
network interface create -auto-revert true -vserver svm_2 -service-policy default-data-files -home-port e0a -address floating_ip -netmask node1Mask -lif ip_nas_floating_2 -home-node cvo-node1-
The floating IP address must be outside of the CIDR blocks for all VPCs in the AWS region in which you deploy the HA configuration. 192.168.209.27 is an example floating IP address. Learn more about choosing a floating IP address.
-
-service-policy default-data-filesindicates that IPs can migrate to the partner node.
-
-
Optional: Create a storage VM management LIF on node 1.
network interface create -auto-revert true -vserver svm_2 -service-policy default-management -home-port e0a -address floating_ip -netmask node1Mask -lif ip_svm_mgmt_2 -home-node cvo-node1 -
Create an iSCSI LIF on node 1.
network interface create -vserver svm_2 -service-policy default-data-blocks -home-port e0a -address private_ip -netmask nodei1Mask -lif ip_node1_iscsi_2 -home-node cvo-node1-
This iSCSI LIF is required to support LIF migration of the floating IPs in the storage VM. It doesn't have to be an iSCSI LIF, but it can't be configured to migrate between nodes.
-
-service-policy default-data-blockindicates that an IP address does not migrate between nodes. -
private_ip is an unused secondary private IP address on eth0 (e0a) of cvo_node1.
-
-
Create an iSCSI LIF on node 2.
network interface create -vserver svm_2 -service-policy default-data-blocks -home-port e0a -address private_ip -netmaskNode2Mask -lif ip_node2_iscsi_2 -home-node cvo-node2-
This iSCSI LIF is required to support LIF migration of the floating IPs in the storage VM. It doesn't have to be an iSCSI LIF, but it can't be configured to migrate between nodes.
-
-service-policy default-data-blockindicates that an IP address does not migrate between nodes. -
private_ip is an unused secondary private IP address on eth0 (e0a) of cvo_node2.
-
-
Assign one or more aggregates to the storage VM.
vserver add-aggregates -vserver svm_2 -aggregates aggr1,aggr2This step is required because the new storage VM needs access to at least one aggregate before you can create volumes on the storage VM.
-
If you're running Cloud Volumes ONTAP 9.11.1 or later, modify the network service policies for the storage VM.
Modifying the services is required because it ensures that Cloud Volumes ONTAP can use the iSCSI LIF for outbound management connections.
network interface service-policy remove-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-files -service data-fpolicy-client network interface service-policy remove-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-files -service management-ad-client network interface service-policy remove-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-files -service management-dns-client network interface service-policy remove-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-files -service management-ldap-client network interface service-policy remove-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-files -service management-nis-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-blocks -service data-fpolicy-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-blocks -service management-ad-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-blocks -service management-dns-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-blocks -service management-ldap-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-blocks -service management-nis-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-iscsi -service data-fpolicy-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-iscsi -service management-ad-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-iscsi -service management-dns-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-iscsi -service management-ldap-client network interface service-policy add-service -vserver <svm-name> -policy default-data-iscsi -service management-nis-client


