ONTAP Select storage: General concepts and characteristics
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


Discover general storage concepts that apply to the ONTAP Select environment before exploring the specific storage components.
Phases of storage configuration
The major configuration phases of the ONTAP Select host storage include the following:
-
Pre-deployment prerequisites
-
Make sure that each hypervisor host is configured and ready for an ONTAP Select deployment.
-
The configuration involves the physical drives, RAID controllers and groups, LUNs, as well as related network preparation.
-
This configuration is performed outside of ONTAP Select.
-
-
Configuration using the hypervisor administrator utility
-
You can configure certain aspects of the storage using the hypervisor administration utility (for example, vSphere in a VMware environment).
-
This configuration is performed outside of ONTAP Select.
-
-
Configuration using the ONTAP Select Deploy administration utility
-
You can use the Deploy administration utility to configure the core logical storage constructs.
-
This is performed either explicitly through CLI commands or automatically by the utility as part of a deployment.
-
-
Post-deployment configuration
-
After an ONTAP Select deployment completes, you can configure the cluster using the ONTAP CLI or System Manager.
-
This configuration is performed outside of ONTAP Select Deploy.
-
Managed versus unmanaged storage
Storage that is accessed and directly controlled by ONTAP Select is managed storage. Any other storage on the same hypervisor host is unmanaged storage.
Homogeneous physical storage
All the physical drives comprising the ONTAP Select managed storage must be homogeneous. That is, all the hardware must be the same regarding the following characteristics:
-
Type (SAS, NL-SAS, SATA, SSD)
-
Speed (RPM)
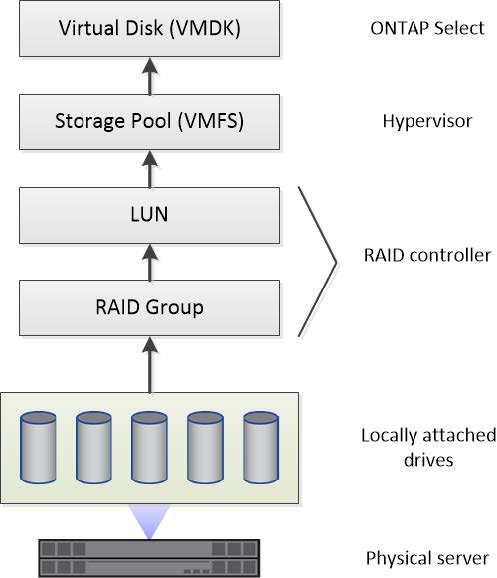
Illustration of the local storage environment
Each hypervisor host contains local disks and other logical storage components that can be used by ONTAP Select. These storage components are arranged in a layered structure, from the physical disk.
Characteristics of the local storage components
There are several concepts that apply to the local storage components used in an ONTAP Select environment. You should be familiar with these concepts before preparing for an ONTAP Select deployment. These concepts are arranged according to category: RAID groups and LUNs, storage pools, and virtual disks.
Grouping physical drives into RAID groups and LUNs
One or more physical disks can be locally attached to the host server and available to ONTAP Select. The physical disks are assigned to RAID groups, which are then presented to the hypervisor host operating system as one or more LUNs. Each LUN is presented to the hypervisor host operating system as a physical hard drive.
When configuring an ONTAP Select host, you should be aware of the following:
-
All managed storage must be accessible through a single RAID controller
-
Depending on the vendor, each RAID controller supports a maximum number of drives per RAID group
One or more RAID groups
Each ONTAP Select host must have a single RAID controller. You should create a single RAID group for ONTAP Select. However, in certain situations you might consider creating more than one RAID group. Refer to Summary of best practices.
Storage pool considerations
There are several issues related to the storage pools that you should be aware of as part of preparing to deploy ONTAP Select.

|
In a VMware environment, a storage pool is synonymous with a VMware datastore. |
Storage pools and LUNs
Each LUN is seen as a local disk on the hypervisor host and can be part of one storage pool. Each storage pool is formatted with a file system that the hypervisor host OS can use.
You must make sure that the storage pools are created properly as part of an ONTAP Select deployment. You can create a storage pool using the hypervisor administration tool. For example, with VMware you can use the vSphere client to create a storage pool. The storage pool is then passed in to the ONTAP Select Deploy administration utility.
Manage the virtual disks on ESXi
There are several issues related to the virtual disks that you should be aware of as part of preparing to deploy ONTAP Select.
Virtual disks and file systems
The ONTAP Select virtual machine is allocated multiple virtual disk drives. Each virtual disk is actually a file contained in a storage pool and is maintained by the hypervisor. There are several types of disks used by ONTAP Select, primarily system disks and data disks.
You should also be aware of the following regarding virtual disks:
-
The storage pool must be available before the virtual disks can be created.
-
The virtual disks cannot be created before the virtual machine is created.
-
You must rely on the ONTAP Select Deploy administration utility to create all virtual disks (that is, an administrator must never create a virtual disk outside of the Deploy utility).
Configuring the virtual disks
The virtual disks are managed by ONTAP Select. They are created automatically when you create a cluster using the Deploy administration utility.
Illustration of the external storage environment on ESXi
The ONTAP Select vNAS solution enables ONTAP Select to use datastores residing on storage that is external to the hypervisor host. The datastores can be accessed through the network using VMware vSAN or directly at an external storage array.
ONTAP Select can be configured to use the following types of VMware ESXi network datastores which are external to the hypervisor host:
-
vSAN (Virtual SAN)
-
VMFS
-
NFS
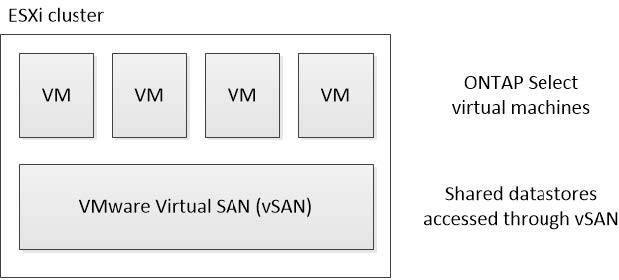
vSAN datastores
Every ESXi host can have one or more local VMFS datastores. Normally these datastores are only accessible to the local host. However, VMware vSAN allows each of the hosts in an ESXi cluster to share all of the datastores in the cluster as if they were local. The following figure illustrates how vSAN creates a pool of datastores that are shared among the hosts in the ESXi cluster.
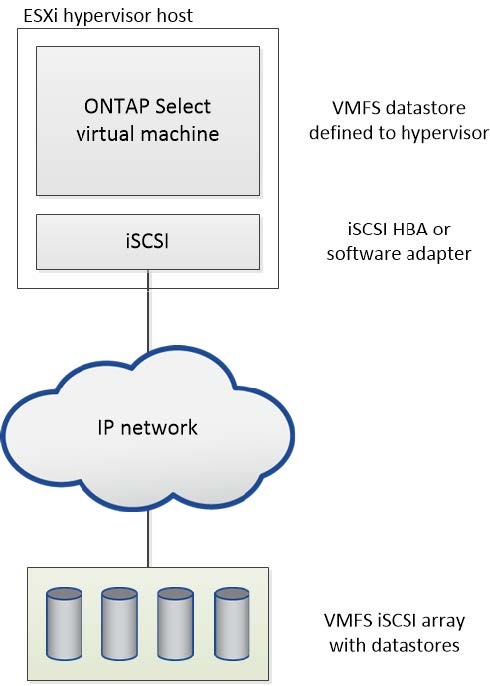
VMFS datastore on external storage array
You can create a VMFS datastore residing on an external storage array. The storage is accessed using one of several different network protocols. The following figure illustrates a VMFS datastore on an external storage array accessed using the iSCSI protocol.

|
ONTAP Select supports all external storage arrays described in the VMware Storage/SAN Compatibility documentation, including iSCSI, Fiber Channel, and Fiber Channel over Ethernet. |
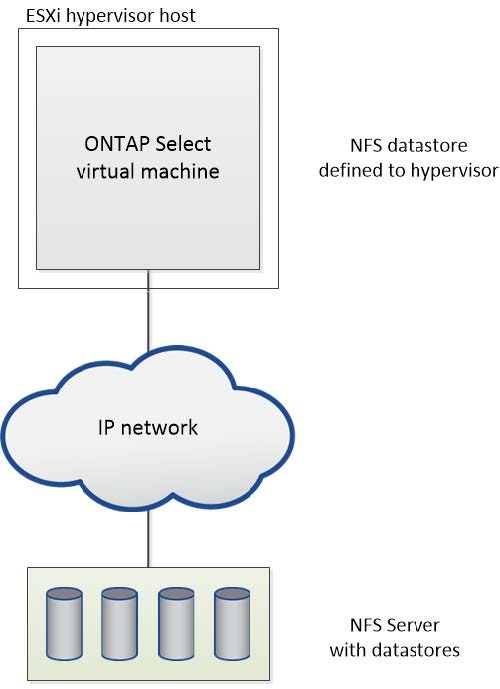
NFS datastore on external storage array
You can create an NFS datastore residing on an external storage array. The storage is accessed using the NFS network protocol. The following figure illustrates an NFS datastore on external storage that is accessed through the NFS server appliance.