SnapMirror active sync preferred site
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


SnapMirror active sync behavior is symmetric, with one important exception - preferred site configuration.
SnapMirror active sync will consider one site the "source" and the other the "destination". This implies a one-way replication relationship, but this does not apply to IO behavior. Replication is bidirectional and symmetric and IO response times are the same on either side of the mirror.
The source designation is controls the preferred site. If the replication link is lost, the LUN paths on the source copy will continue to serve data while the LUN paths on the destination copy will become unavailable until replication is reestablished and SnapMirror reenters a synchronous state. The paths will then resume serving data.
The sourced/destination configuration can be viewed via SystemManager:
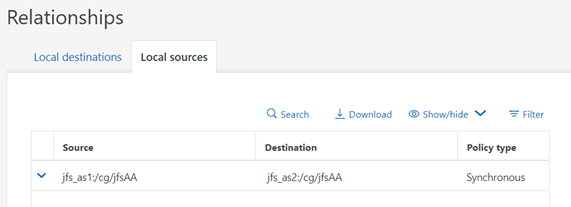
or at the CLI:
Cluster2::> snapmirror show -destination-path jfs_as2:/cg/jfsAA
Source Path: jfs_as1:/cg/jfsAA
Destination Path: jfs_as2:/cg/jfsAA
Relationship Type: XDP
Relationship Group Type: consistencygroup
SnapMirror Schedule: -
SnapMirror Policy Type: automated-failover-duplex
SnapMirror Policy: AutomatedFailOverDuplex
Tries Limit: -
Throttle (KB/sec): -
Mirror State: Snapmirrored
Relationship Status: InSync
The key is that the source is the SVM on cluster1. As mentioned above, the terms "source" and "destination" don't describe the flow of replicated data. Both sites can process a write and replicate it to the opposite site. In effect, both clusters are sources and destinations. The effect of designating one cluster as a source simply controls which cluster survives as a read-write storage system if the replication link is lost.


