SAN (FC, FCoE, NVMe/FC, iSCSI), RDM
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


In vSphere, there are four ways to use block storage devices:
-
With VMFS datastores
-
With raw device mapping (RDM)
-
As an iSCSI-connected LUN or NVMe/TCP-connected namespace accessed and controlled by a software initiator from a VM guest OS
-
As a vVols datastore
VMFS is a high-performance clustered file system that provides datastores that are shared storage pools. VMFS datastores can be configured with LUNs accessed using FC, iSCSI, FCoE, or with NVMe namespaces accessed using the NVMe/FC or NVMe/TCP protocols. VMFS allows storage to be accessed simultaneously by every ESX server in a cluster. The maximum LUN size is generally 128TB beginning with ONTAP 9.12.1P2 (and earlier with ASA systems); therefore, a maximum-size VMFS 5 or 6 datastore of 64TB can be created by using a single LUN.

|
Extents are a vSphere storage concept whereby you can "stitch" multiple LUNs together to create a single larger datastore. You should never use extents to reach your desired datastore size. A single LUN is the best practice for a VMFS datastore. |
vSphere includes built-in support for multiple paths to storage devices. vSphere can detect the type of storage device for supported storage systems and automatically configures the multipathing stack to support the capabilities of the storage system in use, regarldess of the protocol used, or if using ASA, AFF, FAS, or software defined ONTAP.
Both vSphere and ONTAP support Asymmetric Logical Unit Access (ALUA) to establish active/optimized and active/non-optimized paths for Fibre Channel and iSCSI, and Asymmetric Namespace Access (ANA) for NVMe namespaces using NVMe/FC and NVMe/TCP. In ONTAP, an ALUA or ANA-optimized path follows a direct data path, using a target port on the node that hosts the LUN or namespace being accessed. ALUA/ANA is turned on by default in both vSphere and ONTAP. The multipathing software in vSphere recognizes the ONTAP cluster as ALUA or ANA, and it uses the appropriate native plug-in with the round robin load balance policy.
With NetApp's ASA systems, the LUNs and namespaces are presented to the ESXi hosts with symmetric pathing. Meaning that all paths are active and optimized. The multipathing software in vSphere recognizes the ASA system as symmetric, and it uses the appropriate native plug-in with the round robin load balance policy.

|
Refer to Recommended ESXi host and other ONTAP settings for optimized multipathing settings. |
ESXi does not see any LUNs, namespaces, or paths beyond its limits. In a larger ONTAP cluster, it is possible to reach the path limit before the LUN limit. To address this limitation, ONTAP supports selective LUN map (SLM) in release 8.3 and later.

|
Refer to the VMware Configuration Maximums tool for the most up to date supported limits in ESXi. |
SLM limits the nodes that advertise paths to a given LUN. It is a NetApp best practice to have at least two LIFs per node per SVM and to use SLM to limit the paths advertised to the node hosting the LUN and its HA partner. Although other paths exist, they aren't advertised by default. It is possible to modify the paths advertised with the add and remove reporting node arguments within SLM. Note that LUNs created in releases before 8.3 advertise all paths and need to be modified to only advertise the paths to the hosting HA pair. For more information about SLM, review section 5.9 of TR-4080. The previous method of portsets can also be used to further reduce the available paths for a LUN. Portsets help by reducing the number of visible paths through which initiators in an igroup can see LUNs.
-
SLM is enabled by default. Unless you are using portsets, no additional configuration is required.
-
For LUNs created before Data ONTAP 8.3, manually apply SLM by running the
lun mapping remove-reporting-nodescommand to remove the LUN reporting nodes and restrict LUN access to the LUN-owning node and its HA partner.
SCSI-based block protocols (iSCSI, FC, and FCoE) access LUNs by using LUN IDs and serial numbers, along with unique names. FC and FCoE use worldwide names (WWNNs and WWPNs), and iSCSI uses iSCSI qualified names (IQNs) to establish paths based on LUN to igroup mappings filtered by portsets and SLM. NVMe-based block protocols are managed by assigning the namespace with an automatically generated namespace ID to an NVMe subsystem and mapping that subsystem to the NVMe Qualified Name (NQN) of the host(s). Regardless of FC or TCP, NVMe namespaces are mapped using the NQN and not the WWPN or WWNN. The host then creates a software-defined controller for the mapped subsystem to access its namespaces. The path to LUNs and namespaces inside of ONTAP is meaningless to the block protocols and is not presented anywhere in the protocol. Therefore, a volume that contains only LUNs does not need to be internally mounted at all, and a junction path is not needed for volumes that contain LUNs used in datastores.
Other best practices to consider:
-
Check Recommended ESXi host and other ONTAP settings for settings recommended by NetApp in collaboration with VMware.
-
Make sure that a logical interface (LIF) is created for each SVM on each node in the ONTAP cluster for maximum availability and mobility. ONTAP SAN best practice is to use two physical ports and LIFs per node, one for each fabric. ALUA is used to parse paths and identify active optimized (direct) paths versus active nonoptimized paths. ALUA is used for FC, FCoE, and iSCSI.
-
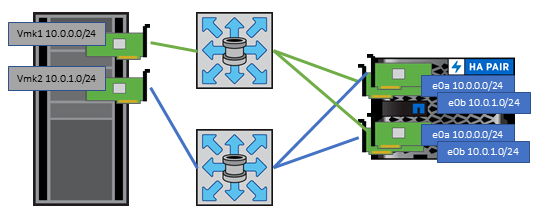
For iSCSI networks, use multiple VMkernel network interfaces on different network subnets with NIC teaming when multiple virtual switches are present. You can also use multiple physical NICs connected to multiple physical switches to provide HA and increased throughput. The following figure provides an example of multipath connectivity. In ONTAP, configure either a single-mode interface group for failover with two or more links that are connected to two or more switches, or use LACP or other link-aggregation technology with multimode interface groups to provide HA and the benefits of link aggregation.
-
If the Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) is used in ESXi for target authentication, it must also be configured in ONTAP using the CLI (
vserver iscsi security create) or with System Manager (edit Initiator Security under Storage > SVMs > SVM Settings > Protocols > iSCSI). -
Use ONTAP tools for VMware vSphere to create and manage LUNs and igroups. The plug-in automatically determines the WWPNs of servers and creates appropriate igroups. It also configures LUNs according to best practices and maps them to the correct igroups.
-
Use RDMs with care because they can be more difficult to manage, and they also use paths, which are limited as described earlier. ONTAP LUNs support both physical and virtual compatibility mode RDMs.
-
For more on using NVMe/FC with vSphere 7.0, see this ONTAP NVMe/FC Host Configuration guide and TR-4684.The following figure depicts multipath connectivity from a vSphere host to an ONTAP LUN.