What is cross-grid replication?
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


Cross-grid replication is the automatic replication of objects between selected S3 buckets in two StorageGRID systems that are connected in a grid federation connection. Account clone is required for cross-grid replication.
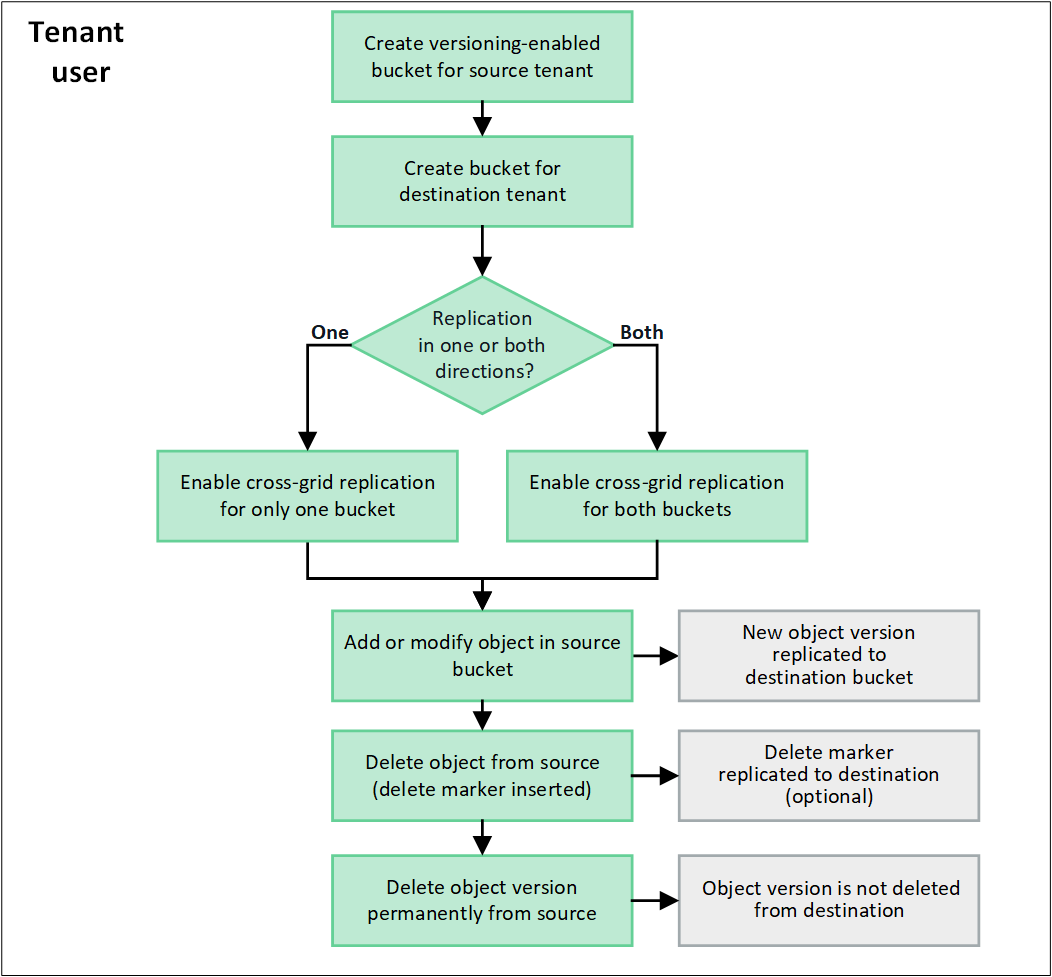
Workflow for cross-grid replication
The workflow diagram summarizes the steps for configuring cross-grid replication between buckets on two grids.
Requirements for cross-grid replication
If a tenant account has the Use grid federation connection permission to use one or more grid federation connections, a tenant user with Root access permission can create buckets in the corresponding tenant accounts on each grid. These buckets:
-
Can have different names from each other
-
Can have different regions
-
Must have versioning enabled
-
Must be empty
After both buckets have been created, cross-grid replication can be configured for either or both buckets.
How cross-grid replication works
You can configure cross-grid replication to occur in one direction or in both directions.
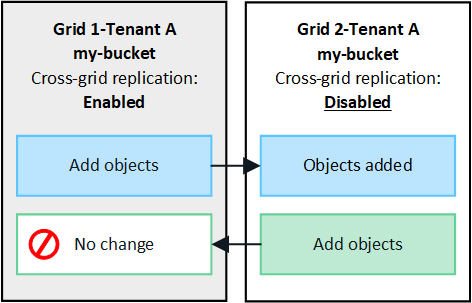
Replication in one direction
If you enable cross-grid replication for a bucket on only one grid, objects added to that bucket (the source bucket) are replicated to the corresponding bucket on the other grid (the destination bucket). However, objects added to the destination bucket aren't replicated back to the source. In the figure, cross-grid replication is enabled for my-bucket from Grid 1 to Grid 2, but it's not enabled in the other direction.
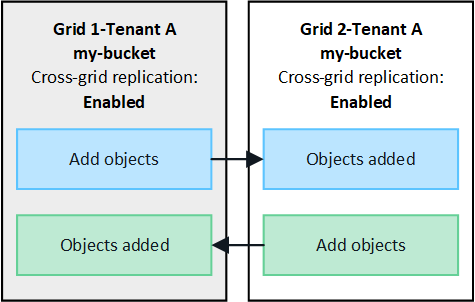
Replication in both directions
If you enable cross-grid replication for the same bucket on both grids, objects added to either bucket are replicated to the other grid. In the figure, cross-grid replication is enabled for my-bucket in both directions.
What happens when objects are ingested?
When an S3 client adds an object to a bucket that has cross-grid replication enabled, the following happens:
-
StorageGRID automatically replicates the object from the source bucket to the destination bucket. The time to perform this background replication operation depends on several factors, including the number of other replication operations that are pending.
The S3 client can verify an object's replication status by issuing a GetObject or HeadObject request. The response includes a StorageGRID-specific
x-ntap-sg-cgr-replication-statusresponse header, which has one of the following values:Grid Replication status Source
-
COMPLETED: The replication was successful for all grid connections.
-
PENDING: The object hasn't been replicated to at least one grid connection.
-
FAILURE: Replication isn't pending for any grid connection and at least one failed with a permanent failure. A user must resolve the error.
Destination
REPLICA: The object was replicated from the source grid.
StorageGRID doesn't support the x-amz-replication-statusheader. -
-
StorageGRID uses each grid's active ILM policies to manage the objects, just as it would any other object. For example, Object A on Grid 1 might be stored as two replicated copies and retained forever, while the copy of Object A that was replicated to Grid 2 might be stored using 2+1 erasure coding and deleted after three years.
What happens when objects are deleted?
As described in Delete data flow, StorageGRID can delete an object for any of these reasons:
-
The S3 client issues a delete request.
-
A Tenant Manager user selects the Delete objects in bucket option to remove all objects from a bucket.
-
The bucket has a lifecycle configuration, which expires.
-
The last time period in the ILM rule for the object ends, and there are no further placements specified.
When StorageGRID deletes an object because of a Delete objects in bucket operation, bucket lifecycle expiration, or ILM placement expiration, the replicated object is never deleted from the other grid in a grid federation connection. However, delete markers added to the source bucket by S3 client deletes can optionally be replicated to the destination bucket.
To understand what happens when an S3 client deletes objects from a bucket that has cross-grid replication enabled, review how S3 clients delete objects from buckets that have versioning enabled, as follows:
-
If an S3 client issues a delete request that includes a version ID, that version of the object is permanently removed. No delete marker is added to the bucket.
-
If an S3 client issues a delete request that doesn't include a version ID, StorageGRID doesn't delete any object versions. Instead, it adds a delete marker to the bucket. The delete marker causes StorageGRID to act as if the object was deleted:
-
A GetObject request without a version ID fails with
404 No Object Found -
A GetObject request with a valid version ID succeeds and returns the requested object version.
-
When an S3 client deletes an object from a bucket that has cross-grid replication enabled, StorageGRID determines whether to replicate the delete request to the destination, as follows:
-
If the delete request includes a version ID, that object version is permanently removed from the source grid. However, StorageGRID doesn't replicate delete requests that include a version ID, so the same object version isn't deleted from the destination.
-
If the delete request doesn't include a version ID, StorageGRID can optionally replicate the delete marker, based on how cross-grid replication is configured for the bucket:
-
If you choose to replicate delete markers (default), a delete marker is added to the source bucket and replicated to the destination bucket. In effect, the object appears to be deleted on both grids.
-
If you choose not to replicate delete markers, a delete marker is added to the source bucket but isn't replicated to the destination bucket. In effect, objects that are deleted on the source grid aren't deleted on the destination grid.
-
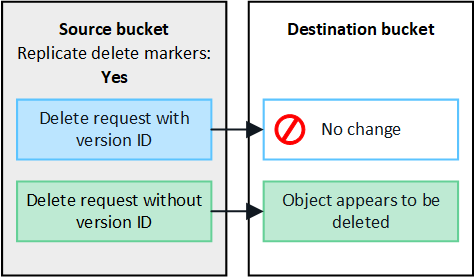
In the figure, Replicate delete markers was set to Yes when cross-grid replication was enabled. Delete requests for the source bucket that include a version ID don't delete objects from the destination bucket. Delete requests for the source bucket that don't include a version ID appear to delete objects in the destination bucket.

|
If you want to keep object deletions synchronized between grids, create corresponding S3 lifecycle configurations for the buckets on both grids. |
How encrypted objects are replicated
When you use cross-grid replication to replicate objects between grids, you can encrypt individual objects, use default bucket encryption, or configure grid-wide encryption. You can add, modify, or remove default bucket or grid-wide encryption settings before or after you enable cross-grid replication for a bucket.
To encrypt individual objects, you can use SSE (server-side encryption with StorageGRID-managed keys) when adding the objects to the source bucket. Use the x-amz-server-side-encryption request header and specify AES256. See Use server-side encryption.

|
Using SSE-C (server-side encryption with customer-provided keys) isn't supported for cross-grid replication. The ingest operation will fail. |
To use default encryption for a bucket, use a PutBucketEncryption request and set the SSEAlgorithm parameter to AES256. Bucket-level encryption applies to any objects ingested without the x-amz-server-side-encryption request header. See Operations on buckets.
To use grid-level encryption, set the Stored object encryption option to AES-256. Grid-level encryption applies to any objects that aren't encrypted at the bucket level or that are ingested without the x-amz-server-side-encryption request header. See Configure network and object options.

|
SSE doesn't support AES-128. If the Stored object encryption option is enabled for the source grid using the AES-128 option, the use of the AES-128 algorithm isn't propagated to the replicated object. Instead, the replicated object uses the destination's default bucket or grid-level encryption setting, if available. |
When determining how to encrypt source objects, StorageGRID applies these rules:
-
Use the
x-amz-server-side-encryptioningest header, if present. -
If an ingest header isn't present, use the bucket default encryption setting, if configured.
-
If a bucket setting isn't configured, use the grid-wide encryption setting, if configured.
-
If a grid-wide setting isn't present, don't encrypt the source object.
When determining how to encrypt replicated objects, StorageGRID applies these rules in this order:
-
Use the same encryption as the source object, unless that object uses AES-128 encryption.
-
If the source object isn't encrypted or it uses AES-128, use the destination bucket's default encryption setting, if configured.
-
If the destination bucket doesn't have an encryption setting, use the destination's grid-wide encryption setting, if configured.
-
If a grid-wide setting isn't present, don't encrypt the destination object.
Cross-grid replication with S3 Object Lock
You can configure cross-grid replication between StorageGRID buckets with S3 Object Lock enabled under the following circumstances.
| When S3 Object Lock on the source bucket is… | And S3 Object Lock on the destination bucket is… |
|---|---|
Enabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Enabled |
When S3 Object Lock on the source bucket is enabled:
-
The objects are locked with retention settings at the destination in this order:
-
The source object's retention header values for:
x-amz-object-lock-modex-amz-object-lock-retain-until-date -
The source bucket's default retention, if set.
-
The destination bucket's default retention, if set.
The destination bucket's default retention doesn’t override the retention settings replicated from the source object.
-
-
You can set the legal hold status for the destination object by using
x-amz-object-lock-legal-holdwhen uploading the object. -
An error occurs if the destination tenant or bucket doesn’t support the source object's S3 Object Lock settings. Refer to Cross-grid replication alerts and errors.
When S3 Object Lock on the source bucket is disabled:
-
You can configure the default retention on the destination bucket to apply S3 Object Lock retention settings to the destination object.
-
The destination object can't set a legal hold status.
PutObjectTagging and DeleteObjectTagging aren't supported
PutObjectTagging and DeleteObjectTagging requests aren't supported for objects in buckets that have cross-grid replication enabled.
If an S3 client issues a PutObjectTagging or DeleteObjectTagging request, 501 Not Implemented is returned. The message is Put(Delete) ObjectTagging isn't available for buckets that have cross-grid replication configured.
PutObjectRetention and PutObjectLegalHold aren't supported
PutObjectRetention and PutObjectLegalHold requests aren't fully supported for objects in buckets that have cross-grid replication enabled.
If an S3 client issues a PutObjectRetention or PutObjectLegalHold request, the source object's settings are modified, but the changes aren't applied to the destination.
How segmented objects are replicated
The source grid's maximum segment size applies to objects replicated to the destination grid. When objects are replicated to another grid, the Maximum Segment Size setting (Configuration > System > Storage options) of the source grid is used on both grids. For example, suppose the maximum segment size for the source grid is 1 GB, while the maximum segment size of the destination grid is 50 MB. If you ingest a 2-GB object on the source grid, that object is saved as two 1-GB segments. It's also replicated to the destination grid as two 1-GB segments, even though that grid's maximum segment size is 50 MB.


