SB-4293: Automating SAP system copy, refresh, and clone workflows with ALPACA and NetApp SnapCenter
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


This document focuses on integrating NetApp® Snapshot™ and FlexClone® technologies into ALPACA automation workflows.
Solution overview
SAP systems and solutions operations are very complex. However, for companies that use SAP, the systems and services are central to their business processes. By automating recurring daily operational tasks, like system copy and refresh operations, SAP system administrators can manage more systems with less effort, produce repeatable results, and reduce human error.
This document focuses on integrating NetApp® Snapshot™ and FlexClone® technologies into ALPACA automation workflows.
The Automating Landscapes Proactively—Cloud and Anywhere (ALPACA) suite is a comprehensive management interface that enables detailed oversight and monitoring across your SAP landscapes. ALPACA streamlines and expedites SAP infrastructure operations, ensuring optimal availability and transparency. It provides a comprehensive array of tools for managing the entire landscape, including infrastructure, and proactively notifies about anomalies such as service disruptions, job halts, and congestion. The suite is designed to operate seamlessly in on-premises, hybrid, and all-cloud environments, including multicloud scenarios, ensuring adaptability to any infrastructure. This module-based framework automates standard and regular SAP admin tasks as well as complex scenarios like failover during an outage. administrators/experts, operators, and managers, ALPACA gives these professionals a high degree of control and automation.
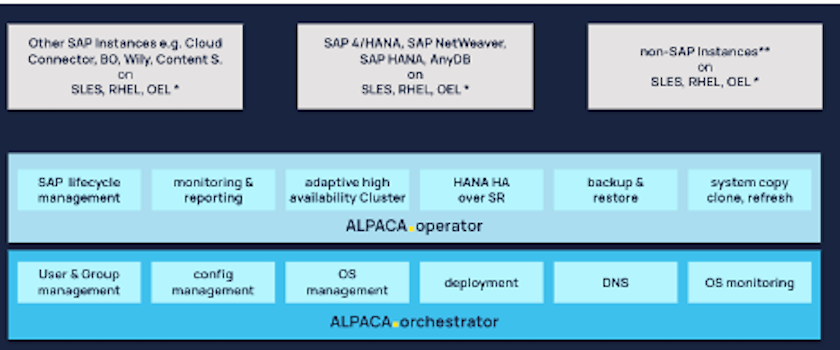
This document describes how ALPACA integrates with NetApp SnapCenter®, the tool to orchestrate Snapshot based backups, perform restores, and create FlexClone volumes. This integration allows SAP administrators to significantly accelerate SAP system daily operational tasks. NetApp Snapshot, FlexClone, and SnapRestore® technologies accelerate backup, restore, and clone operations because NetApp's storage technology is pointer-based. This approach is fast, and it also reduces the storage overhead during clone operations, because only new and changed data (not existing data) must be written to the storage medium. This is true regardless of whether it is an on-premises NetApp storage system or a NetApp storage solution at one of the three major cloud providers.
Target audience
This document is aimed at SAP system administrators who have carried out SAP system copies manually and would like to automate this activity with ALPACA. The intended goal of combining NetApp Snapshot and FlexClone technologies, orchestrated by NetApp SnapCenter, with ALPACA workflows is to reduce the duration of fully automated SAP system copies.
SAP system clone, copy, and refresh scenarios
The term SAP system copy is often used as a synonym for three different processes: SAP system clone, SAP system copy, and SAP system refresh. It is important to distinguish between these operations, because the workflows and use cases differ.
-
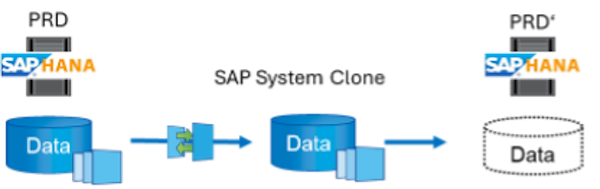
SAP system clone. An SAP system clone is an identical clone of a source SAP system. SAP system clones are typically used to address logical corruption or to test disaster recovery scenarios. With a system clone operation, the host name, instance number, and secure identifier (SID) remain the same. It is therefore important to establish proper network fencing for the target system to make sure that thereis no communication with the production environment.
-
SAP system copy. An SAP system copy is a setup of a new target SAP system with data from a source SAP system. For example, the new target system could be an additional test system with data from the production system. The host name, instance number, and SID are different for the source and target systems.The new system is not isolated from the source system.

-
SAP system refresh. An SAP system refresh is a refresh of an existing target SAP system with data from a source SAP system. The target system is typically part of an SAP transport landscape—for example, a sandbox system—that is refreshed with data from the production system. The hostname, instance number, and SID are different for the source and target systems.

Even though these are three different use cases, the data management process stays the same. All three uses cases use the same underlying data management technology—NetApp Snapshot and FlexClone.
Solution technology
The overall solution consists of these main components:
-
SAP source system with installed SnapCenter agent and SnapCenter database Plug-In
-
SAP target system with installed SnapCenter agent and SnapCenter database Plug-In
-
ALPACA system with configured SAP source and SAP target system
-
NetApp SnapCenter Server
-
NetApp storage system:
-
Physical on-premises hardware: AFF-A, AFF-C, ASA-A, ASA-C, or FAS series
-
Software-defined storage on premises: ONTAP® Select
-
NetApp cloud storage:
-
Cloud Volumes ONTAP for AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure
-
Azure NetApp Files
-
Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP
-
-
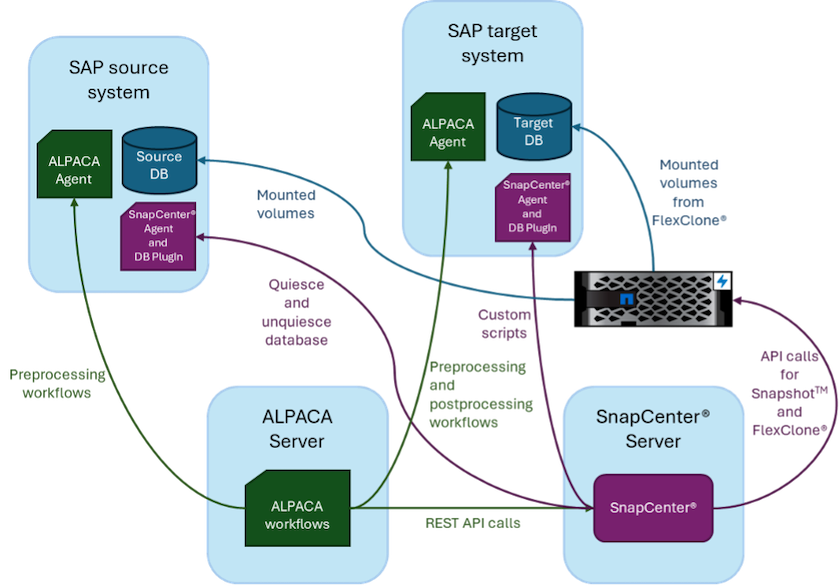
The following image shows the ALPACA server, the NetApp SnapCenter server, the NetApp storage system, the SAP source and SAP target systems, and how everything is integrated. The goal is to make the integration as flexible as possible by using the SnapCenter REST API to ensure maximum reuse of configuration work that has already been done inside exiting components.
Use case summary
There are several scenarios in which data from a source system must be made available to a target system for testing or training purposes. These test and training systems must be updated regularly with data from the source system to make sure that testing and training are performed with the current dataset. These system refresh operations consist of multiple tasks on the infrastructure, database, and application layers, and they can take several days, depending on the level of automation.
To speed up operations, automate tasks, and eliminate human error at the infrastructure, database, and application levels, you can use ALPACA Workflows. Instead of restoring a backup from the source system to the target system, which is time consuming and involves high resource consumption, this integration uses NetApp Snapshot and FlexClone technologies. All the tasks required to spin up a database are completed in minutes rather than hours. The time required for the cloning process does not depend on the size of the database; therefore, even very large systems can be created in just a few minutes. ALPACA further reduces run time by automating tasks at the operating system and database levels as well as on the SAP postprocessing side.
THe following image shows possible operational efficiency improvements when you use automation.

Integrating the technology components
The actual integration of SnapCenter in an ALPACA workflow consists of using shell scripts to access the NetApp SnapCenter REST API. This REST API-based integration creates a Snapshot copy of the SAP source system, creates a FlexClone volume, and mounts it onto the SAP target system.
Storage and SAP administrators know how to develop scripts that are triggered by SnapCenter and executed by the SnapCenter agent to automate recurring daily operation tasks. This loosely coupled architecture, which triggers SnapCenter tasks via shell scripts, enables them to reuse their existing automation procedures to achieve the desired results faster using ALPACA as a workflow engine for end-to-end automation.
Conclusion
The combination of ALPACA and NetApp data management technology provides a powerful solution that can dramatically reduce the time and effort needed for the most complex and time-consuming tasks related to SAP system administration. This combination can also help avoid the configuration drift that human error can cause between the systems.
Because system refreshes, copies, clones, and disaster recovery testing are very sensitive procedures, implementing such a solution can free up precious administration time. It can also reinforce the trust that the line-of-business staff members have in the SAP system administrators. They will see how much troubleshooting time can be saved and how much easier it is to copy systems for testing or other purposes. This is true regardless of where the source and target systems are operated—on premises, in a public cloud, hybrid cloud, or hybrid multicloud.
Where to find additional information
To learn more about the information contained in this document, review the following documents and websites:
Version history
| Version | Date | Update summary |
|---|---|---|
Version 0.1 |
04.2024 |
1st draft. |
Version 0.2 |
06.2024 |
Converted to html format |


