Red Hat Virtualization: NetApp HCI with Cisco ACI
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


Red Hat Virtualization (RHV) is an enterprise virtual data center platform that runs on Red Hat Enterprise Linux using the KVM hypervisor. The key components of RHV include Red Hat Virtualization Hosts (RHV-H) and the Red Hat Virtualization Manager (RHV- M). RHV-M provides centralized, enterprise-grade management for the physical and logical resources within the virtualized RHV environment. RHV-H is a minimal, light-weight operating system based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux that is optimized for the ease of setting up physical servers as RHV hypervisors. For more information on RHV, see the documentation here. The following figure provides an overview of RHV.
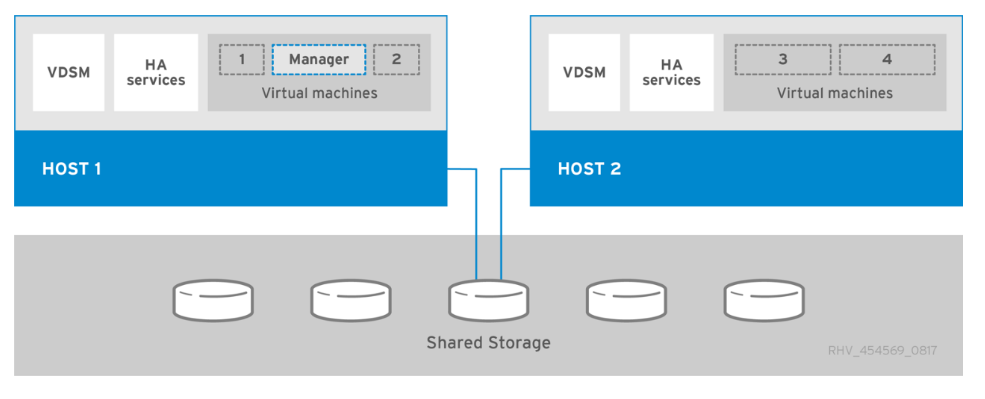
Starting with Cisco APIC release 3.1, Cisco ACI supports VMM integration with Red Hat Virtualization environments. The RHV VMM domain in Cisco APIC is connected to RHV-M and directly associated with a data center object. All the RHV-H clusters under this data center are considered part of the VMM domain. Cisco ACI automatically creates logical networks in RHV- M when the EPGs are attached to the RHV VMM domain in ACI. RHV hosts that are part of a Red Hat VMM domain can use Linux bridge or Open vSwitch as its virtual switch. This integration simplifies and automates networking configuration on RHV-M, saving a lot of manual work for system and network administrators.
Workflow
The following workflow is used to set up the virtual environment. Each of these steps might involve several individual tasks.
-
Install and configure Nexus 9000 switches in ACI mode and APIC software on the UCS C-series server. Refer to the Install and Upgrade documentation for detailed steps.
-
Configure and setup the ACI fabric by referring to the documentation.
-
Configure tenants, application profiles, bridge domains, and EPGs required for NetApp HCI nodes. NetApp recommends using one BD to one EPG framework, except for iSCSI. See the documentation here for more details. The minimum set of EPGs required are in-band management, iSCSI, VM motion, VM-data network, and native.
-
Create the VLAN pool, physical domain, and AEP based on the requirements. Create the switch and interface profiles and policies for vPCs and individual ports. Then attach the physical domain and configure the static paths to the EPGs. see the configuration guide for more details. This table lists best practices for integrating ACI with Linux bridge on RHV.
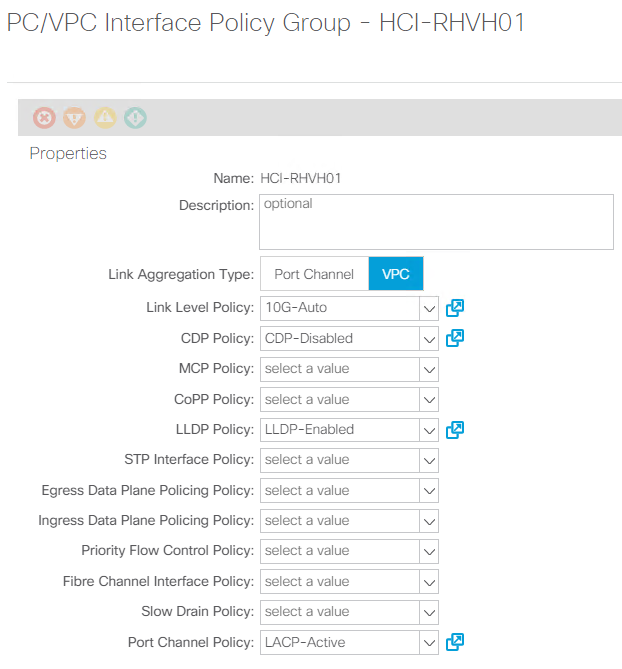
Use a vPC policy group for interfaces connecting to NetApp HCI storage and compute nodes. -
Create and assign contracts for tightly controlled access between workloads. For more information on configuring the contracts, see the guide here.
-
Install and configure the NetApp HCI Element cluster. Do not use NDE for this install; rather, install a standalone Element cluster on the HCI storage nodes. Then configure the required volumes for installation of RHV. Install RHV on NetApp HCI. Refer to RHV on NetApp HCI NVA for more details.
-
RHV installation creates a default management network called ovirtmgmt. Though VMM integration of Cisco ACI with RHV is optional, leveraging VMM integration is preferred. Do not create other logical networks manually. To use Cisco ACI VMM integration, create a Red Hat VMM domain and attach the VMM domain to all the required EPGs, using Pre- Provision Resolution Immediacy. This process automatically creates corresponding logical networks and vNIC profiles. The vNIC profiles can be directly used to attach to hosts and VMs for their communication. The networks that are managed by Cisco ACI are in the format
<tenant-name>|<application-profile-name>|<epg-name>tagged with a label of formataci_<rhv-vmm-domain-name>. See Cisco’s whitepaper for creating and configuring a VMM domain for RHV. Also, see this table for best practices when integrating RHV on NetApp HCI with Cisco ACI.Except for ovirtmgmt, all other logical networks can be managed by Cisco ACI. 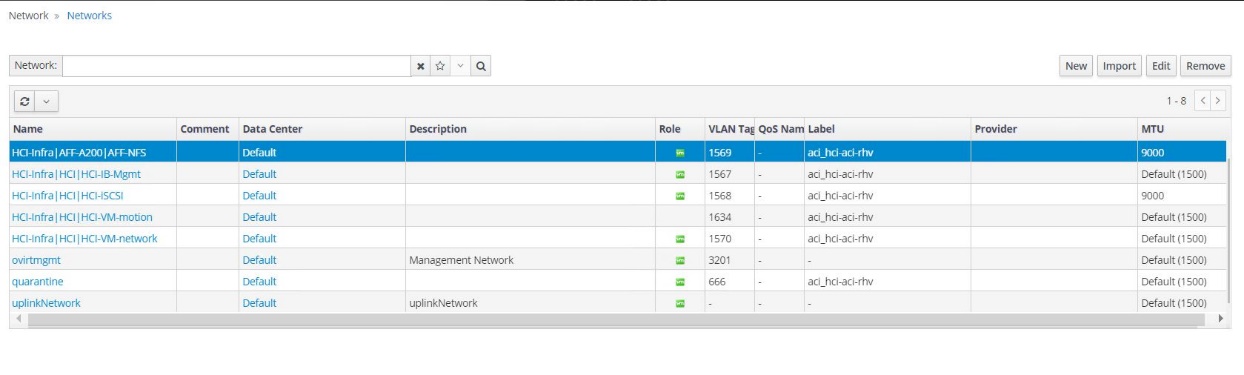
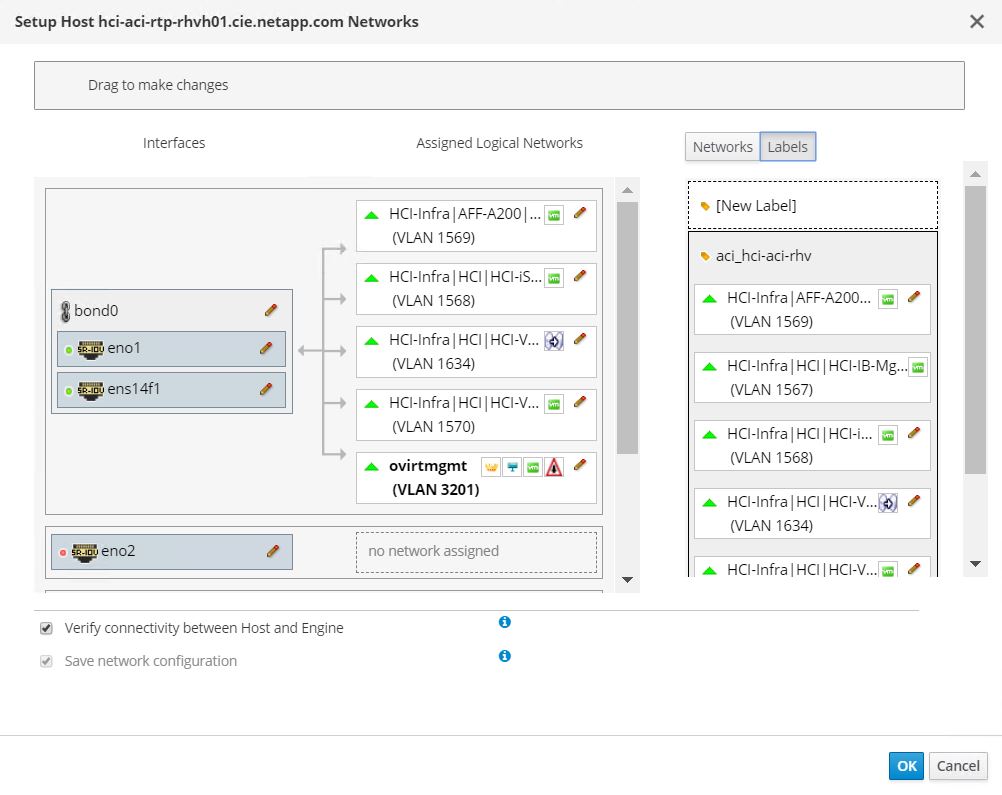
The networking functionality for RHVH hosts in this solution is provided by Linux bridge.
Linux Bridge
Linux Bridge is a default virtual switch on all Linux distributions that is usually used with KVM/QEMU-based hypervisors. It is designated to forward traffic between networks based on MAC addresses and thus is regarded as a layer-2 virtual switch. For more information, see the documentation here. The following figure depicts the internal networking of Linux Bridge on RHV-H (as tested).
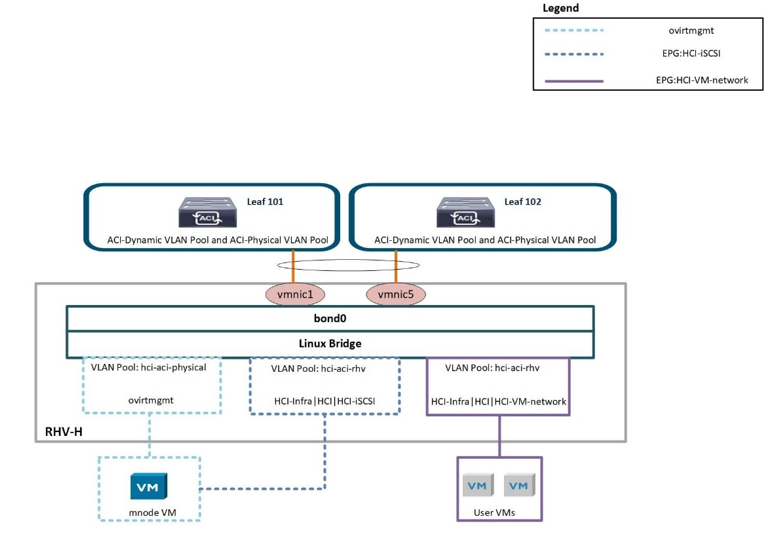
The following table outlines the necessary parameters and best practices for configuring and integrating Cisco ACI with Linux Bridge on RHV hosts.
| Resource | Configuration considerations | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
Endpoint groups |
|
|
Interface policy |
|
|
VMM Integration |
Do not migrate host management logical interfaces from ovirtmgmt to any other logical network |
iSCSI host logical interface to be migrated to iSCSI logical network managed by ACI VMM integration |

|
Except for the ovirtmgmt logical network, it is possible to create all other infrastructure logical networks on Cisco APIC and map them to the VMM domain. ‘ovirtmgmt’ logical network uses the static path binding on the In-band management EPG attached with the physical domain. |


