Optimizing Memory for Red Hat Virtualization: NetApp HCI with RHV
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


One of the primary benefits for deploying a virtual infrastructure is to enable the more efficient use of physical resources in the environment. In a case in which the guest VMs underutilize the memory allotted, you can use memory overcommitment to optimize memory usage. With this feature, the sum of the memory allocated to guest VMs on a host is allowed to exceed the amount of physical memory on that host.
The concept behind memory overcommitment is similar to thin provisioning of storage resources. At any given moment, every VM on the host does not use the total amount of memory allocated to it. When one VM has excess memory, its unused memory is available for other VMs to use. Therefore, an end user can deploy more VMs that the physical infrastructure would not normally allow. Memory overcommitment on the hosts in the cluster is handled by Memory Overcommit Manager (MoM). Techniques like memory ballooning and Kernel Same-page Merging (KSM) can improve memory overcommitment depending on the kind of workload.
Memory ballooning is a memory management technique which allows a host to artificially expand its memory by reclaiming unused memory that was previously allocated to various VMs, with a limitation of the guaranteed memory size of every VM. For memory ballooning to work, each VM by default has a balloon device with the necessary drivers. Ballooning essentially is a cooperative operation between the VM driver and the host. Depending on the memory needs of the host, it instructs the guest OS to inflate (provide memory to host) or deflate (regain the memory) the balloon which is controlled by the balloon device.
Kernel Same-page Merging (KSM) allows the host kernel to examine two or more running VMs and compare their image and memory. If any memory regions or pages are identical, KSM reduces multiple identical memory pages to a single page. This page is then marked ‘copy on write’ and a new page is created for that guest VM if the contents of the page are modified by a guest VM.
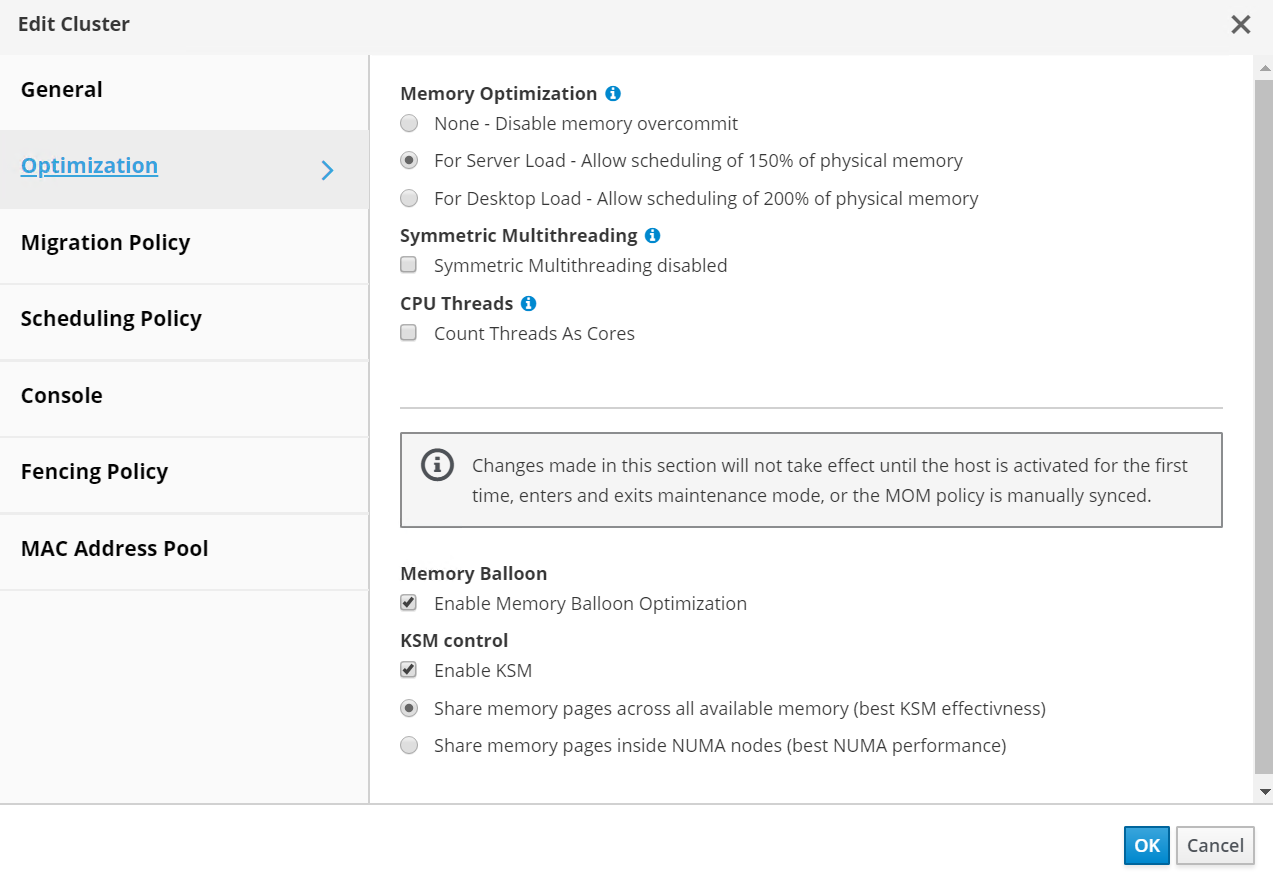
Both features can be enabled at a cluster level to apply to all hosts in that cluster. To enable these features, navigate to Compute > Clusters, select the desired cluster and click Edit. Then click the Optimization sub-tab and perform the following steps based on your requirements:
-
Depending on the use-case and workload, enable Memory Optimization to allow overcommitment of memory to either 150% or 200% of the available physical memory.
-
To enable memory ballooning, check the Enable Memory Balloon Optimization checkbox.
-
To enable KSM, check the Enable KSM checkbox.
-
Click Ok to confirm the changes.
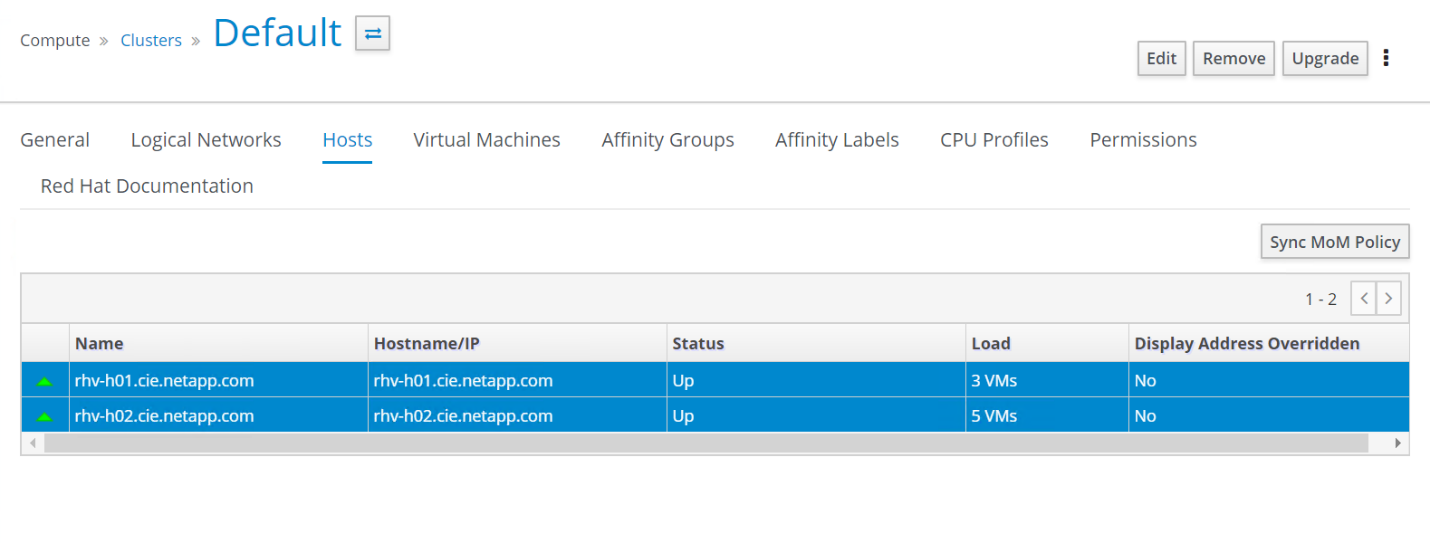
Be aware that after these changes have been applied, they do not take effect until you manually sync the MoM policy. To sync the MoM policy, navigate to Compute > Clusters and click the cluster for which you made the optimization changes. Navigate to the Hosts sub-tab, select all the hosts, and then click Sync MoM Policy.
KSM and ballooning can free up some memory on the host and facilitate overcommitment, but, if the amount of shareable memory decreases and the use of physical memory increases, it might cause an out-of-memory condition. Therefore, the administrator should be sure to reserve enough memory to avoid out-of-memory conditions if the shareable memory decreases.
In some scenarios, memory ballooning may collide with KSM. In such situations, MoM tries to adjust the balloon size to minimize collisions. Also, there can be scenarios for which ballooning might cause sub-optimal performance. Therefore, depending on the workload requirements, you can consider enabling either or both the techniques.


