Integrate Protection into CI/CD Pipelines with NetApp Astra Control
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


NetApp Astra Control Center offers a rich set of storage and application-aware data management services for stateful Kubernetes workloads, deployed in an on-prem environment, powered by NetApp’s trusted data protection technology.
Overview
One of the most common uses of DevOps workflows is continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines that build, integrate, and run automated test suites on applications as developers commit new code. DevOps engineers and site-reliability engineers (SREs) typically have pipelines dedicated to the various workflows for new feature development, regression testing, bug fixes, quality engineering, and other functions in the development process.
As teams increase their level of automation, the pace of change for in-production applications can feel overwhelming. Therefore, some teams prefer to protect in-production applications or services. In addition to protecting the code and container images, they also want to protect the application state, configuration data (such as Kubernetes objects and resources associated with the application), and an application’s persistent data.
In this use case, we take a closer look at a promotion-to-production pipeline that deploys a new version of an application: first into a staging environment and then into a production environment. This example applies equally to the major public clouds and also to an on-premises environment. Although we show the deployment of one version of the app, the pipeline can also be used with other strategies, such as blue/green or canary deployment. As part of the CI/CD pipeline, we’re going to protect the application by creating a complete application backup. An application-aware backup of the in-production application and its data, state, and configuration can be useful for numerous DevOps workflows.
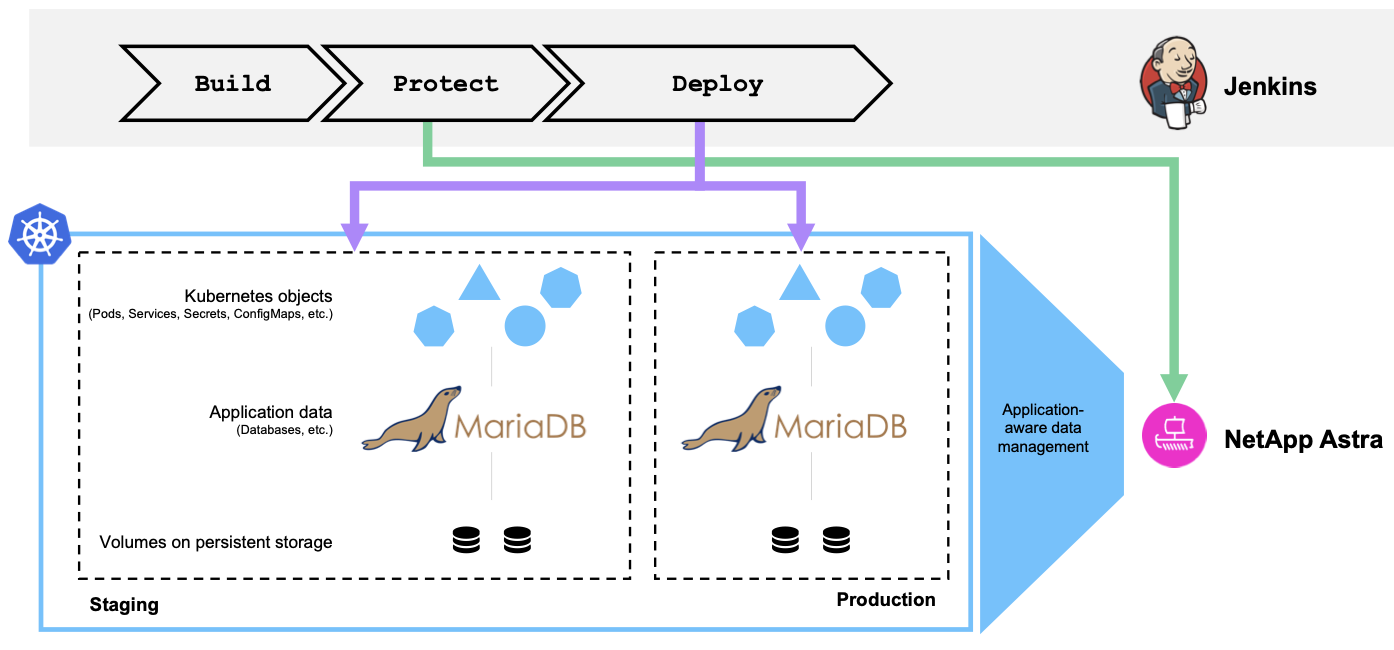
The application used for validating this use-case was Magento, an e-commerce solution with a web-based front end; an Elasticsearch instance for search and analysis features; and a MariaDB database that tracks all the shopping inventory and transaction details. This containerized application was installed in a Red Hat OpenShift cluster. Every pod in the application used persistent volumes to store data. The persistent volumes were automatically created by NetApp Astra Trident, the Container Storage Interface–compliant storage orchestrator for Kubernetes that enables storage to be provisioned on NetApp storage systems. Further, to utilize the Astra Control Center's application protection capabilities, the application in question was managed by Astra Control, which was then used to trigger application backups that stored the state of the application along with the data held in persistent volumes. We used the NetApp Astra Control Python SDK to automate the process of triggering application backups, which was then introduced into a CI/CD pipeline. This pipeline was created and executed using a popular CI/CD tool called [Jenkins] to automate the flow to build, protect, and deploy the application.
Let us run through the prerequisites and procedure to introduce protection in a CI/CD pipeline.
Use-case validation prerequisites
The following tools or platforms were deployed and configured as prerequisites:
-
Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform
-
NetApp Astra Trident installed on OpenShift with a backend to NetApp ONTAP system configured
-
A default storageclass configured, pointing to a NetApp ONTAP backend
-
NetApp Astra Control Center installed on an OpenShift cluster
-
OpenShift cluster added as a managed cluster to Astra Control Center
-
Jenkins installed on an OpenShift cluster and configured with an agent node with a Docker engine installed on it
Installing the application
Let's start with the initial installation of the application in the staging and production environments. For the purpose of this use case, this step is a prerequisite, so it is performed manually. The CI/CD pipeline is used for subsequent build and deploy workflows as a result of new version releases of the application.
The production environment in this use case is a namespace called magento-prod, and the corresponding staging environment is a namespace called magento-staging configured on the Red Hat OpenShift cluster. To intall the application, complete the following steps:
-
Install the Magento application using bitnami helm chart on the production environment. We use RWX PVs for Magento and Mariadb pods.
[netapp-user@rhel7 na_astra_control_suite]$ helm install --version 14 magento bitnami/magento -n magento-prod --create-namespace --set image.tag=2.4.1-debian-10-r11,magentoHost=10.63.172.243,persistence.magento.accessMode=ReadWriteMany,persistence.apache.accessMode=ReadWriteMany,mariadb.master.persistence.accessModes[0]=ReadWriteMany
Magento bitnami helm chart requires a LoadBalancer service to expose the Magento GUI service. We used MetalLB for providing an on-prem load balancer service in this example. -
After a few minutes, verify that all pods and services are running.
[netapp-user@rhel7 na_astra_control_suite]$ oc get pods -n magento-prod NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE magento-9d658fd96-qrxmt 1/1 Running 0 49m magento-elasticsearch-coordinating-only-69869cc5-768rm 1/1 Running 0 49m magento-elasticsearch-data-0 1/1 Running 0 49m magento-elasticsearch-master-0 1/1 Running 0 49m magento-mariadb-0 1/1 Running 0 49m
-
Repeat the same procedure for the staging environment.
Manage the Magento application in Astra Control Center
-
Navigate to Applications and select the Discovered applications tab.
-
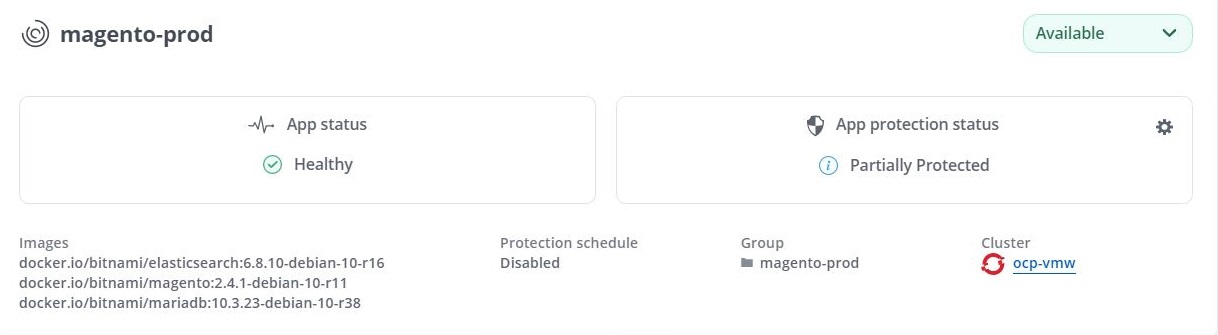
Click the ellipsis against the Magento application in the production environment (
magento-prod), and click Manage. -
The Magento application is now managed by the Astra Control Center. All operations supported by Astra Control can be performed on the application. Note the version of the application as well.
-
Repeat the steps for managing the Magento application in the staging environment (
magento-staging).
CI/CD pipeline with integrated protection
When we work with new versions of applications, we use a CI/CD pipeline to build the container image, take backups of both the staging and production environments, deploy the new version of the application to the staging environment, wait for approval to promotion to production, and then deploy the new version of the application to the production environment. To use a CI/CD pipeline, complete the following steps:
-
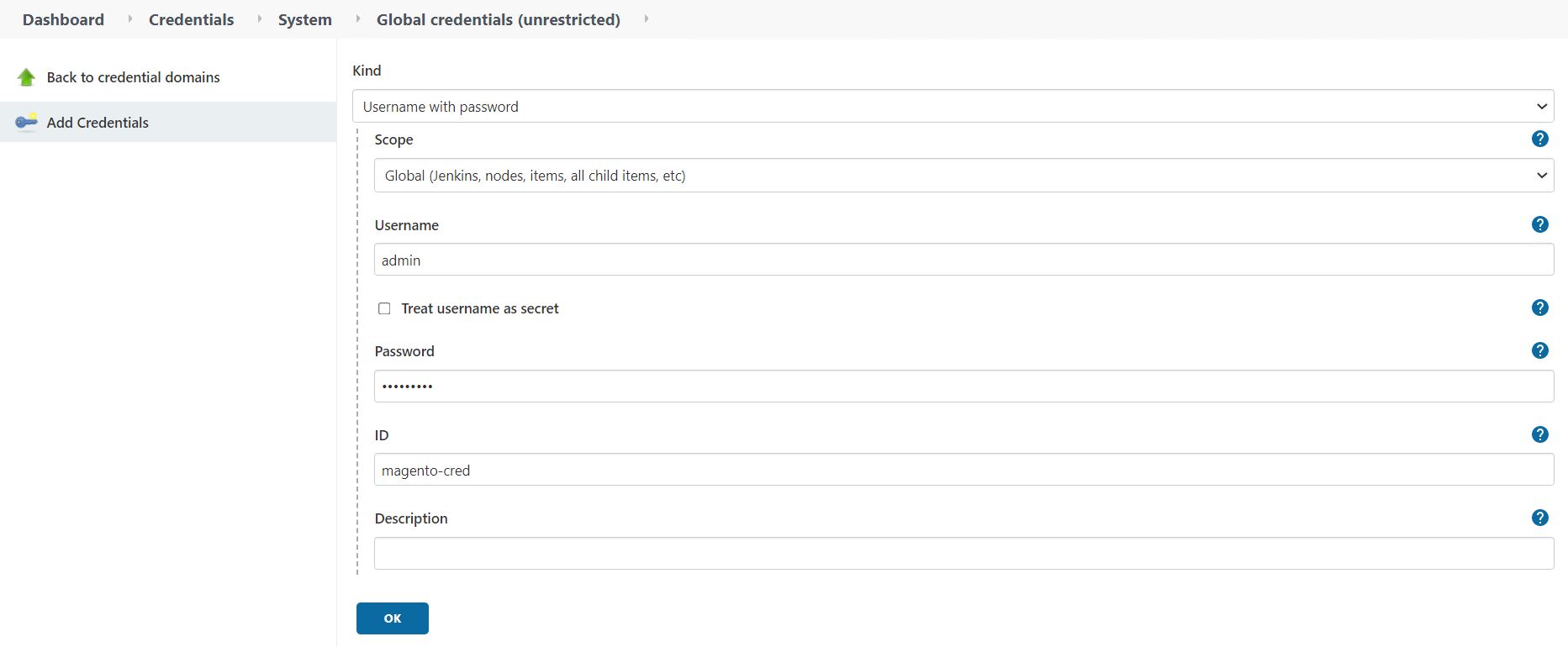
Log into Jenkins, and create the required credentials: one for Magento creds, one for Mariadb admin creds, and the third for Mariadb root creds.
-
Navigate to Manage Jenkins > Manage Credentials and click the appropriate domain.
-
Click Add Credentials, and set the kind to Username with password and scope set to Global. Enter the username, password, and an ID for the credentials and click OK.
-
Repeat the same procedure for the other two credentials.
-
Go back to the Dashboard, create a pipeline by clicking New Item, and then click Pipeline.
-
Copy the pipeline from the Jenkinsfile here.
-
Paste the pipeline into the Jenkins pipeline section and then click Save.
-
Fill the parameters of the Jenkins pipeline with the respective details including the helm chart version, the Magento application version to be upgraded to, the Astra toolkit version, the Astra Control Center FQDN, the API token, and its instance ID. Specify the docker registry, namespace, and Magento IP of both production and staging environments, and also specify the credential IDs of the credentials created.
MAGENTO_VERSION = '2.4.1-debian-10-r14' CHART_VERSION = '14' RELEASE_TYPE = 'MINOR' ASTRA_TOOLKIT_VERSION = '2.0.2' ASTRA_API_TOKEN = 'xxxxxxxx' ASTRA_INSTANCE_ID = 'xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx' ASTRA_FQDN = 'netapp-astra-control-center.org.example.com' DOCKER_REGISTRY = 'docker.io/netapp-solutions-cicd' PROD_NAMESPACE = 'magento-prod' PROD_MAGENTO_IP = 'x.x.x.x' STAGING_NAMESPACE = 'magento-staging' STAGING_MAGENTO_IP = 'x.x.x.x' MAGENTO_CREDS = credentials('magento-cred') MAGENTO_MARIADB_CREDS = credentials('magento-mariadb-cred') MAGENTO_MARIADB_ROOT_CREDS = credentials('magento-mariadb-root-cred') -
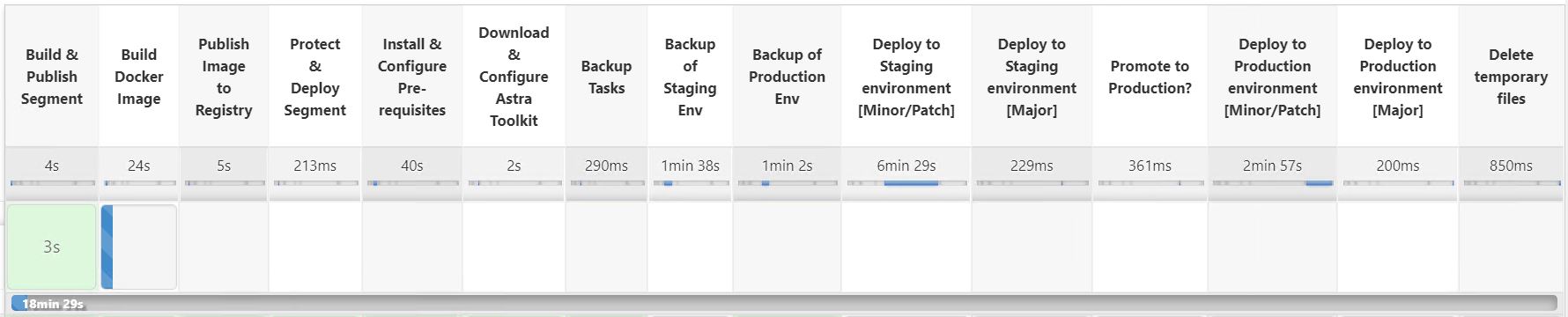
Click Build Now. The pipeline starts executing and progresses through the steps. The application image is first built and uploaded to the container registry.
-
The application backups are initiated via Astra Control.
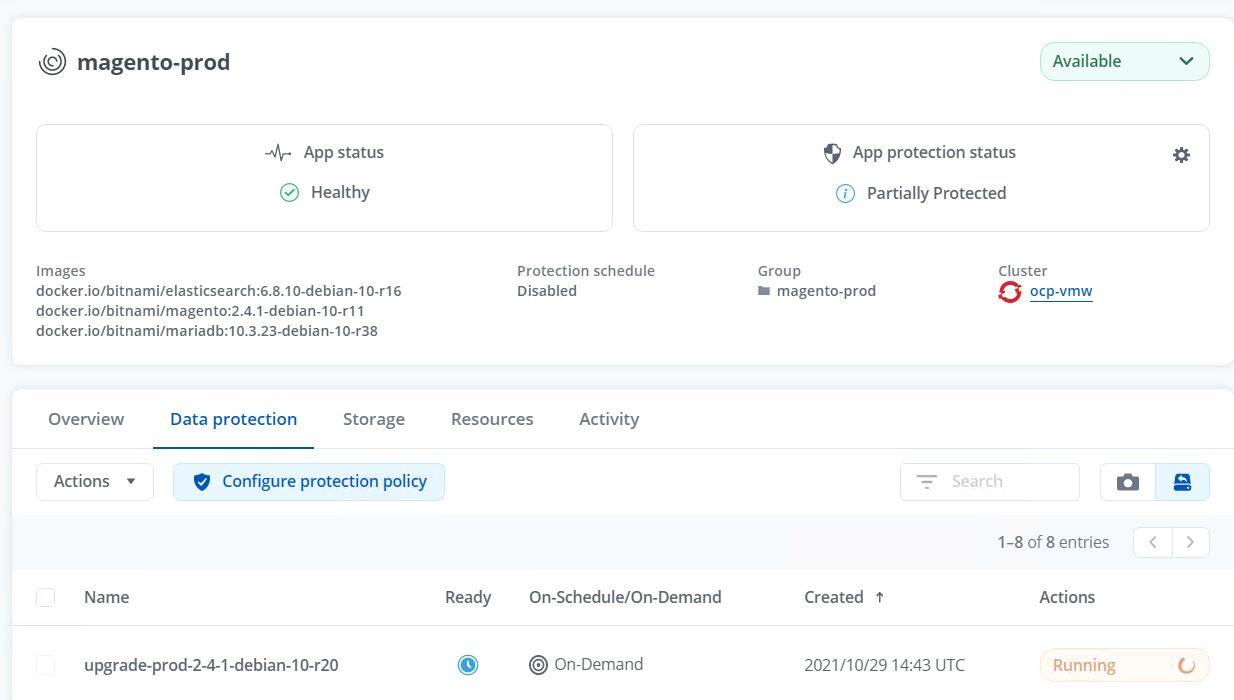
-
After the backup stages have completed successful, verify the backups from the Astra Control Center.
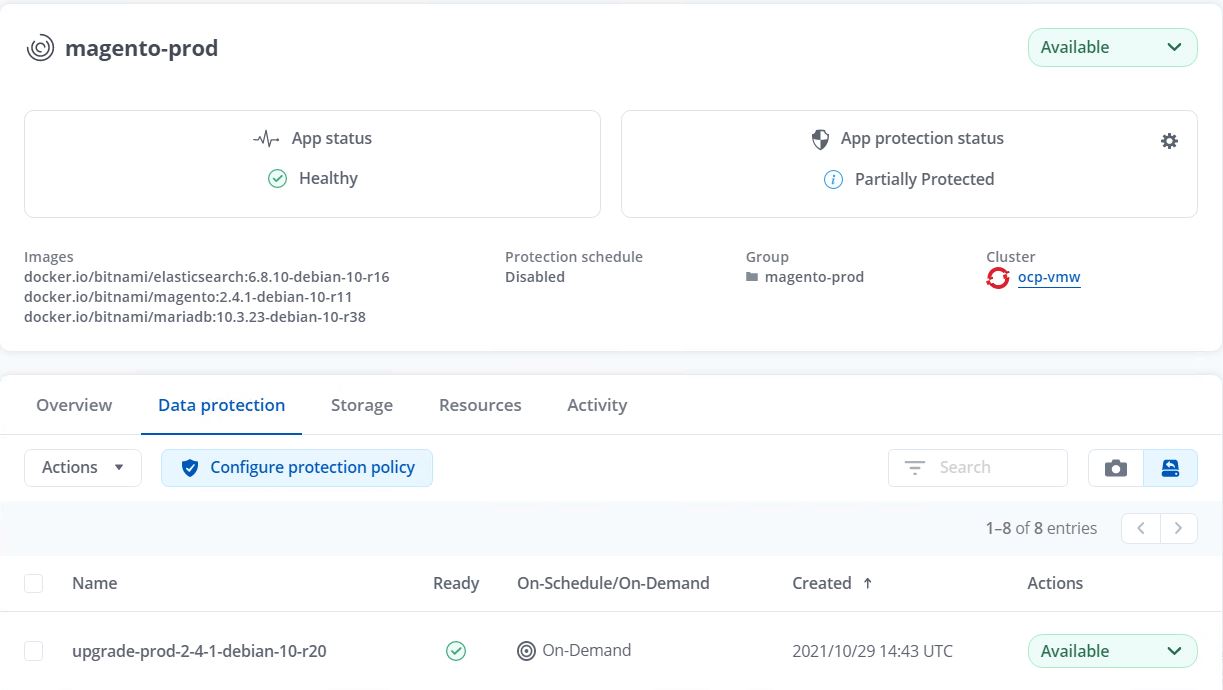
-
The new version of the application is then deployed to the staging environment.

-
After this step is completed, the program waits for the user to approve deployment to production. At this stage, assume that the QA team performs some manual testing and approves production. You can then click Approve to deploy the new version of the application to the production environment.

-
Verify that the production application is also upgraded to the desired version.
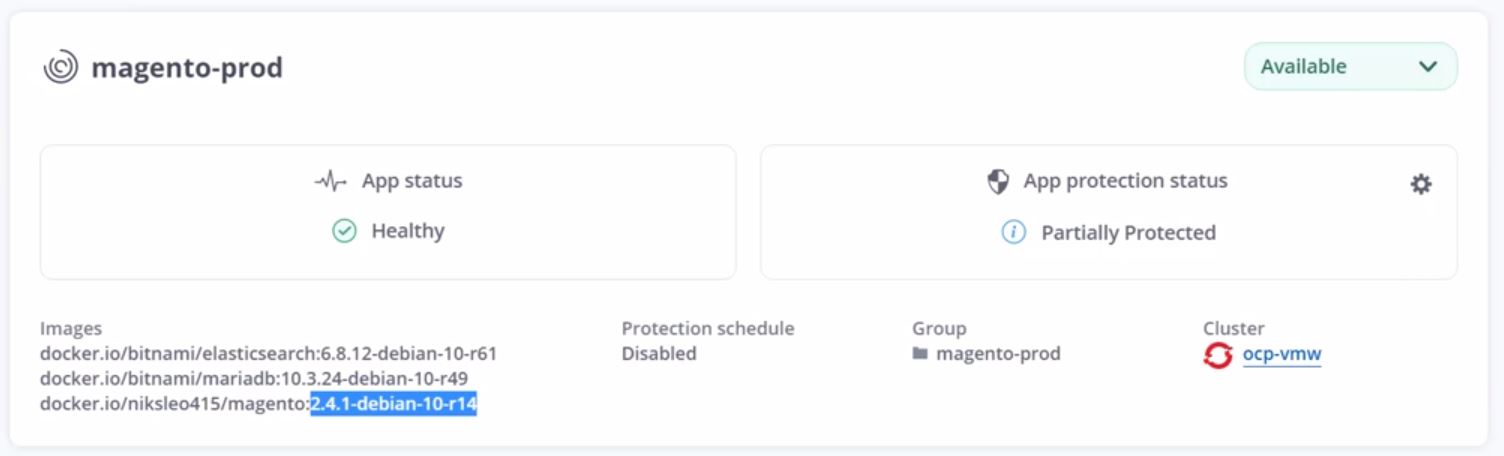
As part of the CI/CD pipeline, we demonstrated the ability to protect the application by creating a complete application-aware backup. Because the entire application has been backed up as part of the promotion-to-production pipeline, you can feel more confident about highly automated application deployments. This application-aware backup containing the data, state, and configuration of the application can be useful for numerous DevOps workflows. One important workflow would be to roll back to the previous version of the application in case of unforeseen issues.
Although we demonstrated a CI/CD workflow through with Jenkins tool, the concept can easily and efficiently be extrapolated to different tools and strategies. To see this use case in action, watch the video below.



 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
