Use Astra Control to facilitate post-mortem analysis and restore the application
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


NetApp Astra Control Center offers a rich set of storage and application-aware data management services for stateful Kubernetes workloads, deployed in an on-prem environment, powered by NetApp’s trusted data protection technology.
Overview
In the first use case, we demonstrated how to use NetApp Astra Control Center to protect your applications in Kubernetes. That section describes how to integrate application backups via Astra Control directly into your development workflow by using the Python SDK in the NetApp Astra toolkit. This approach allows for the protection of development and production environments by automating on-demand backups during the continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) process. With this extra layer of application-consistent data protection added to the CI/CD pipeline and the production applications, the development processes is safe if something goes wrong in the process, which promotes good business-continuity practices.
In a traditional workflow, after encountering a failure when the application is upgraded to a new version, the development team would attempt to troubleshoot the issue in real time based on bug reports being provided by customers. Alternatively, at the first sign of trouble, the team could attempt to redeploy the application to a parallel debugging environment to take that process offline. They could redeploy an older code base from a previous version into production, which would restore the application to working order.
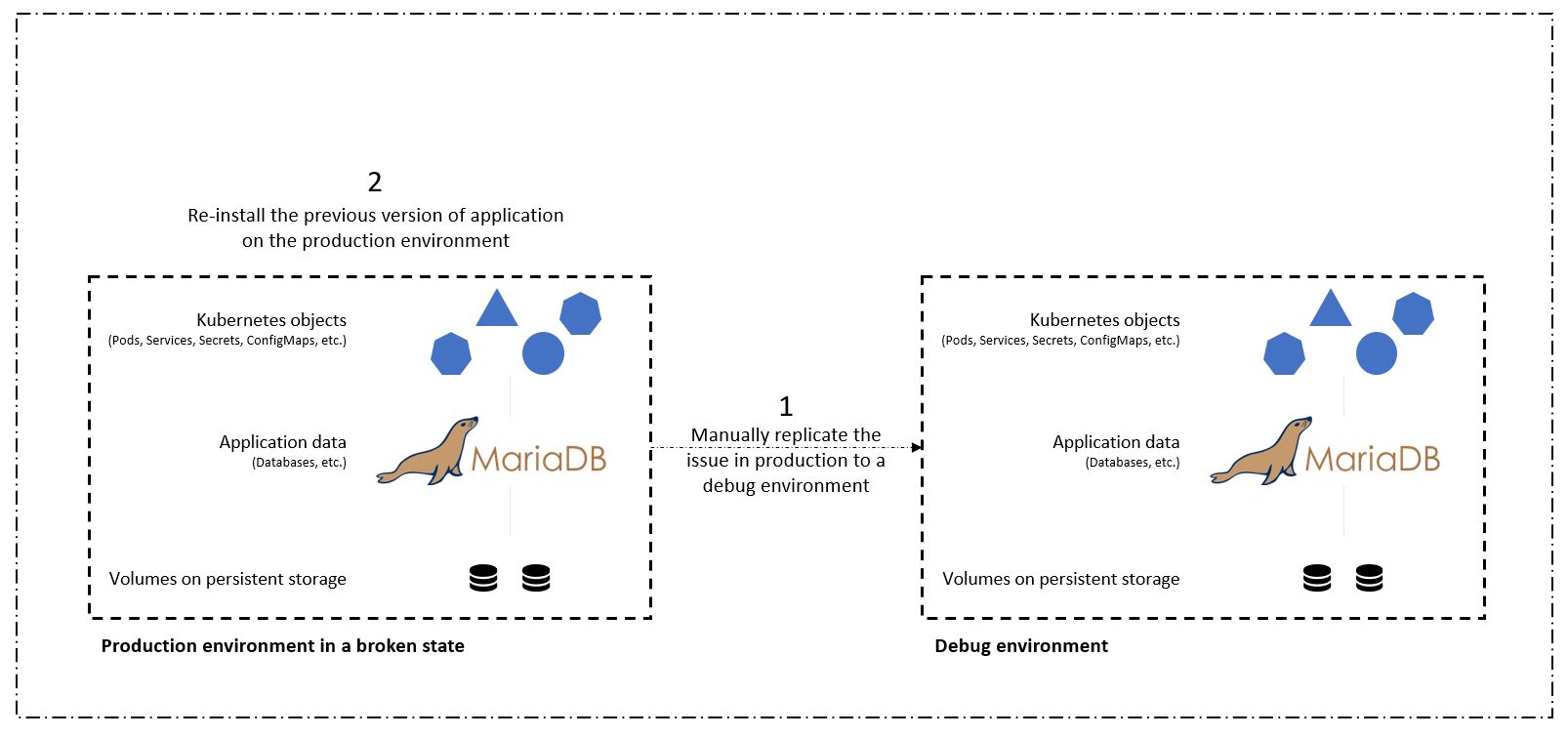
Although this approach works, the team would have to make sure that the state of the broken production app matched that of the version seen in production when the issues occurred. They would also have to spend time promoting the known-good build into production by fetching code from their repository and redeploying the machine images to restore the application to a good running state. Also, in this scenario, we didn't consider whether the production database itself was corrupted by the faulty code. Ideally, there are separate backup processes in place for the database data, but must we assume that they’re consistent with the state of the application as it was published? This is where the benefits of stateful and application-consistent backups, restores and clones with Astra Control really show their value.
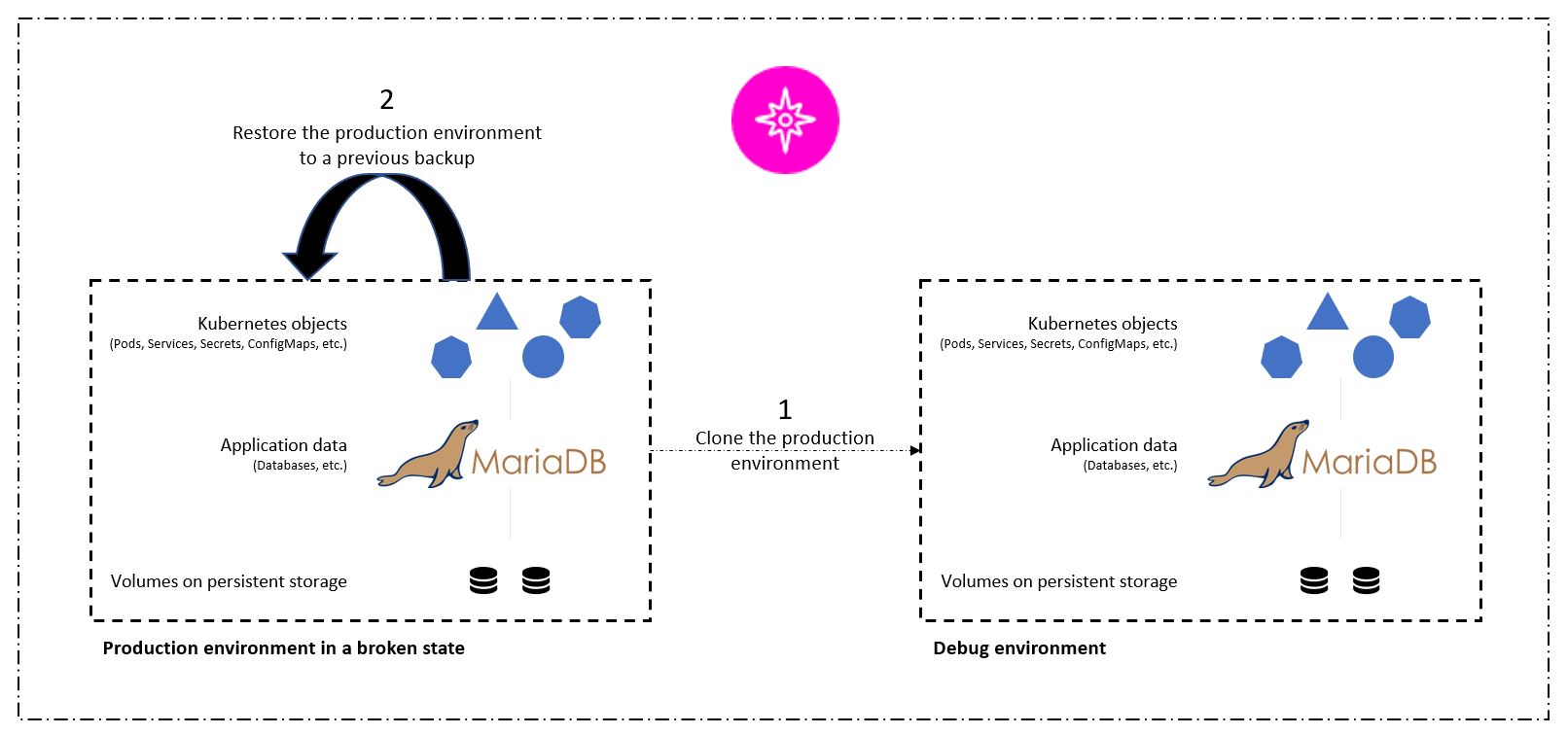
First, we can use Astra Control to facilitate post-mortem analysis on the state of the application. We do this by cloning the buggy production version to a parallel testing environment in an application-consistent manner. Having this environment set aside in its bug-ridden state enable us to troubleshoot the problem in real time.
Furthermore, Astra Control supports the in-place restore capability that allows us to restore the production application to a last acceptable backup (that preceded the afflicted version of code). The restored version assumes the position of the previous, buggy production application, in an application-consistent and stateful manner, including the ingress IP previously assigned. As a result, customers accessing the front end would be unaware of the transition to the backup version.
Use-case validation prerequisites
The following tools or platforms were deployed and configured as prerequisites:
-
Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform.
-
NetApp Astra Trident installed on OpenShift with a backend configured to a NetApp ONTAP system.
-
A default storageclass configured, pointing to a NetApp ONTAP backend.
-
NetApp Astra Control Center installed on an OpenShift cluster.
-
OpenShift cluster added as a managed cluster to Astra Control Center.
-
Jenkins installed on an OpenShift cluster.
-
Magento application installed in the production environment. The production environment in this use case is a namespace called 'magento-prod' in a Red Hat OpenShift cluster.
-
Production application managed by Astra Control Center.
-
Known-good backup(s) of the production application captured with Astra Control.
Clone and restore pipeline
Considering that the application has been upgraded to a new version, the application in the production environment (magento-prod) isn’t behaving as intended after the upgrade. Let's assume that the data being returned by front-end queries doesn’t match the request or that the database has in fact been corrupted. To clone and restore the pipeline, complete the following steps:
-
Log into Jenkins and create a pipeline by clicking New Item and then Pipeline.
-
Copy the pipeline from the Jenkinsfile here.
-
Paste the pipeline into the Jenkins pipeline section and then click Save.
-
Fill the parameters of the Jenkins pipeline with the respective details like the current Magento application version in production, the Astra Control Center FQDN, the API token, the instance ID and application name or namespace of production and debug environments, and the source and destination cluster names. For the purpose of this use case, the production environment is a namespace called 'magento-prod' and the debug environment is a namespace called 'magento-debug' configured on a Red Hat OpenShift cluster.
MAGENTO_VERSION = '2.4.1-debian-10-r14' ASTRA_TOOLKIT_VERSION = '2.0.2' ASTRA_API_TOKEN = 'xxxxx' ASTRA_INSTANCE_ID = 'xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx' ASTRA_FQDN = 'netapp-astra-control-center.org.example.com' PROD_APP_NAME = 'magento-prod' DEBUG_APP_NAME = 'magento-debug' DEBUG_NAMESPACE = 'magento-debug' PROD_KUBERNETES_CLUSTER = 'ocp-vmw' DEBUG_KUBERNETES_CLUSTER = 'ocp-vmw'
-
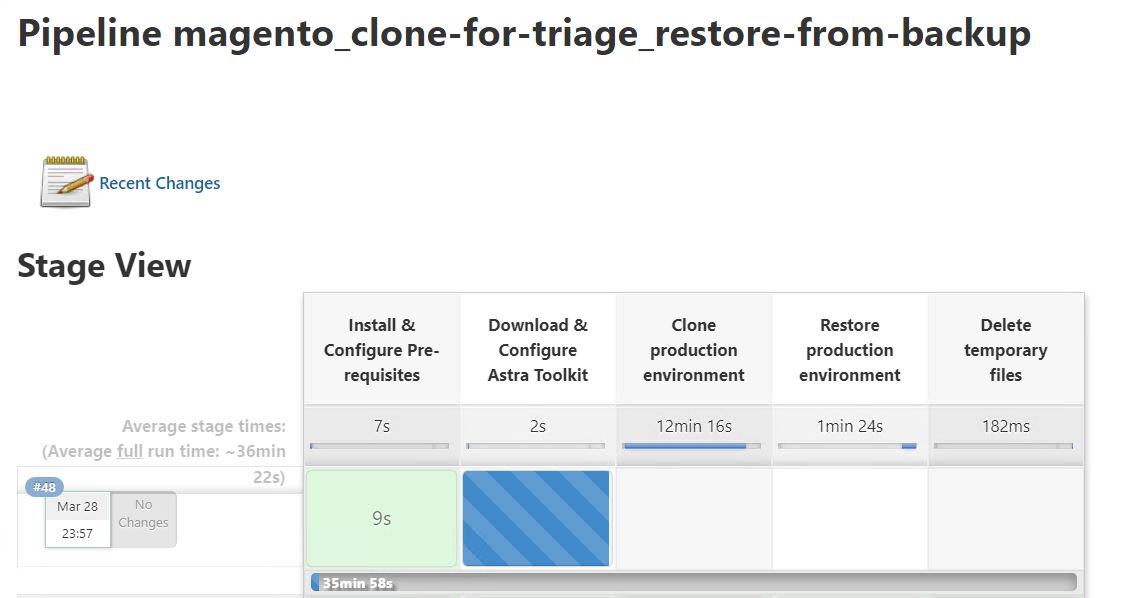
Click Build Now. The pipeline starts executing and progresses through the steps. The application is first cloned in the current state to a debug environment, and the application is then restored to the known-working backup.
-
Verify that the cloned application is the bug-containing version.
-
Verify that the production environment is restored to a working backup, and the application in production works as expected.
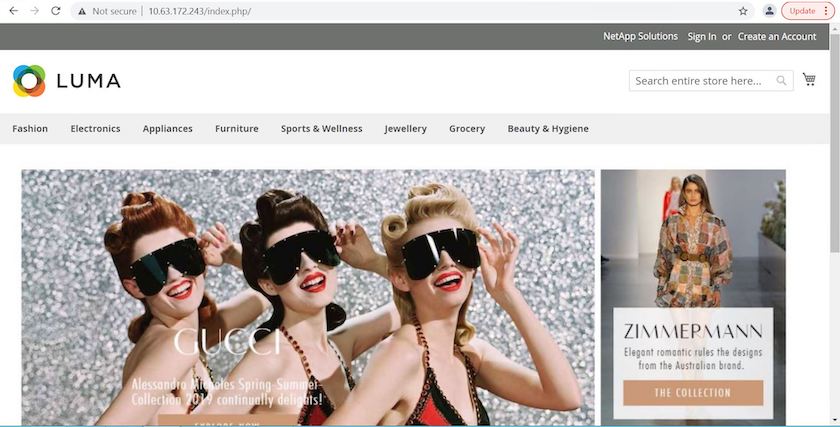
These two operations in tandem expedite the return to normal business operations. To see this use case in action, watch the video below.



 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence