Troubleshoot network, hardware, and platform issues
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


There are several tasks you can perform to help determine the source of issues related to StorageGRID network, hardware, and platform issues.
“422: Unprocessable Entity” errors
The error 422: Unprocessable Entity can occur for different reasons. Check the error message to determine what caused your issue.
If you see one of the listed error messages, take the recommended action.
| Error message | Root cause and corrective action |
|---|---|
422: Unprocessable Entity Validation failed. Please check the values you entered for errors. Test connection failed. Please verify your configuration. Unable to authenticate, please verify your username and password: LDAP Result Code 8 "Strong Auth Required": 00002028: LdapErr: DSID-0C090256, comment: The server requires binds to turn on integrity checking if SSL\TLS are not already active on the connection, data 0, v3839 |
This message might occur if you select the Do not use TLS option for Transport Layer Security (TLS) when configuring identity federation using Windows Active Directory (AD). Using the Do not use TLS option is not supported for use with AD servers that enforce LDAP signing. You must select either the Use STARTTLS option or the Use LDAPS option for TLS. |
422: Unprocessable Entity
Validation failed. Please check
the values you entered for
errors. Test connection failed.
Please verify your
configuration.Unable to
begin TLS, verify your
certificate and TLS
configuration: LDAP Result
Code 200 "Network Error":
TLS handshake failed
(EOF)
|
This message appears if you try to use an unsupported cipher to make a Transport Layer Security (TLS) connection from StorageGRID to an external system used for identify federation or Cloud Storage Pools. Check the ciphers that are offered by the external system. The system must use one of the ciphers supported by StorageGRID for outgoing TLS connections, as shown in the instructions for administering StorageGRID. |
Grid Network MTU mismatch alert
The Grid Network MTU mismatch alert is triggered when the maximum transmission unit (MTU) setting for the Grid Network interface (eth0) differs significantly across nodes in the grid.
The differences in MTU settings could indicate that some, but not all, eth0 networks are configured for jumbo frames. An MTU size mismatch of greater than 1000 might cause network performance problems.
-
List the MTU settings for eth0 on all nodes.
-
Use the query provided in the Grid Manager.
-
Navigate to
primary Admin Node IP address/metrics/graphand enter the following query:node_network_mtu_bytes{interface='eth0'}
-
-
Modify the MTU settings as necessary to ensure they are the same for the Grid Network interface (eth0) on all nodes.
-
For Linux- and VMware-based nodes, use the following command:
/usr/sbin/change-ip.py [-h] [-n node] mtu network [network...]Example:
change-ip.py -n node 1500 grid adminNote: On Linux-based nodes, if the desired MTU value for the network in the container exceeds the value already configured on the host interface, you must first configure the host interface to have the desired MTU value, and then use the
change-ip.pyscript to change the MTU value of the network in the container.Use the following arguments for modifying the MTU on Linux- or VMware-based nodes.
Positional arguments Description mtuThe MTU to set. Must be in the range 1280 to 9216.
networkThe networks to apply the MTU to. Include one or more of the following network types:
-
grid
-
admin
-
client
Optional arguments Description -h, – helpShow the help message and exit.
-n node, --node nodeThe node. The default is the local node.
-
-
Network Receive Error (NRER) alarm
Network Receive Error (NRER) alarms can be caused by connectivity issues between StorageGRID and your network hardware. In some cases, NRER errors can clear without manual intervention. If the errors don't clear, take the recommended actions.
NRER alarms can be caused by the following issues with networking hardware that connects to StorageGRID:
-
Forward error correction (FEC) is required and not in use
-
Switch port and NIC MTU mismatch
-
High link error rates
-
NIC ring buffer overrun
-
Follow the troubleshooting steps for all potential causes of the NRER alarm given your network configuration.
-
Perform the following steps depending on the cause of the error:
FEC mismatchThese steps are applicable only for NRER errors caused by FEC mismatch on StorageGRID appliances. -
Check the FEC status of the port in the switch attached to your StorageGRID appliance.
-
Check the physical integrity of the cables from the appliance to the switch.
-
If you want to change FEC settings to try to resolve the NRER alarm, first ensure that the appliance is configured for Auto mode on the Link Configuration page of the StorageGRID Appliance Installer (see the instructions for your appliance:
-
Change the FEC settings on the switch ports. The StorageGRID appliance ports will adjust their FEC settings to match, if possible.
You can't configure FEC settings on StorageGRID appliances. Instead, the appliances attempt to discover and mirror the FEC settings on the switch ports they are connected to. If the links are forced to 25-GbE or 100-GbE network speeds, the switch and NIC might fail to negotiate a common FEC setting. Without a common FEC setting, the network will fall back to “no-FEC” mode. When FEC is not enabled, the connections are more susceptible to errors caused by electrical noise.
StorageGRID appliances support Firecode (FC) and Reed Solomon (RS) FEC, as well as no FEC.
Switch port and NIC MTU mismatchIf the error is caused by a switch port and NIC MTU mismatch, check that the MTU size configured on the node is the same as the MTU setting for the switch port.
The MTU size configured on the node might be smaller than the setting on the switch port the node is connected to. If a StorageGRID node receives an Ethernet frame larger than its MTU, which is possible with this configuration, the NRER alarm might be reported. If you believe this is what is happening, either change the MTU of the switch port to match the StorageGRID network interface MTU, or change the MTU of the StorageGRID network interface to match the switch port, depending on your end-to-end MTU goals or requirements.
For the best network performance, all nodes should be configured with similar MTU values on their Grid Network interfaces. The Grid Network MTU mismatch alert is triggered if there is a significant difference in MTU settings for the Grid Network on individual nodes. The MTU values don't have to be the same for all network types. See Troubleshoot the Grid Network MTU mismatch alert for more information. Also see Change MTU setting. High link error rates-
Enable FEC, if not already enabled.
-
Verify that your network cabling is of good quality and is not damaged or improperly connected.
-
If the cables don't appear to be the problem, contact technical support.
You might notice high error rates in an environment with high electrical noise.
NIC ring buffer overrunIf the error is a NIC ring buffer overrun, contact technical support.
The ring buffer can be overrun when the StorageGRID system is overloaded and unable to process network events in a timely manner.
-
-
After you resolve the underlying problem, reset the error counter.
-
Select SUPPORT > Tools > Grid topology.
-
Select site > grid node > SSM > Resources > Configuration > Main.
-
Select Reset Receive Error Count and click Apply Changes.
-
Time synchronization errors
You might see issues with time synchronization in your grid.
If you encounter time synchronization problems, verify that you have specified at least four external NTP sources, each providing a Stratum 3 or better reference, and that all external NTP sources are operating normally and are accessible by your StorageGRID nodes.

|
When specifying the external NTP source for a production-level StorageGRID installation, don't use the Windows Time (W32Time) service on a version of Windows earlier than Windows Server 2016. The time service on earlier versions of Windows is not sufficiently accurate and is not supported by Microsoft for use in high-accuracy environments, such as StorageGRID. |
Linux: Network connectivity issues
You might see issues with network connectivity for StorageGRID grid nodes hosted on Linux hosts.
MAC address cloning
In some cases, network issues can be resolved by using MAC address cloning. If you are using virtual hosts, set the value of the MAC address cloning key for each of your networks to "true" in your node configuration file. This setting causes the MAC address of the StorageGRID container to use the MAC address of the host. To create node configuration files, see the instructions for Red Hat Enterprise Linux or CentOS or Ubuntu or Debian.

|
Create separate virtual network interfaces for use by the Linux host OS. Using the same network interfaces for the Linux host OS and the StorageGRID container might cause the host OS to become unreachable if promiscuous mode has not been enabled on the hypervisor. |
For more information about enabling MAC cloning, see the instructions for Red Hat Enterprise Linux or CentOS or Ubuntu or Debian.
Promiscuous mode
If you don't want to use MAC address cloning and would rather allow all interfaces to receive and transmit data for MAC addresses other than the ones assigned by the hypervisor, ensure that the security properties at the virtual switch and port group levels are set to Accept for Promiscuous Mode, MAC Address Changes, and Forged Transmits. The values set on the virtual switch can be overridden by the values at the port group level, so ensure that settings are the same in both places.
For more information about using Promiscuous Mode, see the instructions for Red Hat Enterprise Linux or CentOS or Ubuntu or Debian.
Linux: Node status is “orphaned”
A Linux node in an orphaned state usually indicates that either the storagegrid service or the StorageGRID node daemon controlling the node's container died unexpectedly.
If a Linux node reports that it is in an orphaned state, you should:
-
Check logs for errors and messages.
-
Attempt to start the node again.
-
If necessary, use container engine commands to stop the existing node container.
-
Restart the node.
-
Check logs for both the service daemon and the orphaned node for obvious errors or messages about exiting unexpectedly.
-
Log in to the host as root or using an account with sudo permission.
-
Attempt to start the node again by running the following command:
$ sudo storagegrid node start node-name$ sudo storagegrid node start DC1-S1-172-16-1-172
If the node is orphaned, the response is
Not starting ORPHANED node DC1-S1-172-16-1-172
-
From Linux, stop the container engine and any controlling storagegrid-node processes. For example:
sudo docker stop --time secondscontainer-nameFor
seconds, enter the number of seconds you want to wait for the container to stop (typically 15 minutes or less). For example:sudo docker stop --time 900 storagegrid-DC1-S1-172-16-1-172
-
Restart the node:
storagegrid node start node-namestoragegrid node start DC1-S1-172-16-1-172
Linux: Troubleshoot IPv6 support
You might need to enable IPv6 support in the kernel if you have installed StorageGRID nodes on Linux hosts and you notice that IPv6 addresses have not been assigned to the node containers as expected.
You can see the IPv6 address that has been assigned to a grid node in the following locations in the Grid Manager:
-
Select NODES, and select the node. Then, select Show more next to IP Addresses on the Overview tab.
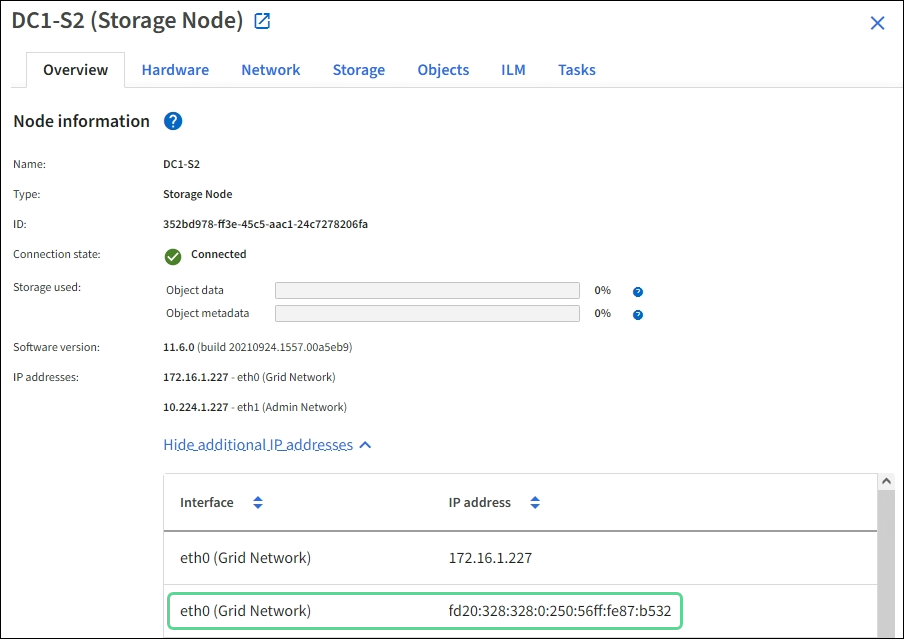
-
Select SUPPORT > Tools > Grid topology. Then, select node > SSM > Resources. If an IPv6 address has been assigned, it is listed below the IPv4 address in the Network Addresses section.
If the IPv6 address is not shown and the node is installed on a Linux host, follow these steps to enable IPv6 support in the kernel.
-
Log in to the host as root or using an account with sudo permission.
-
Run the following command:
sysctl net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6root@SG:~ # sysctl net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6
The result should be 0.
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 0
If the result is not 0, see the documentation for your operating system for changing sysctlsettings. Then, change the value to 0 before continuing. -
Enter the StorageGRID node container:
storagegrid node enter node-name -
Run the following command:
sysctl net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6root@DC1-S1:~ # sysctl net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6
The result should be 1.
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
If the result is not 1, this procedure does not apply. Contact technical support. -
Exit the container:
exitroot@DC1-S1:~ # exit
-
As root, edit the following file:
/var/lib/storagegrid/settings/sysctl.d/net.conf.sudo vi /var/lib/storagegrid/settings/sysctl.d/net.conf
-
Locate the following two lines and remove the comment tags. Then, save and close the file.
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 0
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 0
-
Run these commands to restart the StorageGRID container:
storagegrid node stop node-name
storagegrid node start node-name


