Root-data partitioning
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


Every node must have a root aggregate for storage system configuration files. The root aggregate has the RAID type of the data aggregate.
System Manager does not support root-data or root-data-data partitioning.
A root aggregate of type RAID-DP typically consists of one data disk and two parity disks. That's a significant “parity tax” to pay for storage system files, when the system is already reserving two disks as parity disks for each RAID group in the aggregate.
Root-data partitioning reduces the parity tax by apportioning the root aggregate across disk partitions, reserving one small partition on each disk as the root partition and one large partition for data.
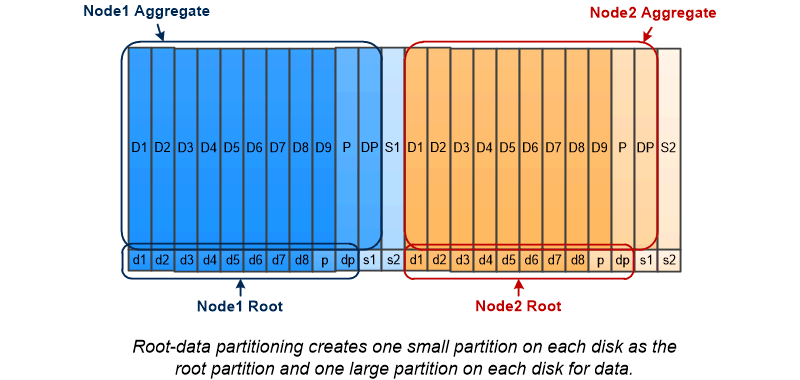
As the illustration suggests, the more disks used to store the root aggregate, the smaller the root partition. That's also the case for a form of root-data partitioning called root-data-data partitioning, which creates one small partition as the root partition and two larger, equally sized partitions for data.
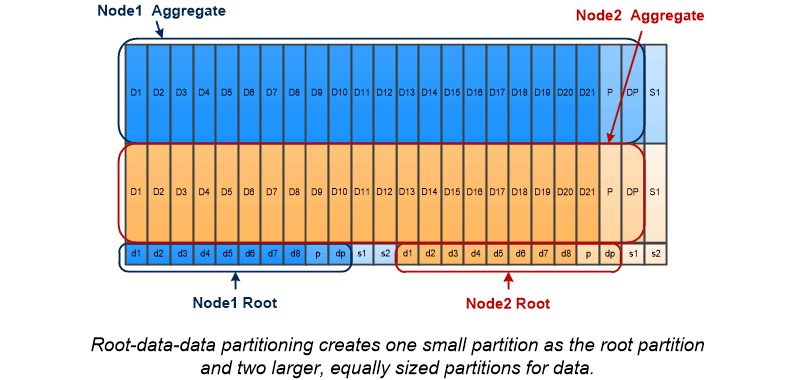
Both types of root-data partitioning are part of the ONTAP Advanced Drive Partitioning (ADP) feature. Both are configured at the factory: root-data partitioning for entry-level FAS2xxx, FAS9000, FAS8200, FAS80xx and AFF systems, root-data-data partitioning for AFF systems only.
Learn more about Advanced Drive Partitioning.
Drives partitioned and used for the root aggregate
The drives that are partitioned for use in the root aggregate depend on the system configuration.
Knowing how many drives are used for the root aggregate helps you to determine how much of the drives' capacity is reserved for the root partition, and how much is available for use in a data aggregate.
The root-data partitioning capability is supported for entry-level platforms, All Flash FAS platforms, and FAS platforms with only SSDs attached.
For entry-level platforms, only the internal drives are partitioned.
For All Flash FAS platforms and FAS platforms with only SSDs attached, all drives that are attached to the controller when the system is initialized are partitioned, up to a limit of 24 per node. Drives that are added after system configuration are not partitioned.


