Learn about CHAP authentication for iSCSI initiators in ONTAP
 Suggest changes
Suggest changes


The Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) enables authenticated communication between iSCSI initiators and targets. When you use CHAP authentication, you define CHAP user names and passwords on both the initiator and the storage system.
During the initial stage of an iSCSI session, the initiator sends a login request to the storage system to begin the session. The login request includes the initiator's CHAP user name and CHAP algorithm. The storage system responds with a CHAP challenge. The initiator provides a CHAP response. The storage system verifies the response and authenticates the initiator. The CHAP password is used to compute the response.
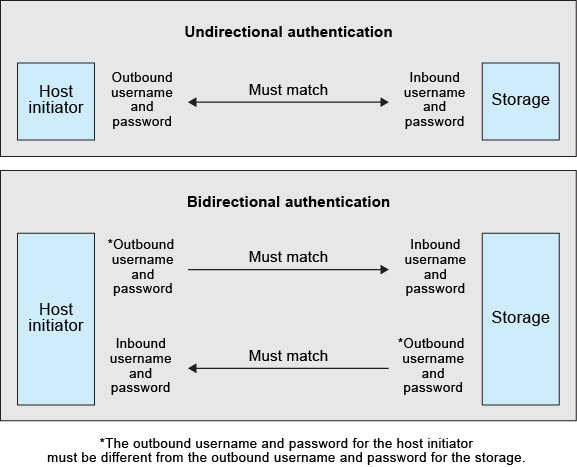
Authentication |
Outbound |
Inbound |
Match? |
|---|---|---|---|
Unidirectional |
Host initiator user name and password |
Storage user name and password |
Must match |
Bidirectional |
Host initiator user name and password |
Storage user name and password |
Must match |
Bidirectional |
Storage user name and password |
Host initiator user name and password |
Must match |
The outbound user name and password for the host initiator must be different than the outbound user name and password for the storage system.
Guidelines for using CHAP authentication
Follow these guidelines when using CHAP authentication.
-
If you define an inbound user name and password on the storage system, you must use the same user name and password for outbound CHAP settings on the initiator. If you also define an outbound user name and password on the storage system to enable bidirectional authentication, you must use the same user name and password for inbound CHAP settings on the initiator.
-
You cannot use the same user name and password for inbound and outbound settings on the storage system.
-
CHAP user names can be 1 to 128 bytes.
The system does not allow null user names.
-
CHAP passwords (secrets) can be 1 to 512 bytes.
Passwords can be hexadecimal values or strings. For hexadecimal values, you should enter the value with a prefix of “0x” or “0X”.
The system does not allow a null password.

|
ONTAP allows the use of special characters, non-English letters, numbers and spaces for CHAP passwords (secrets). However, this is subject to host restrictions. If any of these are not allowed by your specific host, they cannot be used. For example, the Microsoft iSCSI software initiator requires both the initiator and target CHAP passwords to be at least 12 bytes if IPsec encryption is not being used. The maximum password length is 16 bytes regardless of whether IPsec is used. See the initiator's documentation for additional restrictions. |


